Go To Index
POC- Paper 2
For Class XII (Commerce Group)
Model papers 2020 -2021
SECTION"B" (Short Answer Questions) (Marks 25)
Note: Answer any 5 Part Questions from this Section. All Questids carry equal marks. No answer should exceed 6-10 lines.
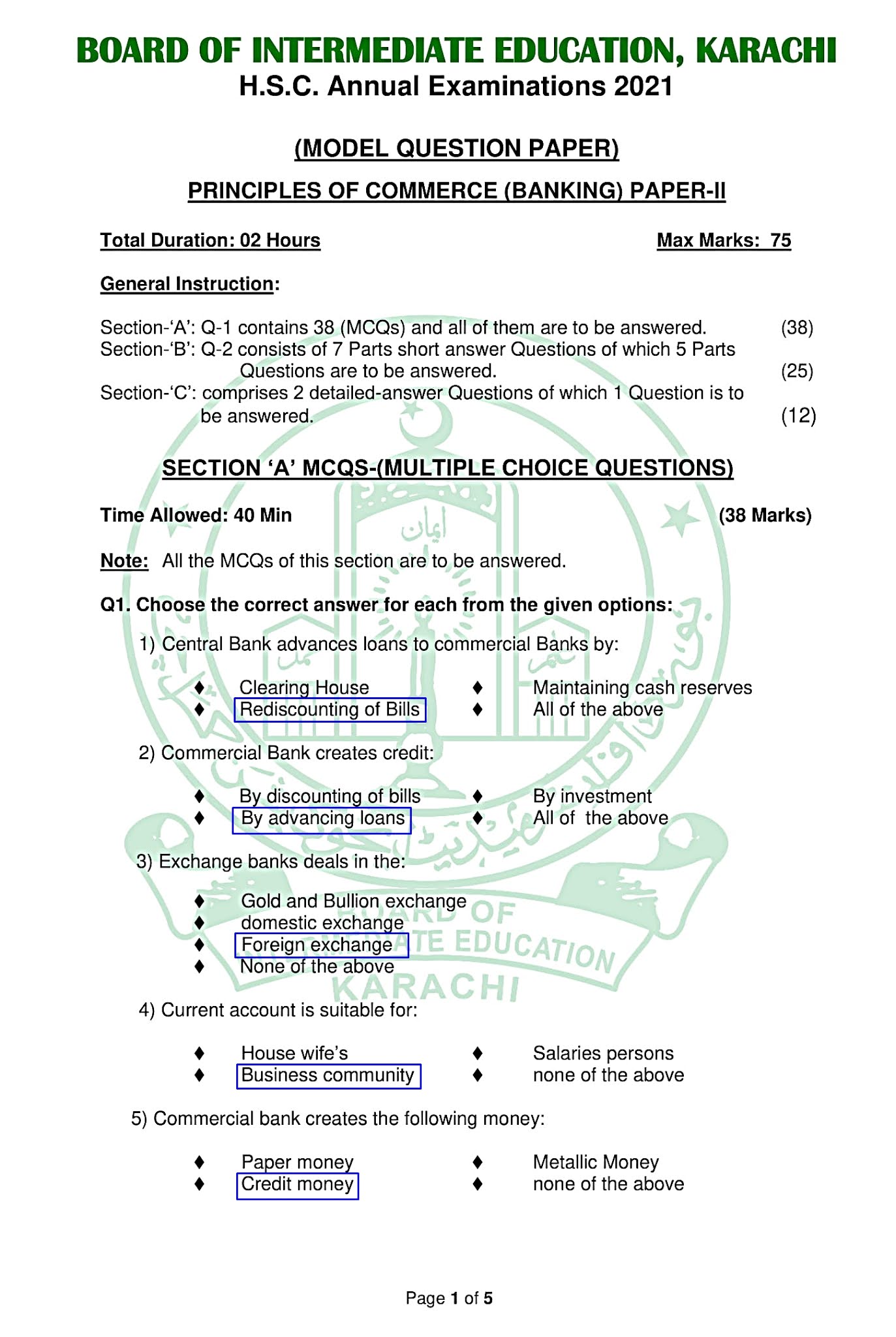
Q.2(i): How was the word "Bank" derived.
Ans: The term bank is either derived from Old Italian word banca or from a French word banque both mean a Bench or money exchange table. In olden days, European money lenders or money changers used to display (show) coins of different countries in big heaps (quantity) on benches or tables for the purpose of lending or exchanging. According to some authorities, the work "Bank" itself is derived from the words "bancus" or "banqee", that is, a bench.
The early bankers, the Jews in Lombardy, transacted their business on benches in the market place. There are others, who are of the opinion that the word "bank" is originally derived from the German word "back" meaning a joint stock fund. which was Italianized into "banco" when the Germans were masters of a great part of Italy. This appears to be more possible.
(ii) Define briefly types of Bank Account.
Ans: Types of Bank Accounts:
There are basically three types of accounts, which arc kept with a bank by customers. They are called:
- Current Account
- Saving Account
- Fixed Account
a) Current Account:
The current account is easily one of the most popular types of bank accounts in Pakistan, widely used by working individuals, businessmen and commercial entities. This account is ideal for making business transactions on a day-to-day basis, which means you can deposit and withdraw your money at any time.
Current Accounts are usually used by entrepreneurs, salaried individuals, traders and companies. Almost all At-Work accounts are also current.
b) Saving Account:
As the name suggests, savings account, are meant for securing your savings. In addition to that, unlike the current account, they also allow you to earn a certain percentage of interest over time. It means the amount you deposit in your savings account will accumulate a modest profit.
Moreover, banks in Pakistan offer a number of different savings accounts for individuals who want to earn income through interest.
c) Fixed Deposits Account:
Fixed deposit accounts also known as Term Deposit Accounts, allows customers to deposit a large amount into their accounts and earn a profit on them. Compared to the savings account, the rate of return is higher on the amount invested in fixed deposit. However, account holders cannot withdraw their funds from a fixed deposit for a certain period or time.
Usually, fixed deposit accounts hold funds for a time frame ranging from one month to 10 years.
(iii) List down the Quantitative method of credit control.
Ans:
Quantitative Method Of Credit Control:
Under the general or quantitative controls bank use the following weapons.
- bank Rate Policy
- Open Market Operation
- Variable reserve system
- Selective Credit Control
(iv) List down the secondary functions of a commercial Bank?
Ans:
Secondary Functions Of A Commercial Bank:
With the advancement of the world, banks are growing as well.
They now have gone a step further by performing the following functions as well.
(1) Public Utility Services:
Under this heading, a bank performs the following functions:
-
(i) Accepting and Discounting bills of exchange.
-
(ii) Creation of Credit Money.
-
(iii) Transfer of Money.
-
(iv )Underwriting of Shares.
-
(v) Locker Services.
-
(vi) Issuing of Letter of credit.
(2) Agency Services:
Commercial banks also works as an attorney for their clients. Under this heading, a commercial hank performs the following functions.
-
(i) Accepting Cheques.
-
(ii) Accepting Utility Bills.
-
(iii) Acting as Attorney.
-
(iv) Dealing in Shares and Bonds
(v) Define scheduled and non-scheduled Bank.
Ans:
Scheduled Bank:
The hanks which are registered in the list of central bank under its charter are known as scheduled banks. They are bound to perform banking services, according to the policies and instructions of central bank.
Non-scheduled Bank:
The banks which Are not registered in the list of central bank under its charter are known as non-scheduled banks. They are not bound to perform banking services according to the policies and instructions of central bank.
(vi) What is meant by crossing of Cheque?
Ans:
Crossing Of Cheque:
A crossing is a direction to the paying banker that the cheque should be paid only to banker and if the banker is names in the crossing, only to the banker It can be easily identified because it bears two parallel lines across. This ensures the safety of payment by means of cheques. The holder of the cheque is not allowed to cash it across the counter. Therefore it minimizes the possibility of falling the cash into wrong hands. Crossing is an indication to the drawee bank that the payment should be made, only through a banker Cheque not crossed sre called open cheques. There are two kinds of crossing, namely:
-
(a) General crossing
-
(b) Special crossing
(vii) List down the characteristics/features of Bill of Exchange.
Ans:
Characteristics of a Bill of Exchange:
A Bill of Exchange, at instrument must possess the following essentials characteristics.
In writing:
It must be in writing.
Express order to pay:
There must be an express order to pay and not a mere request to pay.
Definite and unconditional order:
The order must be definite and unconditional.
Order to pay certain sum:
The order must be to pay a certain sum.
Order to pay money only:
The order must be to pay money only.
Certain three parties:
The three parties (i.e., drawer, drawee and payee) must be certain and must be mentioned in the instrument. It may be noted that the drawer and payee can be the same person but the drawer and drawee cannot be the same person.
Signed by the drawer:
It must be signed by the drawer.
SECTION "C" (Descriptive Answer Questions) (Marks:12)
Note: Answer any ONE question (with detail) from this section.
Q.3: Define Commercial Bank or Central Bank. Describe functions of Commercial Bank or Central Bank in details.
Ans:
Definition of Commercial Bank:
Banks come to play a significant role in the development of any country. Among different types of banks, commercial banks are the most popular and successful kind of bank. It is not an easy task to define commercial banks because any bank can be defined on the bases of its functions, while it is very much difficult to identify commercial banks on the bases of their operations. It is rather easy to talk about, what is not commercial bank? For instance. institutions that face a variety of legal constraints on their powers to lend to businesses are not commercial banks. This permit to exclude saving institutions, credit unions and non depository institutions.
So by a process of elimination commercial banks can be define in the following way:
"A commercial bank is a depository institution that faces few legal restrictions on its power to lend to business and that authority to issue checking deposits from which holders may write unlimited numbers of check."
A dictionary of Economic and commerce define commercial banks as:
"A bank which-undertake all kinds of ordinary banking business."
Function of Commercial Bank:
Commercial banks are truly the identity of modern banking system. There importance is due to their functions which they perform in the modern world. These functions can be easily divided into two categories.
(i) Primary Function:
Primary functions can be defined as the basic and essential duties of a commercial banks. These functions can be divided into the following categories.
(1) Receiving Deposits:
It is the basic function of commercial banks. Small savers, salaried people, traders, manufactures and others, deposit their money with the bank.
(2) Advancing Loans:
The banks advance loans on an interest rate. It is the source of bank's income.
Today, banks are very much important from economic point of view due to their advancing loans.
(ii) Secondary Functions:
With the advancement of the world banks are growing as well. They now have gone a step further by performing the following functions as well.
(1) Public Utility Services:
Under this heading, a bank performs the following functions.
- Accepting and Discounting bills of exchange:
The bank except the bill on behalf of the debtor and discount it for the creditor.
- Creation of Credit Money:
The whole banking system in any country makes way to the creation of credit money through the deposits which they receives.
- Transfer of Money:
Commercial banks play an important role in the transferring of money from one person, company or city to another. Banks performs this functions between two countries as well and channelize the money from one country to another.
- Underwriting of Shares:
Underwriting refers to purchasing the whole issue of bonds and shares and reselling it to the public. Banks also takes the responsibility to sell the newly issued bonds or shares without underwriting them.
- Locker Services:
Bank offer lockers services for the safe custody of jewel, or other precious items.
- Issuing L/C:
Letter of credit is an open letter which is a reliable guarantee for the exporter or seller froth the bank. Bank also issue travelers cheques to the travelers and tourists.
(2) Agency Services:
Commercial banks also works as an attorney for their clients Under this heading a commercial bank performs the following functions.
- Accepting cheques:
"
This is the most valuable service that the bank performs for its clients. Businessmen receive cheques in payments from other parties. They deposit these cheques with their banks and get the payment. other parties. They deposit these cheques with their banks and get the payments.
- Accepting Utility Bills:
Banks also receive payments against utility bills like gas, electricity, phone etc. It also receives and pays premiums, interest, dividends and rent on behalf of its clients.
- Acting as Attorney:
The bank acts as attorney to its clients and thus performs legal and commercial functions for them.
- Dealing in Shares and Bonds:
On the instructions of its clients the bank buys and sells shares and bonds on the stock exchange.
(OR)
Definition of Central Bank:
A central bank is an entity responsible for overseeing the monetary system for a nation (or group of nations). Central banks have a wide range of responsibilities, from overseeing monetary policy to implementing specific goals such as currency stability, low inflation and full employment. Central banks also generally issue currency. function as the bank of the government, regulate the credit system, oversee commercial banks, manage exchange reserves and act as a lender of last resort.
Functions of Central Bank:
State Bank's basic function is to carry the monetary policy of a country and this requires that it should work closely with the government and must have some means of controlling the commercial banks. On the basis of this information it is clear that State Bank performs broadly the following functions.
-
(a) Government bank's functions
-
(b) Banker's bank functions
(a) Government bank's functions:
As a government bank, State Bank performs the following functions.
(1) Note Issue:
One of the most important function of State Bank of Pakistan is the issue of legal tender currency, the main reason for the concentration of note issue is a state bank may be found in the necessity of bringing about uniformity in the note circulation of a country and of avoiding the anomaly of over issue by many banks established with the primary motive of securing profit.
(2) Control over Credit Creation:
Closely connected with the function of currency regulation is the function of credit control this function assumed importance with the growing popularity of bank credit. The state banks controls and regulate credit money in a country in order to expand or contact it to the requirement of the economy. The state bank's function is to control the credit money and keep it at certain level.
(3) Custodian of National Reserves in a Country:
The state bank of a country is generally entrusted with the custody of the nations reserves. This function was derived from the role of the central bank as the sole authority of note Issue. The reserves are is the main, kept in the form of gold or silver or both. Not infrequently state bank is also consider as the custodian of foreign reserves.
(4) Custodian of Foreign exchange Reserves:
Pakistan is involved in international trade now-a-days. During this processor our country earns foreign exchange, which is kept by the state bank. When businessmen trade their goods, they gets international currency which is not handed in to them and instead it is held with the state bank.
(5) Fiscal Agent:
A state bank is also worked as a fiscal agent of government. The state bank function as the government meaning that it issues, services and redeems debt on the treasury's behalf. The government issue debt instruments i.e. bills, notes and bonds that the government uses to cover short falls between its tax. receives and its expenditures on goods and services.
(6) Development of Financial Institutions:
The state bank is responsible to develop financial institutions, which plays a vital role in industrial, agricultural and capital development of the country. It also facilitate the money market and stock exchanges. All of the above functions clearly indicates that the state bank works as the right hand of government.
(b) State Bank (Central Bank) as a Banker's Bank:
As a sole authority of note issue and as the government's bank, the state bank stands at a privileged position in the money market. This has made the commercial banks to recognize the supremacy and to consider it as their banker. The state bank in turn recognize its duty to help the commercial banks in times of emergencies by extending financial help. Being a banker's bank, state bank performs the following functions.
(l) Lender of the last resort:
In its role, as the banker's bank, the state bank extends financial facilities to commercial banks in times of emergency, In fact, it is the most important duty of state bank in its capacity as the banker's bank.
"The essential duly of the state bank as the lender of the last resort is to make good shortage of each among the competitive banks."
In crises when a commercial bank has exhausted all its resources and still finds itself unable to meet all its obligations and outstanding duties the state bank comes forward to rescue it. The state bank is extending financial accommodation mainly through rediscounts of first class bills of exchange, government securities and such other eligible papers.
(2) Clearing House Service:
Being the holder of the balances of the commercial banks, the state bank is specially qualified to act as a bank of state clearance.
Krick and Klikin mentoined that:
"It is for the central bank to setup an expedition, and economical machinery for the clearance of draft and settlement of internal account."
The bank performs this function for commercial banks. Every bank receives cheques drawn on other banks, because of which every bank becomes creditor or debtor to the other bank or banks. All these cheques are sent to the state bank where it settles all the accounts of the banks by adjusting their debit or credit balances.
(3) Rediscounting bills of Exchange:
Another valuable service performed by the bank is to rediscount bill of exchange. Commercial banks discount bills of exchange of businessmen. Discounting encashment of the bill before it matures, at a certain rate of interest. As a result commercial banks fall short of cash. So they approach the state bank for rediscounting of the same bills.
(4) Cash reserves:
Under banking law, every commercial schedule bank is bound to deposit a certain percentage of all its deposits with the state bank. This service serves many objects.
(i) It provides safety to commercial bank's account holder.
(ii) It makes easy for state bank to control over credit creation.
(iii) These reserves may be used to finance commercial banks in need.
(5) Counseling service:
The state bank offers precious advice and counseling services. In the light of its export opinion and advice commercial banks formulates and read just their policies.
Q.4 What is meant by Rate of Exchange? Describe the factors that affect the rate of Exchange.
Ans:
Rate of Exchange: It is defined as:"The rate of exchange between two countries is the amount o f one currency that will be exchanged for one unit of another currency".
For instance, of $1 can be exchanged for Rs.106, then the rate of exchange between dollar and rupee is $1 = Rs. 106.
Factors Influencing the Exchange Rate:
The market rate of exchange existing on any particular day need not be the same. It is liable to fluctuate. The causes given rise to such fluctuations are as follows:
(1) Trade Factor:
Trade factor relate, to the influences arising from the exports and imports. Suppose the equilibrium rate of exchange between Pakistan and US is $1 = Rs. 150. For some reasons the exports from U.S increase more than the import. That mean Pakistan have to pay more dollar to U.S. the demand for dollar increase and the exchange rate of dollar increase.
(2) Stock exchange factor:
Stock exchange factor relates to the influence arising from granting of loans, repayment of loans, receipt of interest, payment of interest, purchase and sales of foreign securities etc, for e.g. Suppose U.S is granting a loan to Pakistan. The demand for rupees will increases in U.S. The result is the fluctuation of exchange rate in Pakistanis favour.
(i) Banking Factor:
Banking factor relate to the influences arising front the activities of banks such as purchases or sales banker's draft, travelers cheque, arbitrage operations etc. For instance the sale of a draft on a foreign centre creates demand for foreign currency and raise it value. The exchange rate will move in the favour of the foreign currency.
(ii) Currency and credit conditions:
Currency and credit conditions of a country, also influence the rate of exchange. Exchange dealers are always careful to watch the probable trend of the internal and external value of a country's currency. If the total quantity of note-issue is steadily increasing without a corresponding increase in the total volume of goods the result will be inflation.
The increased in price of the commodity will cause a decrease in its exports. An adverse balance of payment position will develop. Such situation induces the exchange dealers to dispose off their stock of home currency relative to its demand thus causing a fluctuation in the rate of exchange unfavourable to the home currency.
(3) Budgetary policies of Country:
Budgetary polices of a country will also cause fluctuations in the rate of exchange. Where it appears than the extent of public expenditure is in compatible with the national stock of that currency.
(4) Political and Internal Industrial Situation:
The political conditions and internal industrial situation of country also cause fluctuation in the rate of exchange. A stable government, the stick maintenance of law and order, the protection of property and of the rights of owners of wealth will all induce an inflow of foreign capital, either for interest gaining purpose or for safety. The adverse situation will induce the withdrawal of capital and cause the unfavourable exchange rate. While stable political and industrial conditions will cause the fluctuation of exchange rate in favour of a country.
SOURCE: Board Of Intermediate Education Karachi