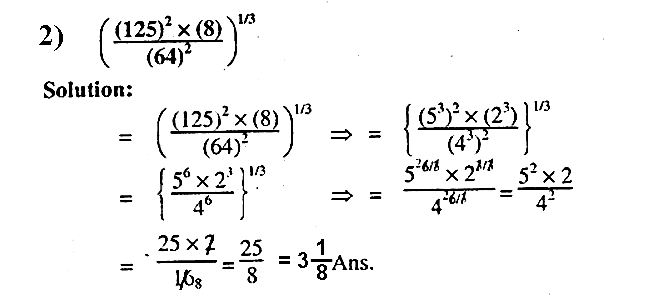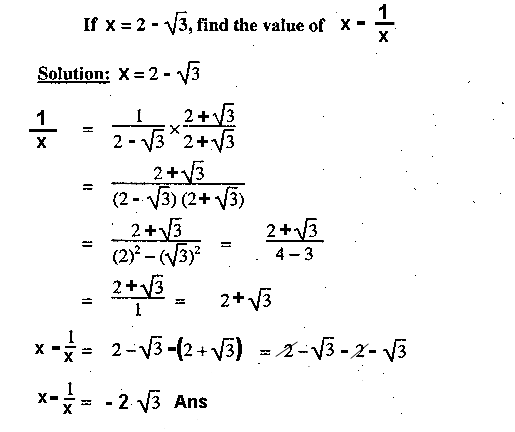Search This Blog
Saturday 15 May 2021
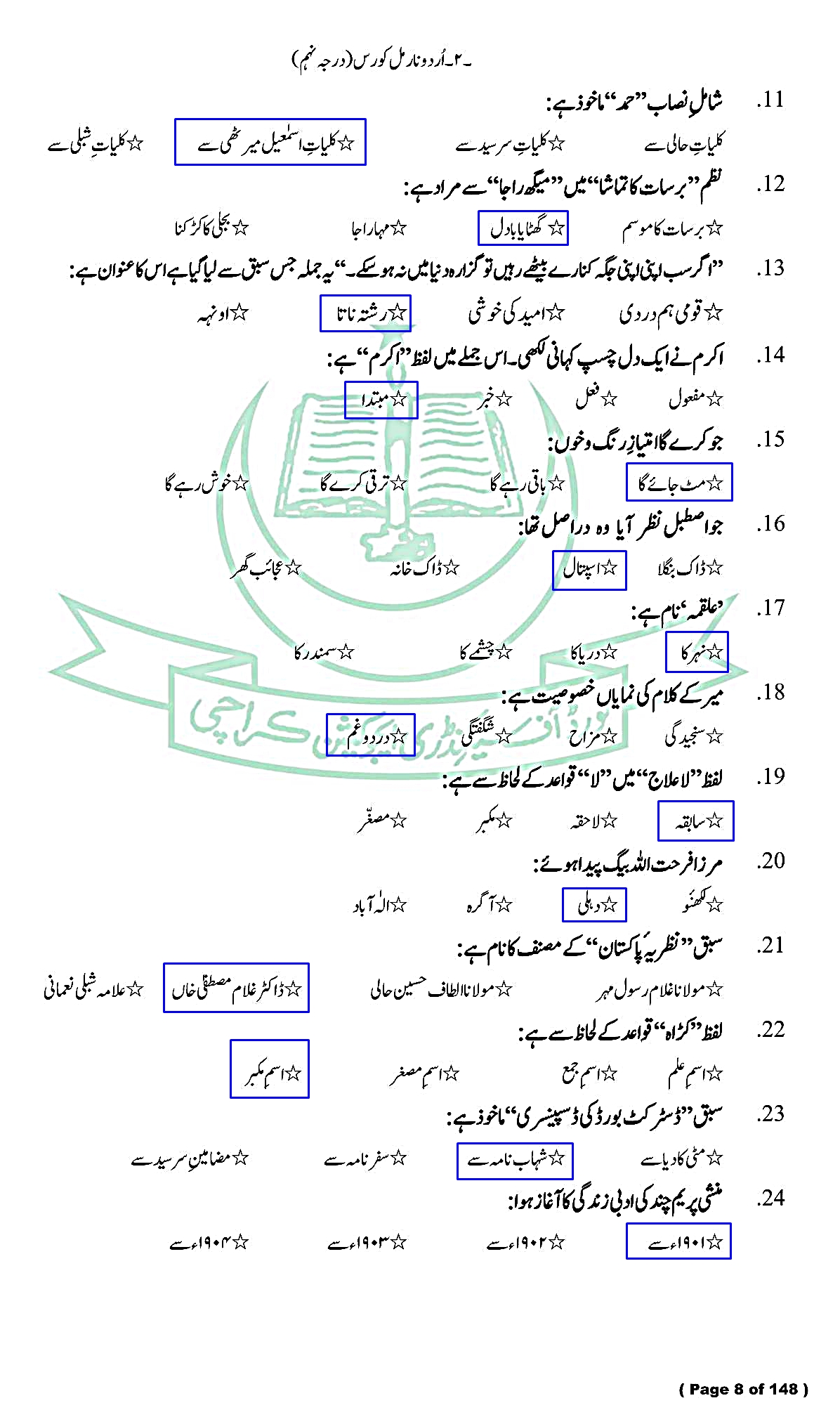
Urdu (Compulsory) - For Class SSC - Part 1 (Arts / General Group) - Solved Model papers 2020 -2021- AS PER CONDENSED SYLLABUS
GO TO INDEX
Urdu (Compulsory)
For Class SSC - Part 1 (Arts / General Groups)
Solved Model papers 2020-2021
As Per condensed Syllabus
Friday 14 May 2021
Computer Science (New) - For Class IX - UNIT. 5. Computer Security and Ethics - MCQs, Fill In The Blanks And Abbreviations
GO TO INDEX
Chapter No.5. Computer Security and Ethics
MCQs And Fill In The Blanks
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Choose the right answer
1. The broad term that encompasses different harmful software is:
(a) virus
(b) malware ✓
(c) adware
(d) spyware
2. The authentication mechanism that only allows the real person to access data or device is:
(a) username and password
(b) PIN
(c) biometric ✓
(d) scan code
3. Software are mostly protected under:
(a) patents
(b) copyrights ✓
(c) trademarks
(d) logos
4. The professional ethics in computer held is important because:
(a) it is necessary by law
(b) violation can cause serious penalties
(c) it is useful for financial benefits
(d) it creates healthy and positive work environment ✓
5. Free Antivirus Software often:
(a) expire after sometimes
(b) offer only limited service ✓
(c) cannot be updated
(d) cannot be purchased
6. Copying and pasting some texts from internet without acknowledging the real author is an example of:
(a) plagiarism ✓
(b) illegal use of patent
(c) information piracy
(d) copyright violation
7. Since it does not harm or steal data, the least harmful malware is:
(a) virus
(b) adware ✓
(c) spyware
(d) Trojan
8. The malware that replicates itself and doesn't need to attach with any files is:
(a) virus
(b) adware ✓
(c) spyware
(d) worm
9. Through which virus spreads?
(a) Email Attachments
(b) Internet Downloads
(c) Flash Disks and CDs
(d) All of them ✓
10. "Click this link and win a $5 voucher at McDonald's". This is an example of:
(a) scam
(b) phishing
(c) clickjacking ✓
(d) hacking
11. According to Pakistan's Cybercrime Law, any offender may be sent to jail for:
(a) 1 to 3 years
(b) 3 to 5 years ✓
(c) 5 to 7 years
(d) 7 to 10 years
12. It is a method of trying to gather personal information using false e-mails and websites.
(a) Hacking
(b) Clickjacking
(c) Phishing ✓
(d) Cracking
13. Boot Sector, Resident, and File Infector are some examples of:
(a) viruses ✓
(b) adware
(c) spyware
(d) worms
14. Advertising-supported software which presents endless ads and pop-up windows that could potentially consume memory and processing resources is called:
(a) viruses
(b) adware ✓
(c) spyware
(d) worm
15. A malware that monitors a device and steals important information and sends such information to another person or organization is called:
(a) viruses
(b) adware
(c) spyware ✓
(d) worm
16. System monitors cookies trackers, rootkits and key-loggers are few examples of:
(a) viruses
(b) adware
(c) spyware ✓
(d) worm
17. It is one of the largest computer security companies in the world.
(a) Avira
(b) McAfee
(c) Norton
(d) Avast ✓
18. PIN stands for:
(a) Personal Identification Number ✓
(b) Proper Identification Number
(c) Post Identification Number
(d) Paid Identification Number
19. It is presenting someone else's work or ideas as your own without full acknowledgment to the author or conceiver.
a) Trademark
(b) Patent
(c) Copyright
(d) Plagiarism ✓
20. Turnitin is a popular service for checking:
(a) Copyright
(b) Plagiarism ✓
(c) Software piracy
(d) Patent
21. The crime that is committed though a computer and network.
(a) Net-crime
(b) Internet crime
(c) Cyber-crime ✓
(d) Online crime
22. Hacker uses his or her skills to identify and overcome a network:
(a) loophole
(b) error
(c) fault
(d) mistake ✓
23. Persons who gain unauthorized access to another system are:
(a) hackers
(b) phishers
(c) crackers ✓
(d) None of them
24. It is done when a cybercriminal uses computer or any device to enter or attacks to other single or multiple computer networks.
(a) cyber-war
(b) cyber-attack ✓
(c) cyber-strike
(d) cyber-sin
25. It is a broad term that encompasses computer viruses, worms, spyware, adware and others that is written generally to cause a mess.
(a) Malware
(b) Malicious software
(c) Both 'a' and 'b' ✓
(d) None of them
26. Utility software designed to protect computers from any potential threats of data or hardware loss from viruses or malware are called:
(a) Firewalls
(b) Anti-spywares
(c) Security-wares
(d) Antiviruses ✓
27. The illegal use, copying or distribution of copyrighted software is called:
(a) software piracy ✓
(b) software theft
(c) software threat
(d) software robbery
28. Stealing passwords and important information are some of the examples of:
(a) Net-crime
(b) Internet crime
(c) Cyber-crime ✓
(d) Online crime
29. Hacking social media accounts, accessing anyone else's account and making transactions, committing online frauds are some of the examples of:
(a) Net-crime
(b) Internet crime
(c) Cyber-crime ✓
(d) Online crime
30. _________ can also help us to improve the data and network security.
(a) Hackers ✓
(b) Phishers
(c) Crackers
(d) None of them
31. Credit and Debit Card Scam, Phishing, Clickjacking, Cyber Bullying or Harassment are examples of:
(a) Net-crime
(b) Internet crime
(c) Cyber-crime ✓
(d) Online crime
32. ______ is perhaps the most common crime in the computer world.
(a) Hacking ✓
(b) Phishing
(c) Cracking
(d) None of them
33. _______ can steal our WiFi, email or social media accounts' passwords.
(a) Hackers ✓
(b) Phishers
(c) Crackers
(d) None of them
34. _______ also attack a website and take it down.
(a) Hackers ✓
(b) Phishers
(c) Crackers
(d) None of them
35. ______ can make fraudulent transactions by stealimg information of our debit or credit card.
(a) Hackers
(b) Phishers
(c) Crackers
(d) Scammers ✓
36. The culprit tries to enter in a computer system and network through cracking, scam links, phishing or any other method.
(a) cyber-warrior
(b) cyber-attacker ✓
(c) cyber-striker
(d) cyber-sinner
37. The victims of cybercrimes may complaint by calling helpline ____ which is available 24/7.
(a) 1199
(b) 9911
(c) 1991 ✓
(d) 9191
(Note: In text book 9911 is given but correct help line number in Pakistan is for complaint for cybercrime is 1991)
38. Types of ____ can include computer viruses, worms, adware, and spyware.
(a) cyber-attack
(b) malware ✓
(c) hackers
(d) cybercrime
39. This malware programs include games, desktop toolbars or utilities.
(a) viruses
(b) adware ✓
(c) spyware
(d) worm
40. This malware is web-based and collects web browser data to target advertisements, especially pop-ups.
(a) viruses
(b) adware ✓
(c) spyware
(d) worm
41. Trojan horses, Rootkit, Backdoors, and Bots are example of:
a) viruses ✓
(b) adware
(c) spyware
(d) worm
42. It is a security code for verifying your identity.
a) Username and Password
b) PIN ✓
c) Biometric
d) Scan Code
43. The ______ provides security when a credit/debit card is lost or stolen.
a) Username and Password
b) PIN ✓
c) Biometric
d) Scan Code
44. It causes a signicant loss of revenue for developers and vendors.
(a) Copyright
(b) Plagiarism
(c) Software piracy ✓
(d) Patent
Fill In The Blanks
1. Computer security is the protection against damage or theft of computer hardware, its software, and information present on them from threat of viruses or unauthorized use.2. Cybercrime is illegal and also punishable.
3. Government and business organizations are now hiring ethical hackers, also known as white hat hackers, to prevent data theft.
4. The hackers can steal sensitive information from government and business organizations, make fraudulent transactions and erase data on the cloud or network computers.
5. Debit and credit cards are also secured with PIN codes.
6. Electronic means like a computer, mobile phone or internet are also used for online bullying or harassment and giving threats.
7. Cyber-attack or cyber harassment victim should report to the trusted people and government authorities.
8. A cyber-attack either disables the targeted computer, deletes information or knocks it offline.
9. A cyber-attack may also steal information from the computer or network.
10. The term malware is the contraction of malicious software.
11. Commonly malware encrypt, steal or delete data, hijack core functions of computing and disturb different activities.
12. Viruses or malware can be spread from USB Flash Disks and CDs, Internet Downloads, Computer Networks and Email Attachments.
13. A computer virus is just like a flu virus.
14. Paid customers are called premier users and they get advance security features.
15. Norton antivirus has been a popular antivirus utility since 1991.
16. Norton antivirus is a part of a large family of security and other utility software by Symantec Corporation.
17. McAfee claims that it provides a combination of antivirus, privacy and identity tools and features.
18. McAfee enables users to stay protected against the latest virus, malware, ransomware and spyware attacks while keeping their identity and privacy protected and personal.
19. For data safety, the back-up of important files should be made at more than one place.
20. The authentication mechanism is the hardware or software-based mechanisms that make sure the only authenticated user gets access to data or devices.
21. A username and password are the pair of keywords known by the user.
22. Usernames and passwords are the default authentication mechanism on the web today.
23. Biometric authentication relies on the unique biological characteristics of a person.
24. Scanning fingerprints are the most common way of biometric.
25. Retinal scans and iris, facial and voice recognitions are the other advance ways of biometric.
26. Professional ethics involve the personal and corporate principles and rules that guide behavior within the context of a profession.
27. The information accuracy is the type of measurement that assures the information is correct and true.
28. Intellectual property is intangible creations of the human intellect.
29. To prevent theft or illegal use or spread of intellectual property, Intellectual Property Right is exercised.
30. The intellectual property rights are protected with the help of copyrights, patents, and trademarks.
31. A patent is a grant of exclusive rights for an invention to make, use and sell the invention for a limited period.
32. Copyright is a legal instrument that provides legal rights to the creator of artwork, literature, or a work that conveys information or ideas.
33. Copyright is the right of copying.
34. The © sign is also often displayed on copyrighted objects.
35. Trademark identifies a product or service and distinguishes it from other products and services.
36. Trademark helps organizations to market their products and services locally and globally.
37. Pirated software users cannot access customer support, upgrades, technical documentation, training, and bug fixes.
38. Copy- protection demands the user to enter certain keys or credentials.
Abbreviations
ATM: Automated Teller Machine© : Copyright
CD: Compact Disk
DVD: Digital Versatile Disc
IPO: Intellectual Property Organization
LAN: Local Area Network
Malware: Malicious software
OMG: Oh! My God
OS: Operating system
PIN: Personal Identification Number
SD cards: Secure Digital cards
TM or TM : Trade Mark
USB: Universal Serial Bus
WiFi: Wireless Fidelity
Refence links Given In Text Book
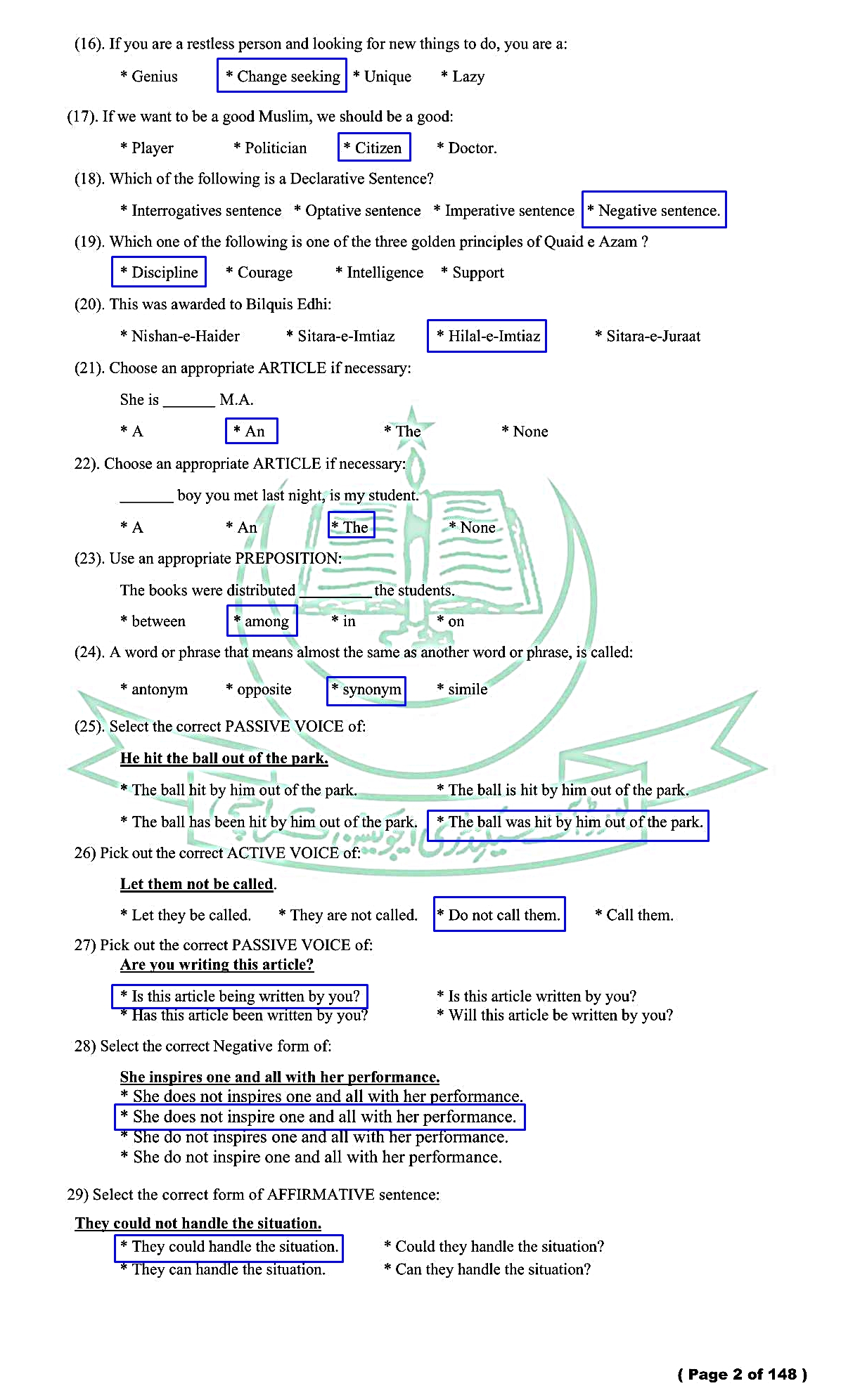
English (Compulsory) - For Class SSC - Part 1 (Arts / General Group) - Solved Model papers 2020 -2021- AS PER CONDENSED SYLLABUS
GO TO INDEX
English (Compulsory)
For Class SSC - Part 1 (Arts / General Groups)
Solved Model papers 2020-2021
As Per condensed Syllabus
Thursday 29 April 2021
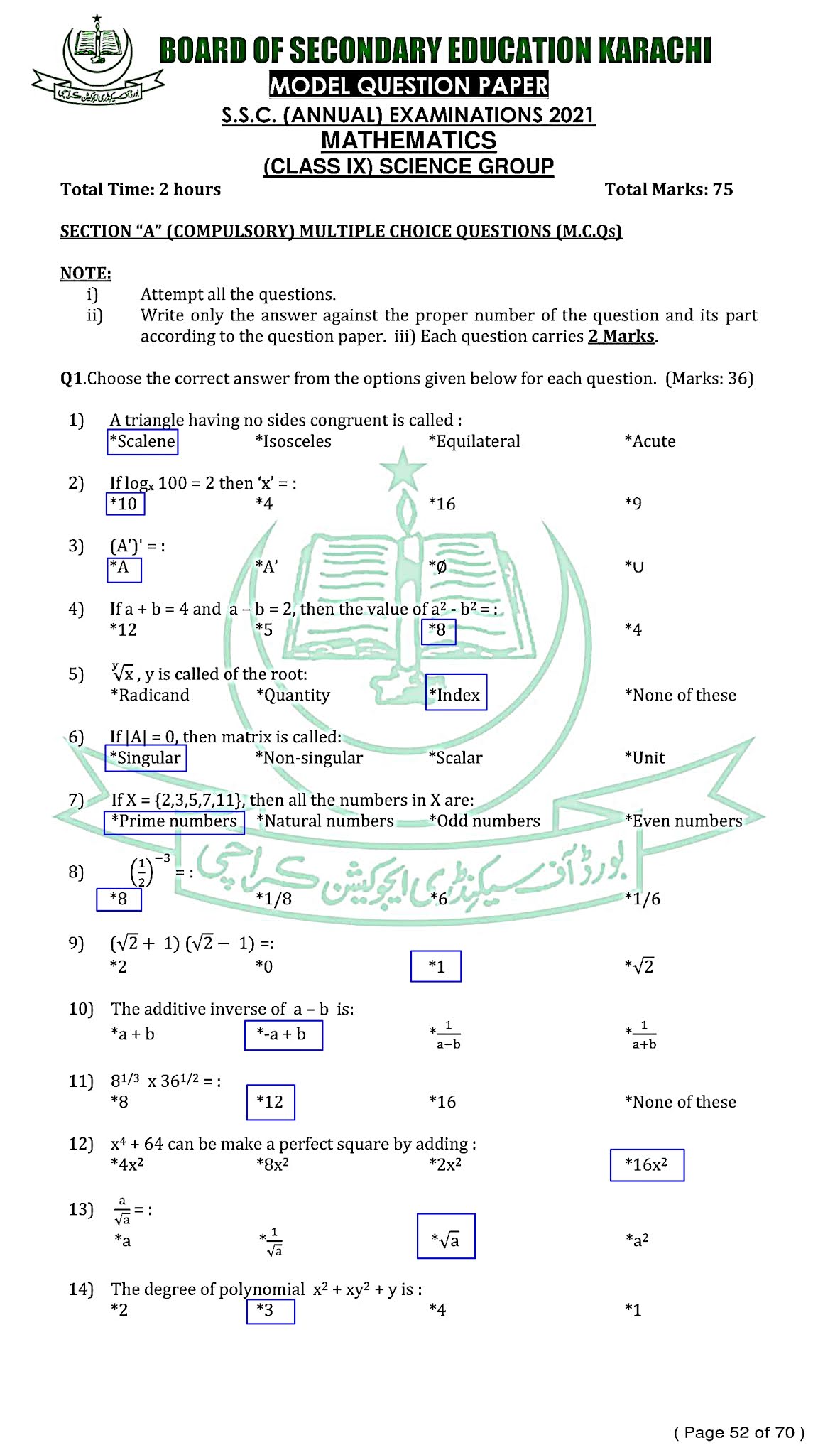
Mathematics (English) - For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Group) - Solved Model papers 2020 -2021- AS PER CONDENSED SYLLABUS
GO TO INDEX
Mathematics (English)
For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Groups)
Solved Model papers 2020 -2021
As Per condensed Syllabus
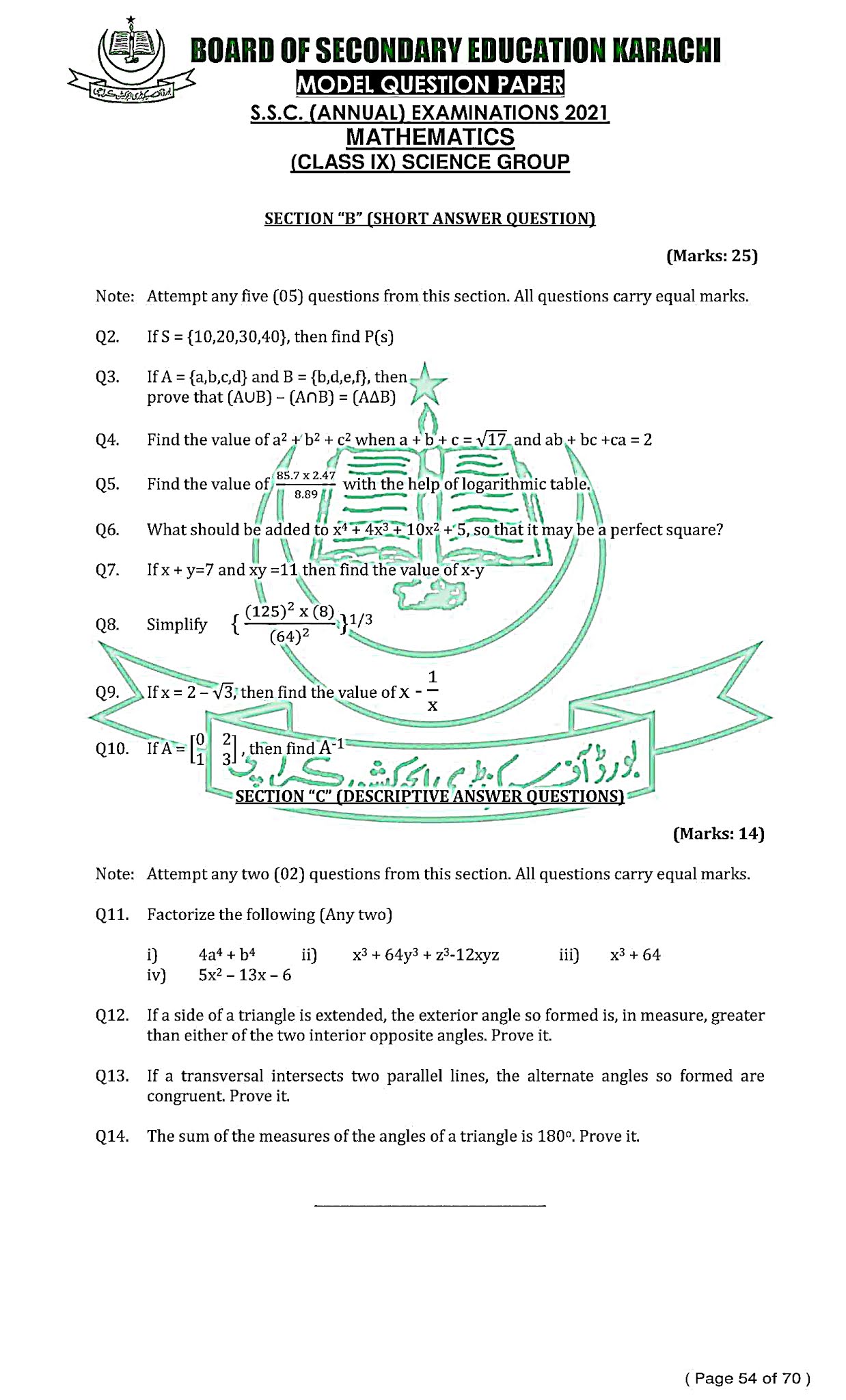
SECTION "B"
(Short Answer Question)
Q.2: If S = {10, 20, 30, 40}, then find P (S)
Solution:-
|P (S)| = 2n = 24 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16 (where 'n' is number of elements in set S.)
(Hence, Set S has 16 subsets or power sets.)
|P (S)| = { { }, {10}, {20}, {30}, {40}, {10, 20}, {10, 30}, (10, 40), {20, 30}, {20, 40}, {30, 40}, {10, 20, 30), {10, 20, 40}, {10, 30, 40}, {20, 30, 40}, {10, 20, 30, 40} } Ans.
Q.3: If A = {a, b, c, d} and B = {b, d, e, f}, then
Prove that (AUB) - (A∩B) = (A ∆ B)
Solution:
Taking R.H.S:
AΔB = {a, b, c, d} Δ {b, d, e, f}
(By selecting uncommon members among both sets)
We get AΔB = {a, c, e, f} ....... (1)
Taking L.H.S:
AUB = {a, b, c, d} U {b, d, e, f}
AUB = (a, b, c, d, e, f)
A∩B = {a, b, c, d} ∩ {b, d, e, f}
A∩B = (b, d)
AUB - A∩B = (a, b, c, d, e, f) - (b, d)
We get AUB - A∩B = {a, c, e, f} ....... (2)
By (1) and (2)
AΔB = AUB - A∩B Hence Proved
Q.4: Find the value of a2+b2+c2 when a+b+c = √ 17 and ab+bc+ca = 2.
Solution:
Given that:
(a+b+c) = √ 17
By squaring on both side
(a+b+c)2 = (√ 17)2
From Formula:
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca = 17
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 2 (ab + bc + ca) = 17
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 2 (2) = 17
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 4 = 17
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 = 17 - 4
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 = 13 ANSWER
Q.5: Find the value of 85.7 x 2.47 / 8.89 with the help of logarithmic table.
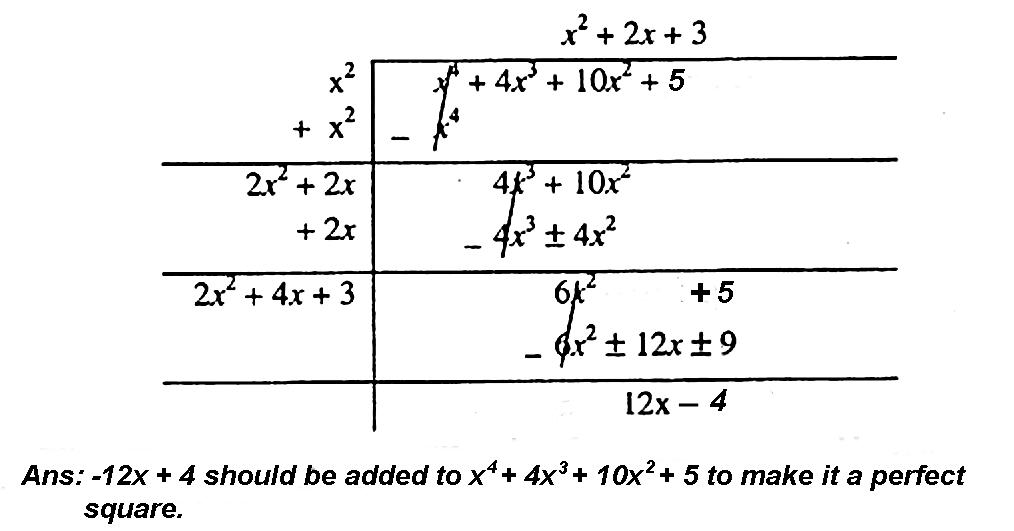
Q.6: What should be added to x4 + 4x3 + 10x2 + 5, so that it may be a perfect square?
Q.7: If x + y = 7 , xy = 11, then find the value of x - y
Solution:
Data:
x + y = 7
xy = 11
x - y = ?
Using Formula
4ab = (a + b)2 - (a - b)2
⇒ 4xy = (x + y)2 - (x - y)2
⇒ 4(11) = (7)2 - (x - y)2
⇒ 44 = 49 - (x - y)2
⇒ (x - y) 2 + 44 = 49
⇒ (x - y) 2 = 49 - 44
⇒ (x - y) 2 = 5
By taking square root on both side
⇒ √ (x - y) 2 = √ 5
⇒ x - y = √ 5 Ans
Q.8: Simplify:
Q.9:
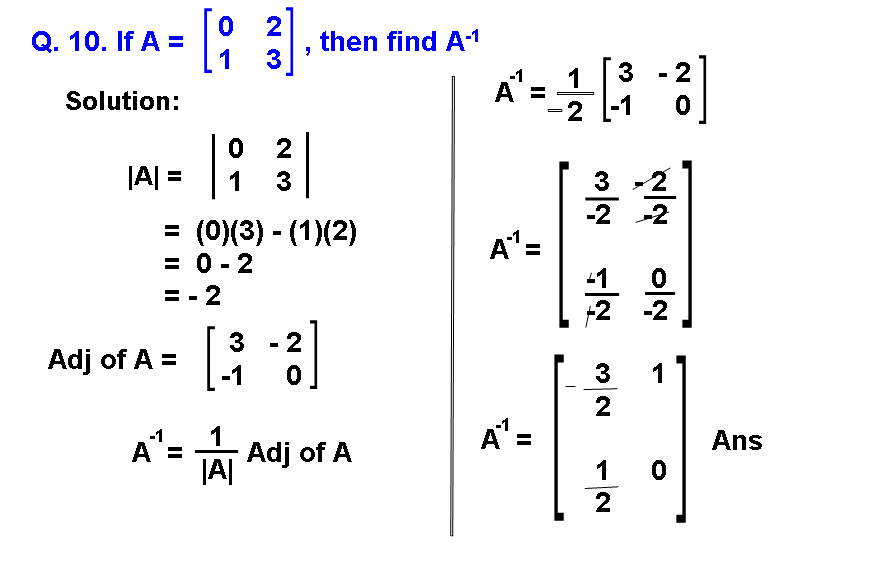
Q.10: Find A-1
SECTION "C"
(Descriptive Answer Question)
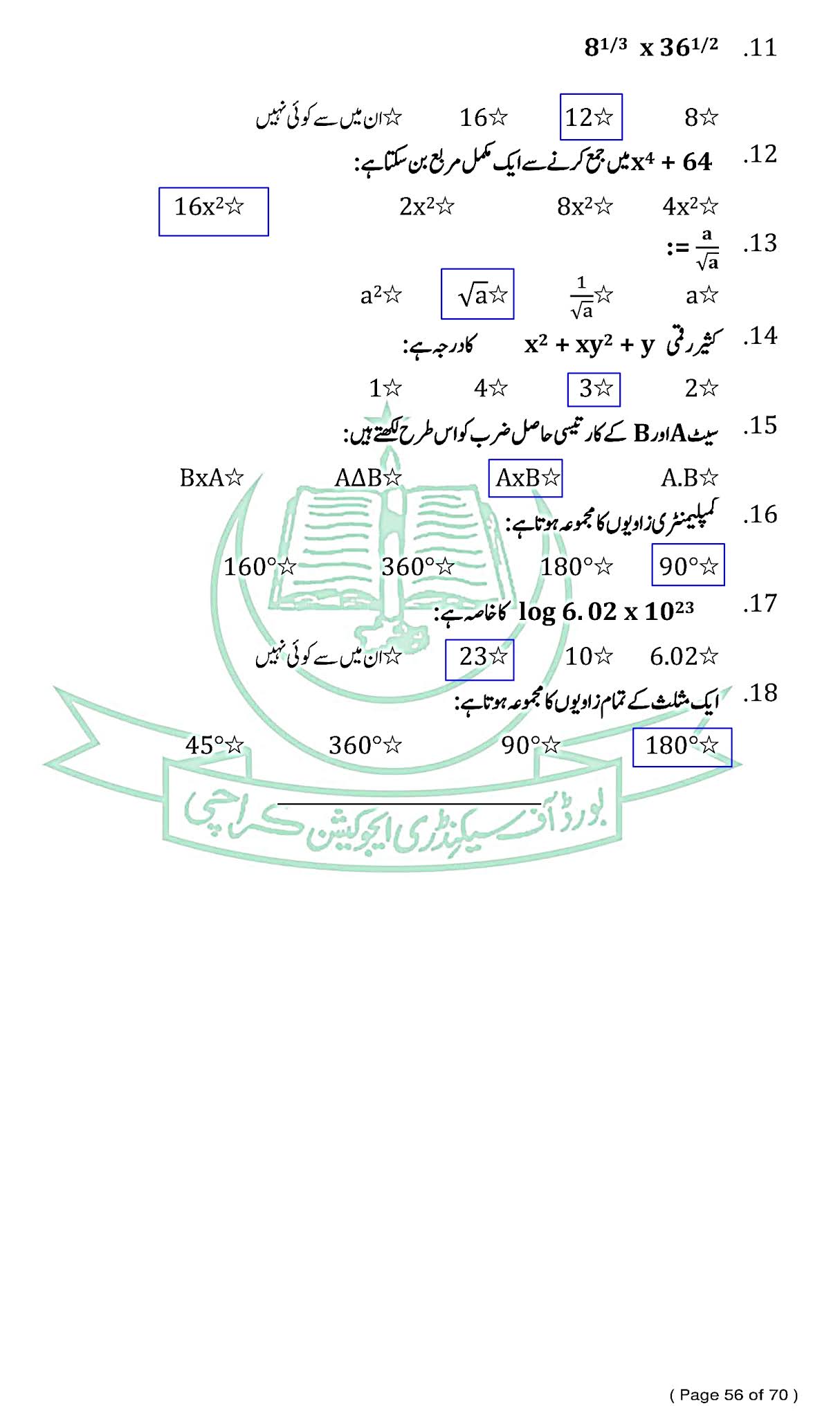
Q.11: Factorization
Sequence to apply formula for factorization
1) Try Common
2) Perfect square (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
3) a2 - b2 = (a-b)(a+b)
4) Middle term breaking
5) (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ac
6) (a3 + b3) = (a + b)(a2 + ab + b2)
7) a3 + b3 + c3 - 3abc = (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 - ab - bc -ac)
I) 4a4 + b4
By applying perfect square formula
(a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
⇒ [(2a2)2 + 2(2a2)(b2) + (b2)2 - 4a2b2]
⇒(2a2 + b2)2 - (2ab)2
By applying Formula
a2 - b2 = (a-b)(a+b)
⇒ (2a2 + b2 - 2ab) (2a2 + b2 + 2ab)
⇒ Or (2a2 -2ab + b2) (2a2 + 2ab + b2) Ans.
II) x3 + 64y3 + z3 - 12xyz
By applying formula
a3 + b3 + c3 - 3abc = (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 - ab - bc -ac)
⇒ (x)3 + (4y)3 + (z)3 - 3(x)(4y)(z)
⇒ {(x) + (4y) + (z)}{(x)2 + (4y)2 + (z)2 -(x)(4y) - (4y)(z) - (z)(x)}
⇒ (x + 4y + z)(x2 + 16y2 + z2 -4xy - 4yz - xz) Ans.
III) x3 + 64
By applying formula
(a3 + b3) = (a + b)(a2 + ab + b2)
⇒ (x)3 + (4)3
⇒ (x + 4) {(x)2 + (x)(4) + (4)2}
⇒ (x + 4) (x2 + 4x + 16)Ans.
IV) 5x2 - 13x - 6
By applying formula
Middle term breaking
⇒ 5x2 - 15x + 2x - 6
⇒ 5x(x - 3) + 2(x - 3)
⇒ (5x + 2)(x - 3) Ans.
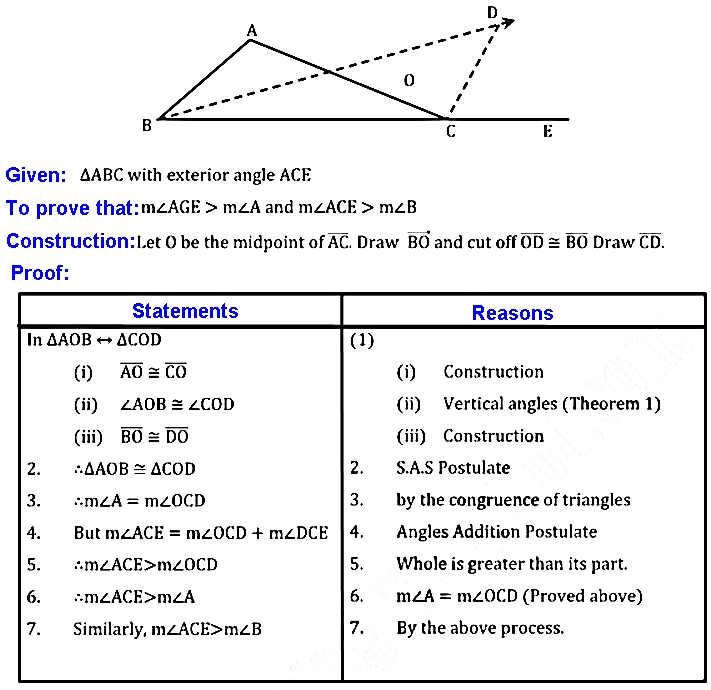
Q.12: If a side of a triangle is extended, the exterior angle so formed is, in measure, greater than either of the two interior opposite angles.
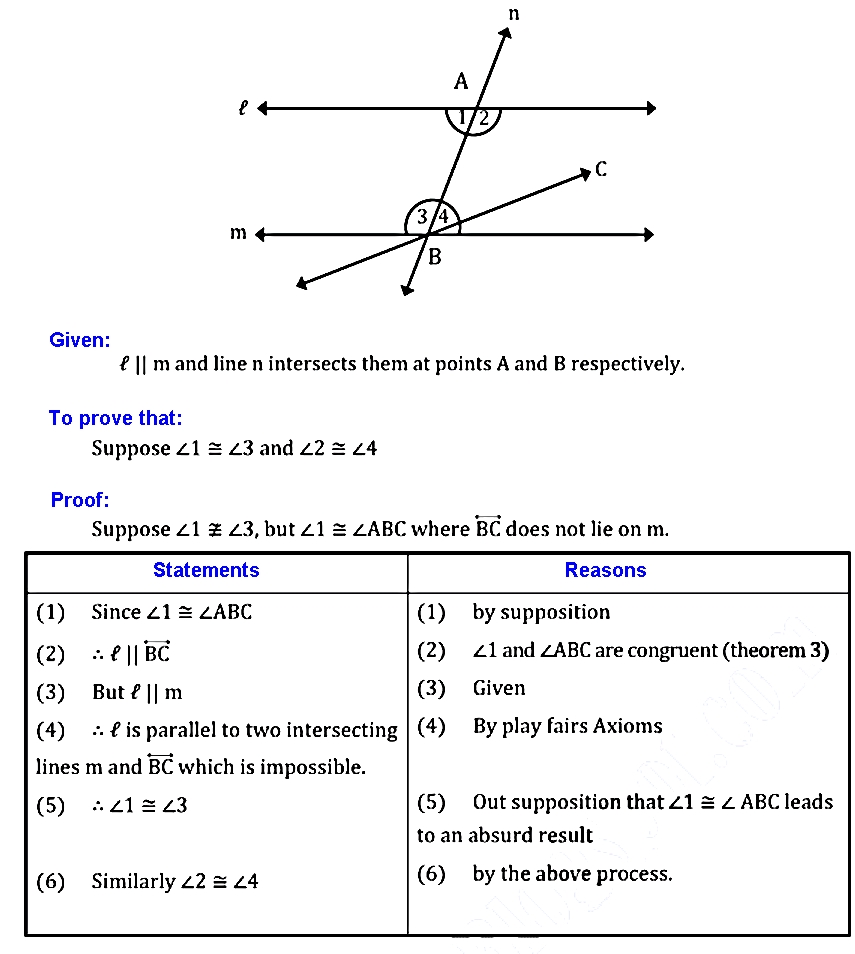
Q.13: If a transversal intersect two parallel lines, the alternate angles so formed are congruent.
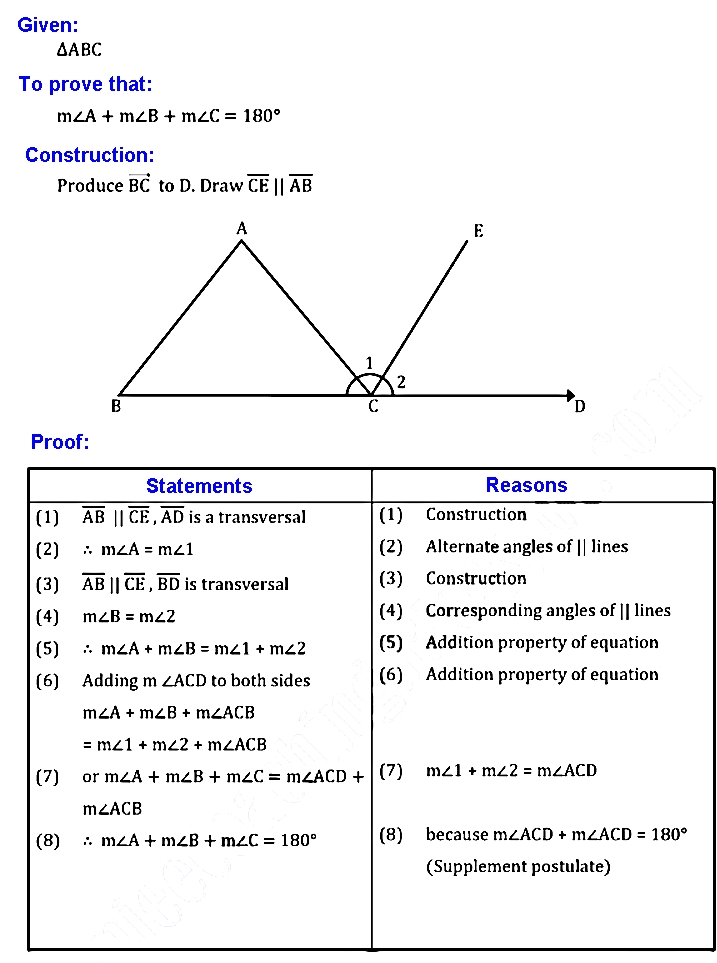
Q 14: The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180°.
Special Thanks To Sir Sajjad Akber Chandio
Mathematics (Urdu) - ریاضی - For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Group) - Solved Model papers 2020 -2021- AS PER CONDENSED SYLLABUS
GO TO INDEX
Mathematics (Urdu) - ریاضی
For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Groups)
Solved Model papers 2020 -2021
As Per condensed Syllabus
SECTION "B"(Short Answer Question)
Q.2: If S = {10, 20, 30, 40}, then find P (S)
Solution:-
|P (S)| = 2n = 24 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16 (where 'n' is number of elements in set S.)
(Hence, Set S has 16 subsets or power sets.)
|P (S)| = { { }, {10}, {20}, {30}, {40}, {10, 20}, {10, 30}, (10, 40), {20, 30}, {20, 40}, {30, 40}, {10, 20, 30), {10, 20, 40}, {10, 30, 40}, {20, 30, 40}, {10, 20, 30, 40} } Ans.
Q.3: If A = {a, b, c, d} and B = {b, d, e, f}, then
Prove that (AUB) - (A∩B) = (A ∆ B)
Solution:
Taking R.H.S:
AΔB = {a, b, c, d} Δ {b, d, e, f}
(By selecting uncommon members among both sets)
We get AΔB = {a, c, e, f} ....... (1)
Taking L.H.S:
AUB = {a, b, c, d} U {b, d, e, f}
AUB = (a, b, c, d, e, f)
A∩B = {a, b, c, d} ∩ {b, d, e, f}
A∩B = (b, d)
AUB - A∩B = (a, b, c, d, e, f) - (b, d)
We get AUB - A∩B = ({a, c, e, f} ....... (2)
By (1) and (2)
AΔB = AUB - A∩B Hence Proved
Q.4: Find the value of a2+b2+c2 when a+b+c = √ 17 and ab+bc+ca = 2.
Solution:
Given that:
(a+b+c) = √ 17
By squaring on both side
(a+b+c)2 = (√ 17)2
From Formula:
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca = 17
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 2 (ab + bc + ca) = 17
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 2 (2) = 17
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 + 4 = 17
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 = 17 - 4
(a+b+c)2 = a2+b2+c2 = 13 ANSWER
Q.4: Find the value of 85.7 x 2.47 / 8.89 with the help of logarithmic table.
Monday 26 April 2021
Chemistry (English) - For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Group) - Solved Model papers 2020 -2021- AS PER CONDENSED SYLLABUS
GO TO INDEX
Chemistry (English)
For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Groups)
Solved Model papers 2020 - 2021
As Per condensed Syllabus
Special Thanks To Sir Waseem Ahmed Qureshi
BS Zoology (UOK)
# 0315 - 0226373
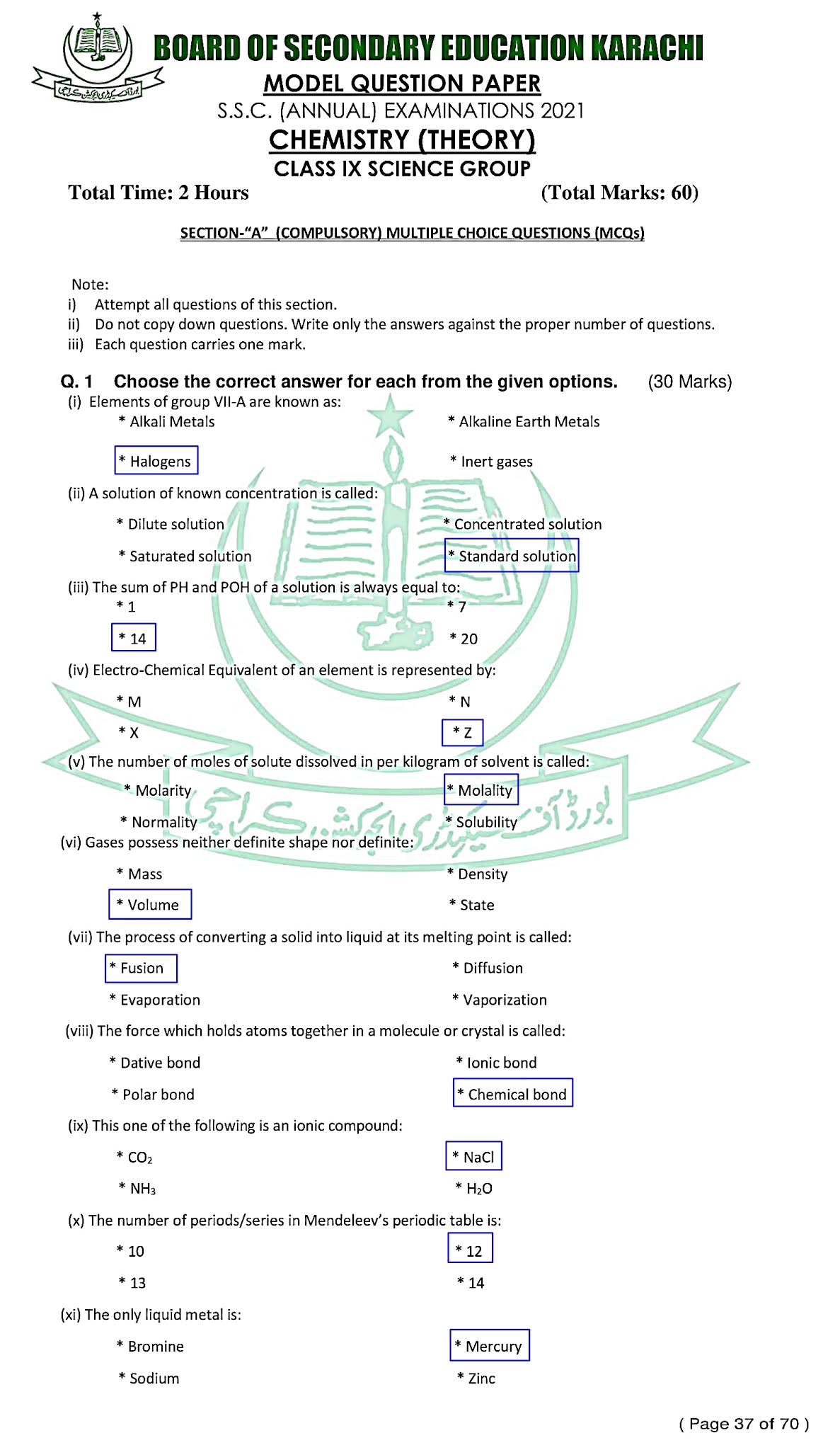
Note: The correct answer of XXI is Molecular Mass
SECTION "B" (SHORT ANSWERS QUESTIONS) (18 Marks)
Note: Answer any six (6) questions from this section. Each carries 3 marks.Q.2: What is meant by Mole? Calculate the number of moles in 96g of SO2.
Ans: Mole:
The molecular mass, atomic mass and formula mass of a substance expressed in grams is called mole.
Data:
No. of Mass = ?
Given Mass = 96 g
Molecular Mass Of SO2 = ( 32 + 16 x 2) = 32 + 32 = 64 a.m.u
Solution:
We know that:
Mole = Given Mass of a substance/Atomic mass OR Molecular mass
=
= 3/2
= 1.5 moles Ans
Q.3: Write down any three chemical properties of acids.
Ans: CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ACIDS:
"Acid react with bases, metals, non-metals and other things etc. Some of the properties are given below."
1. Neutralization:
"Acids react with bases to form salt and water, this is called Neutralization."
HCl + NaOH → NaCl↓ + H2O
Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride (salt) + Water
2. Reaction with metals:
"Dilute acid reacts with certain metals such as (Zn, Mg and Fe to produce H2 gas)"
For example: Dilute Hydrochloric acid reacts with Zn metal to produce H2 gas.
Zn + 2HCl(dil) → ZnCl↓2 + H2↑
Zinc + Hydrochloric acid (dilute) → Zinc chloride (salt) + Hydrogen gas
3. Reaction with carbonate and bicarbonates:
Acid react with carbonate and bicarbonate salts to produce CO2 gas.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
Sodium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid → Sodium chloride + Carbon dioxide
4. Reaction with oxides and hydroxides of metals:
Metal oxide and hydroxide react with acid to form salt and water like neutralization.
FeO + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2O
Ferrous oxide + Sulphuric acid → Ferrous sulphate + water
(Note: Do any three properties as mentioned in question)
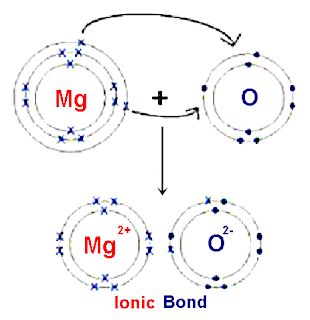
Q.4. Define Ionic bond. Describe the mechanism of formation of NaCl.
Ans: IONIC BOND:
The electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions is called ionic bond or electrovalent bond.
Example #1:
Formation Of Ionic Bond In Sodium Chloride (NaC1):
The combination of sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) atom to form common salt. sodium chloride (NaC1), An atom of sodium (Na) transfers one electron and become positive sodium ions (Na+) and an atom of chlorine gains that electron to complete octet and becomes chloride negative ions (Cl-)
Na → Na+ + e-
2,8,1 → 2,8 + 1 (electronic configuration)
2,8,1 → 2,8 + 1 (electronic configuration)
Cl + e- → C1-
2,8,7 + 1 → — 2,8,8 (electronic configuration)
2,8,7 + 1 → — 2,8,8 (electronic configuration)
Na+ + Cl- → NaC1
The oppositely charged Na+ and Cl+ are held together By electrostatic force of attraction and ionic bond produced between them.
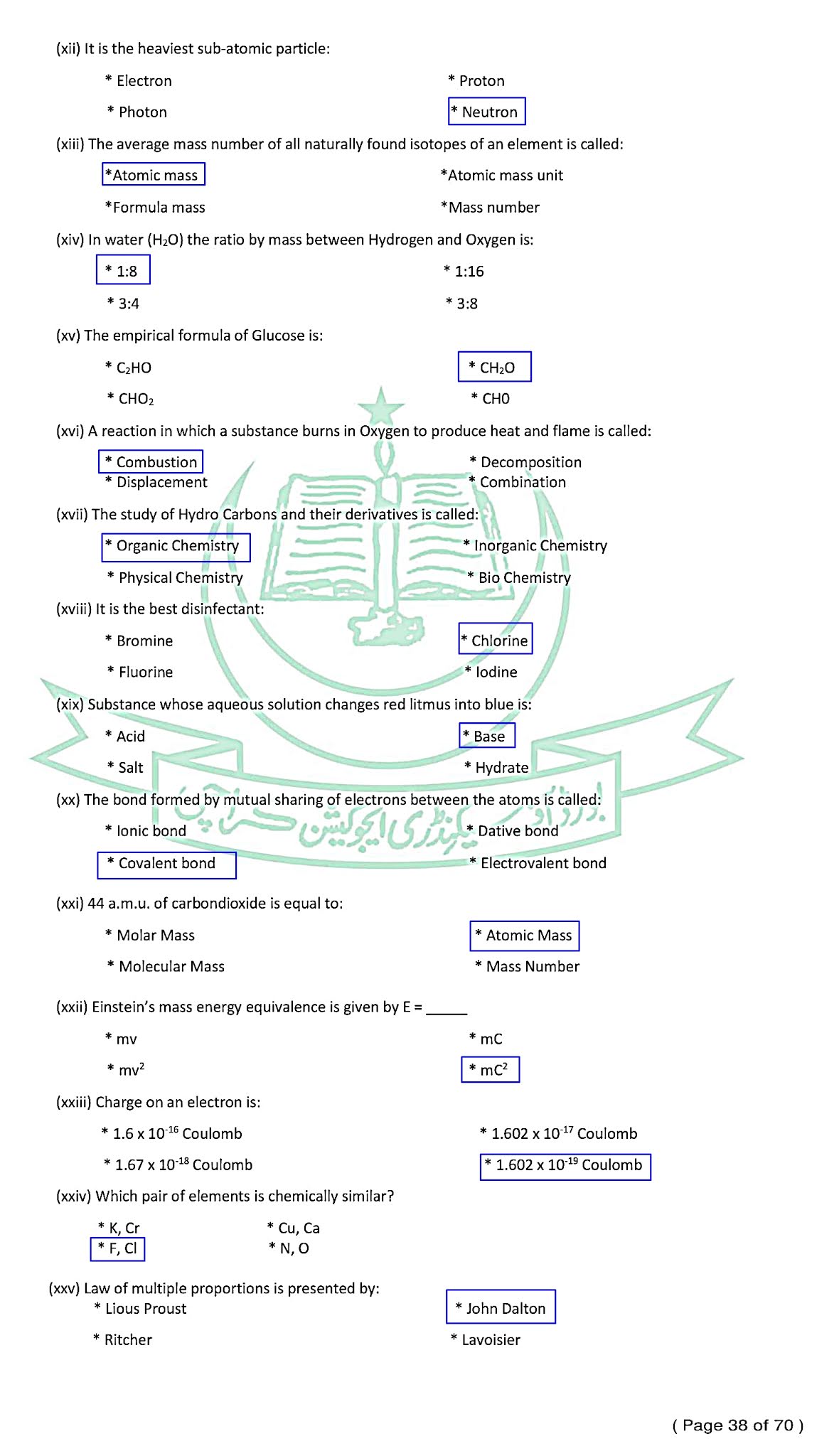
Example #2:
Formation Of Ionic Bond In Magnesium Oxide:
Magnesium (Mg) has two electrons in its valance shell while Oxygen has six electrons in its valence shell. Magnesium atom losses two electrons and become magnesium ion (Mg+2) and Oxygen (0) gains two electrons and becomes oxygen ion (O-2). thus attain a stable noble gas structure by having eight 8 electrons in their valence shell. Mg+2 and O-2 attracts each other to form Mg+2O-2.
Mg → Mg+2 + 2e-
2,8,2 → 2,8 + 2 (electronic configuration)
2,8,2 → 2,8 + 2 (electronic configuration)
O + 2e- → O-2
2,6 + 2 → — 2,8
2,6 + 2 → — 2,8
Mg+2 + O-2 → MgO
Q.5: Balance the following Chemical equations by using co-efficient:
i) N2 + H2 → NH3 (Hint: Balance hydrogen on R.H.S first)
| N2 + H2 → NH3 | |
|---|---|
| N = 2 | N = 1 x 2 = 2 |
| H = 2 x 3 = 6 | H = 3 x 2 = 6 |
| N2 + 6H2 → 2NH3 (Balanced) | |
ii) CH4+ O2 → CO2 + H2O (Hint: Balance hydrogen on R.H.S first)
| CH4+ O2 → CO2 + H2O | |
|---|---|
| C = 1 | C = 1 |
| O = 2 x 2 = 4 | O = 2 + 1 = 3 = 2 + 1 x 2 = 2 + 2 = 4 |
| H = 4 | H = 2 x 2 = 4 |
| CH4+ 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O (Balanced) | |
iii) KNO3 → KNO2 + O2 (Hint: Balance Oxygen on L.H.S first)
| KNO3 → KNO2 + O2 | |
|---|---|
| K = 1 x 2 = 2 | K = 1 x 2 = 2 |
| N = 1 x 2 = 2 | N = 1 x 2 = 2 |
| O = 3 x 2 = 6 | O = 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2 + 2 = 4 + 2 = 6 |
| 2KNO3 → 2KNO2 + O2 (Balanced) | |
Q.6: Find out Protons and Neutrons present in the following atoms
- 7N14
- 17Cl37
- 92U235
i) Nitrogen 7N14
Data:
Mass number Or Atomic mass = A = 14
Atomic number = Number of electrons = Z = 7
Proton or P+ = ?
Neutron no. = N = ?
Solution:
We know that Proton number is equal to electrons or Atomic number So,
Proton (P+) = Z = 7
We also know that
Mass number = No. of Proton + No. of Neutron
A = P+ + N or
N = A - P
= 14 - 7 = 7
Ans:
Number of Proton = 7
Number of Neutron = 7
i) Chlorine 17Cl37
Data:
Mass number Or Atomic mass = A = 37
Atomic number = Number of electrons = Z = 17
Proton or P+ = ?
Neutron no. = N = ?
Solution:
We know that Proton number is equal to electrons or Atomic number So,
Proton (P+) = Z = 17
We also know that
Mass number = No. of Proton + No. of Neutron
A = P+ + N or
N = A - P
= 37 - 17 = 20
Ans:
Number of Proton = 17
Number of Neutron = 20
i) Uranium 92U235
Data:
Mass number Or Atomic mass = A = 235
Atomic number = Number of electrons = Z = 92
Proton or P+ = ?
Neutron no. = N = ?
Solution:
We know that Proton number is equal to electrons or Atomic number So,
Proton (P+) = Z = 92
We also know that
Mass number = No. of Proton + No. of Neutron
A = P++ N or
N = A - P
= 235 - 92 = 143
Ans:
Number of Proton = 92
Number of Neutron = 143
Q.7: What are Transition Elements? Describe any two general characteristics of these elements?
Ans: TRANSITION ELEMENTS:
Elements in group IB, IIB to VIIB are known as transition elements because they show their variable valency which are transitional between highly reactive and strong positive elements of S-Block elements which form ionic compounds and P-Block which form largely covalent compounds.
Characteristics:
- Transition elements have incomplete inner electron shells and are characterized by their varaiable valencies and show similar behaviors.
- All transition elements are metals, in which bonds between the atoms are very strong.
- They have high melting point.
- The compounds are formed by coordinate covalent bonds.
8. Define both kinds of Displacement reaction with an appropriate chemical equation as example for each.
Ans:
1) SINGLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION: (2006, 2007, 2008)
A reaction in which one atom or groups of atoms of a compound replaced by another atom or group of atom in a compound is called single displacement reaction.
Example:
Fe + CuO → FeO + Cu
Cu + HSO4 → CuSO4 + H2
2) DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION: (2013)
A reaction in which two compounds exchange their partners, so that two new compounds are formed is called double displacement reaction. Insoluble salts are formed by mixing soluble salts.
Example:
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
AgNO3 + HCl → AgCl + HNO3.
Q.9: What is diffusion? State Graham's law of diffusion of gases.
Ans: DIFFUSION: (2007, 2008, 2010, 2013, 2012, 2014, 2016, 2019)
The spreading of substance from higher concentration level to lower concentration level is called diffusion.
GRAHAM'S LAW OF DIFFUSION:(2005,2009,2010,2015,2019)
Thomas Graham in 1864 studied the rate of diffusion of different gases and formulated Graham's law.
Statement:
The rate of diffusion of gas at a constant temperature and pressure is inversely proportional to the square root of its density or Molar mass.
Mathematically:
Q.10.:Calculate the molarity of a solution that contains 2 moles of NaOH dissolved in 0.5 liter of the solution.
Data:
No. of moles = 2 moles
Volume of solution = 0.5 liter
Molarity = ?
Solution
We know that;
Molarity = Moles of solute/Volume of solu. (liter)
Molarity = 2/0.5
Molarity = 4 M Ans.
SECTION- "C" (DESCRIPTIVE ANSWER QUESTIONS)
Note: Answer any two (2) questions from this section. Each carries 6 marks.Q.11: Define Solubility then list the factors affecting solubility and elaborate any two of them.
Ans: SOLUBILITY: (2008, 2009, 2015, 2016)
The amount of solute dissolved at a room temperature in 100 gm of the solvent is called solubility.
Factors Affecting the Solubility: (2008)
Many factors are affecting the solubility of a solute in a solvent, these factors may be:
- Temperature
- Pressure (for gasses)
- Nature of solute and solvent
1) Temperature: (2008,2016)
The solubility of many solutes generally increase with the increase in temperature such solute absorb heat when they dissolved in water.
Example: solubility of sugar in water at 0 °C is 179 g / 100 ml where as at 100 °C it is 487 g / 100.
2) Pressure: (2016)
Solubility of Solids and Liquids:
The solubility of solid and liquid are not affected by pressure.
Henry's Law:
Solubility of a Gas of gas in a liquid:
"The solubility of gas in liquids is directly proportional to the pressure of gas."
This is
called Henry's law.m ∝ P
m = KP
where,m = amount of gas
K = constant and
P = pressure
Example: This effect is used in manufacture of bottled soft-drinks as coca-cola; 7-up etc. these are bottled under a carbon dioxide (CO2) pressure slightly greater than 1 atm. When the bottles are opened, pressure decreases, solubility of CO2 also decreases, hence bubbles of CO2 comes out of solution.
3) Nature of solute and solvent:
Solubility:
If a solute is also depends upon nature of the solute and the solvent. Polar compound is more soluble in polar solvent than non-polar solvent. Similarly covalent compounds are more soluble in non-polar solvent.
Example: Napthalene being a non-polar solute is more soluble in benzene (non-polar solvent).
Q.12: State Faraday's law of Electrolysis and explain any one of them.
Ans: FARADAYS LAW OF ELECTROLYSIS:
Introduction: Michael Faraday in 1833, discovered laws of electrolysis which are known as Faraday's law of electrolysis put forward by Faraday.
FIRST LAW OF FARADAY:
"The amount of any substance deposited or liberated at an electrode during electrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through electrolyte."
Explanation: Faraday's law expressed mathematically.W ∝ A X t
W = Z x A x t
Where,A = Current in amperes
Z = Electrochemical equivalent of substance.
T = Time in seconds.
W = mass of substance
The quantity of substance deposited by one faraday (96,500 coulombs) of electricity through an electrolyte is called one Gram chemical equivalent of that substance.
SECOND LAW OF FARADAY:
"When the same quantity of electricity is passed for the same time through different electrolytes connected in series, the substances deposited at the electrode will be in the proportional to their equivalent masses."
13. What is Salt? On the basis of chemical properties describe its three kinds with example.
Ans: SALT:
A salt is ionic compound produced when acid is neutralized by a base.
For example:
Potassium hydroxide neutralized hydrochloric acid to form potassium chloride (salt) and water.
KOH + HCl → KCl + H2O
Types of Salts:
On the basis of their chemical nature salts can be divided into three groups which are:
- Normal salt
- Acidic salt
- Basic salt
1. Normal Salts:
Salts which are formed by the complete neutralization of an acid by a base. These salts do not have replaceable hydrogen ions (H+ or hydroxyl ion (OH-).
Example: NaC1, NaNO3, K2SO4 etc. are normal salts.
HCl + H2O → NaCl + H2O
2. Acidic Salts:
Salts which are formed by the partial or incomplete neutralization of an acid by a base. These salts have replaceable hydrogen ions (H+. They react further with base to form normal salts.
Example: KHSO4, NaHCO3, NaHSO4, KHCO3etc are acidic salts.
KOH + H2SO2 → KHSO2 + H2O
NaOH + H2CO3 → NaHCO3 + H2O
3. Basic Salts:
Salts, which are formed by the partial or incomplete neutralization of a base by an acid. These salts have replaceable hydroxyl ions (OH-.
Example: Mg (OH)Cl, Zn (OH) Cl etc. are basic salts.
Q.14: Write down any four differences between covalent bond and co-ordinate covalent bond.
Ans: Differences Between Covalent Bond And Co-ordinate Covalent Bond.
| S.NO. | COVALENT BOND | CO-ORDINATE COVALENT BOND |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A covalent bond forms by mutual sharing of electrons from both atoms. | A co-ordinate covalent bond forms by one sided sharing of electrons. |
| 2. | The covalent bond is formed between the similar or dissimilar atoms. | Co-ordinate covalent bond is formed between two unlike or dissimilar ateats. |
| 3. | Covalent bond maybe polar or non-polar. | Co-ordinate covalent bond is always polar. |
| 4. | Covalent bond is associated with only covalent character. | Co-ordinate covalent bond is associated with ionic and covalent character, |
For More Guess Papers Click Here
Chemistry (Urdu) - علم کیمیاء - For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Group) - Solved Model papers 2020 -2021- AS PER CONDENSED SYLLABUS
GO TO INDEX
Chemistry (Urdu) - علم کیمیاء
For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Groups)
Solved Model papers 2020 - 2021
As Per condensed Syllabus
Sunday 25 April 2021
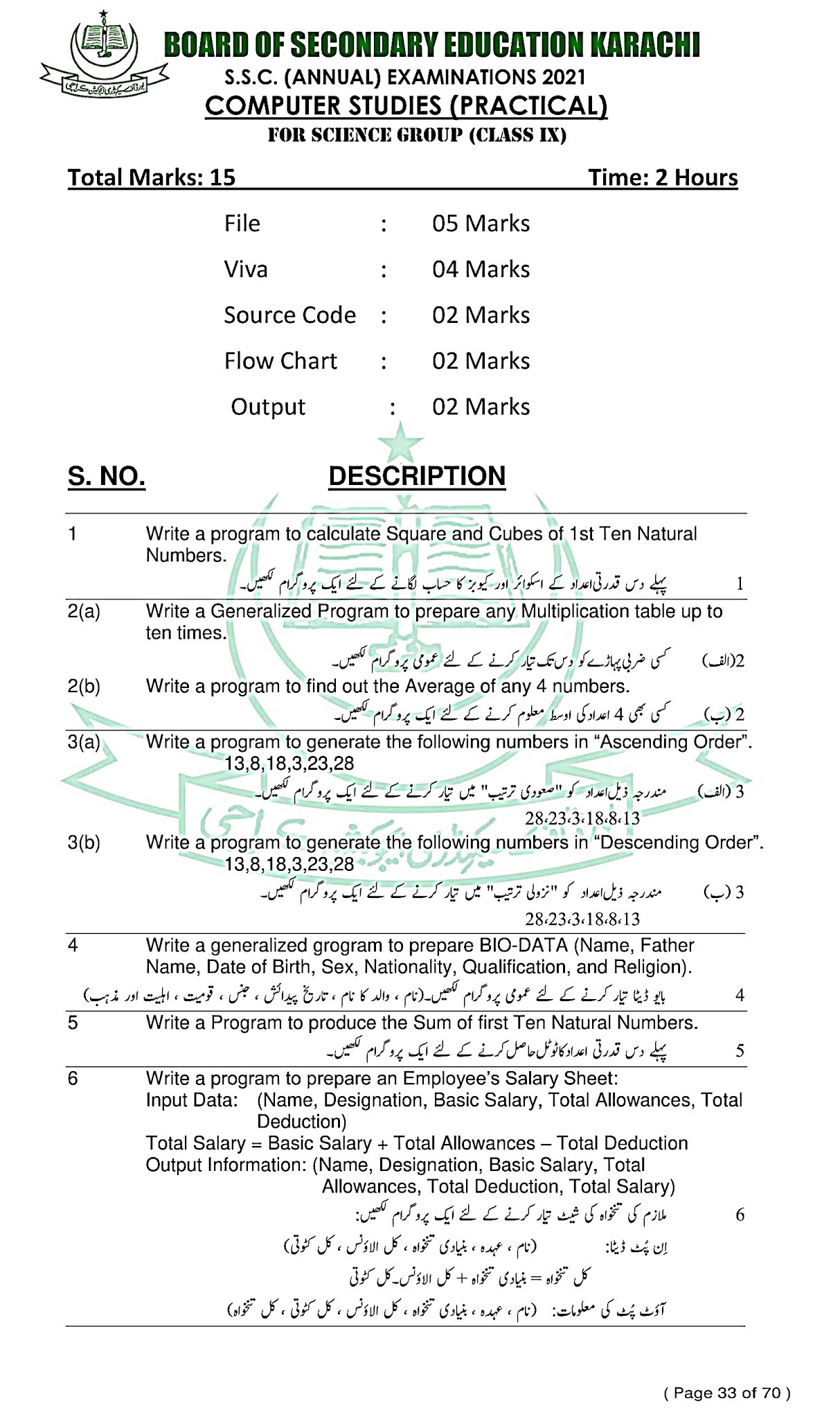
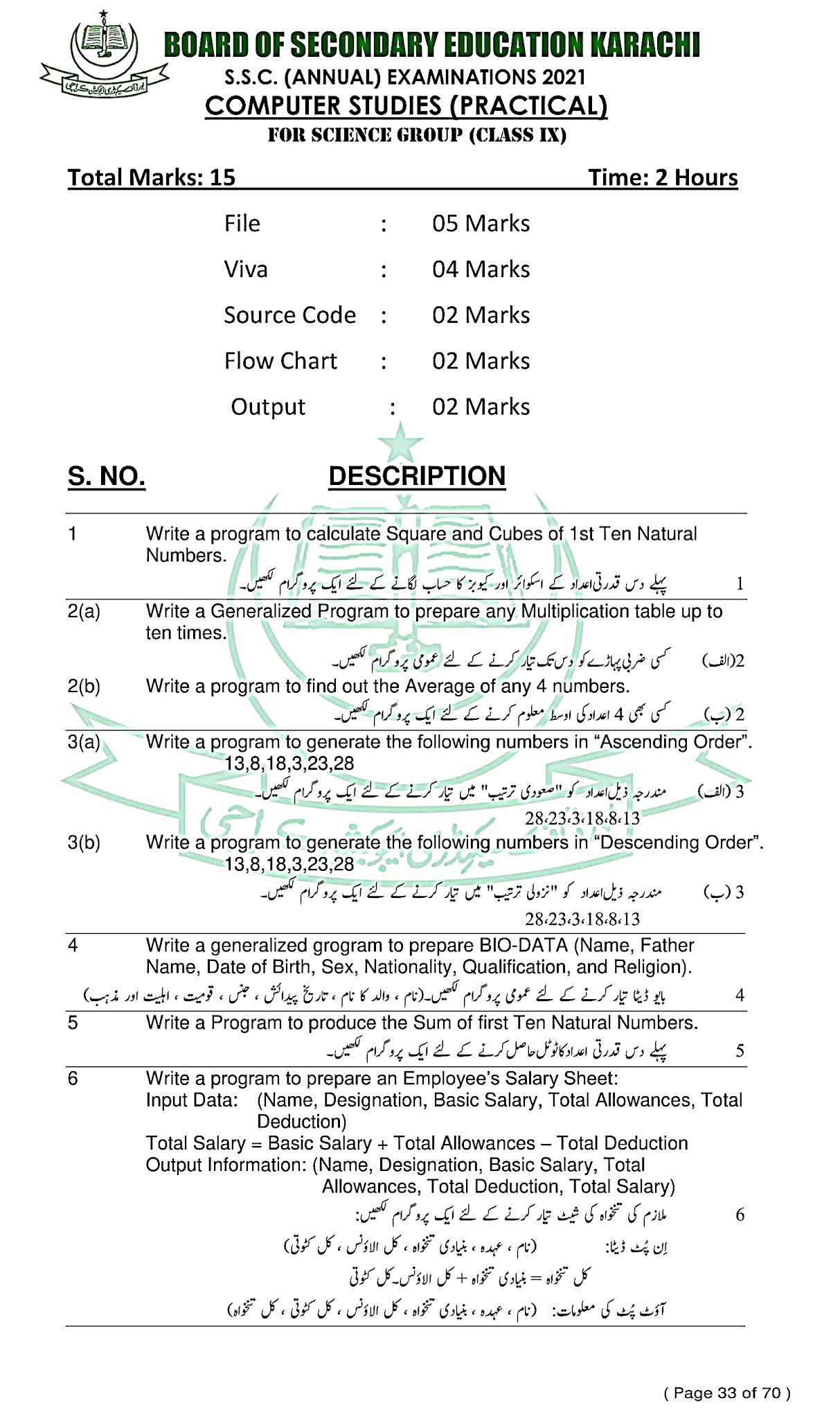
Computer Studies (English) - For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Group) - Solved Model papers 2020 -2021- AS PER CONDENSED SYLLABUS
GO TO INDEX
Computer Studies (English)
For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Groups)
Solved Model papers 2020 -2021
As Per condensed Syllabus
SECTION "B"
SHORT ANSWERS QUESTIONS (18 Marks)
Note: Answer any Two (2) questions from this section. All questions carry equal marks.Q.2: What a hacker can do to your computer?
Ans: Hackers: Hackers are cyber criminals. Hacker can be a person who has in-depth knowledge of computer systems, networks, and programs. Hacker maybe someone who uses his or her extensive skills to identify and overcome a network loophole. Hackers constantly seek further knowledge and freely share what they have discovered.
Q.3: Why do we use "Arrange group" in the Page Layout Tab?
Ans: Arrange Group:
The buttons in Arrange Group help the users to quickly arrange graphical and other elements of the document in relation to the main textual content. These buttons are:
- Position
- Wrap Text
- Bring Forward
- Send Backward
- Selection Pane
- Align
- Group
- Rotate
Q.4: Define any three functions of operating system?
Ans: Functions Of Operating System:
(i) Booting:
Booting is a process of starting the computer operating system.
It checks the computer resources and makes it ready to perform different tasks.
(ii) Resource Management:
Operating system automatically manages all the hardware and software resources of a computer when application programs are executed by computer users.
This includes allocation and de-allocation of processor, memory, access to shared cache memory and access to network resources.
(iii) User Interface or Command Interpreter:
We interact with operating system through user interface or Command Interpreter.
User Interface or command interpreter is one of the parts of operating system which reads the commands from user, interprets them and translates them into machine language instructions that the computer hardware can understand.
(Note: There are given eight functions of operating system in text book Chapter No.2, you can write others of your choice also.)
Q.5: Write three differences between Physical address and Logical address?
Ans: Differences Between Physical Address And Logical address
| S.No. | Physical Address | Logical address |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Physical address is attached with ROM of the NIC card. | Logical address is assigned to a device. |
| 2. | Physical Addressing means MAC (Media Access Control) provided by manufacture and attached address of the NIC. The card which is used to connect your machine to the internet. | Logical addressing means IP addressing that is provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or set by network administrator. |
| 3. | Physical addressing cannot be can be changed. They are also called hardware address. | Logical Address can be changed. |
| 4. | Physical address is a 48 bit mac address. | Logical address is a 32 bit IP Address. |
| 5. | It is globally Unique and permanent. | It is unique in one network and temporary. |
(Note: Do any three if mentioned in question)
Q.6: Define BUS? How many types of buses are there? write their name?
Ans: Buses
In computer, Buses are the electric paths on which data is sent and received by different components. They are just like roads. As roads connect different places, buses connect all the parts of the computer to each other. They also connect all internal components on the motherboard.
Types Of BUS:
There are three types of buses;
- Control Bus
- Data Bus
- Address Bus
Q.7: Define Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)?
Ans: Hypertext Markup Language (HTML):
- HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language.
- It is standard markup language for text documents.
- HTML is used to create web pages that are displayed by web browsers mainly on internet.
- HTML consists of a series of elements. These elements tell the browser how to display the content.
- It allows the user to create structured content by adding headings, paragraphs, links, blockquotes and other media.
- It takes advantage of simple code structures called tags and attributes to achieve formatting, graphic and navigation effects on web pages.
Q.8: Why is computer security being important? Write any two reasons?
Ans: Importance of Computer Security:
Computer security is important for our computer's overall health, because the computer has become an important part of our life. We store important data on our computers in the shape of documents, pictures, programs, etc. Therefore, we expect that all our information must remain safe and our computer runs properly without any problem.
Reasons Of Importance of Computer Security:
1. Prevent from viruses and malware:
It keeps our information protected and helps prevent viruses and malware, which allows programs to run quicker and smoother.
2. Secure Private Information:
It safeguards confidential and sensitive information. This information may include our passwords, banking details, contacts, pictures, etc. To protect this information we need to make our devices secured that no one can damage or access this information without our consent.
3. Provide Safe Environment:
Computer Security is important as it enables people to perform their work in safe environments.
It helps in the execution of essential business processes.
(Note: write down any two as mentioned in question)
Q.9: Define the following : (any one)
- Computer Network
- Data Communication
Computer networks are just like a highway on which data can travel. It connects parts of distributed system including hardware and software. It shares common functions and features like data and devices which is very important nowadays.
A computer network is a group of computers and related equipment connected by a communication links to share data and other resources.
The Related Equipment may be printer, scanners, fax machines, server, etc.
The Resources may include a file server, internet connection, etc.
2. Data communication:
Data communications refers to the sharing of a virtual message. Data communication is the exchange of digital messages between two devices. It involves a sender and a receiver which communicate via some form of transmission medium such as a cable.
Example:
Electronic communications, like emails and instant messages and phone calls are examples of data communications.
Q.10: Write any three differences between Analog Signals and Digital signals?
Ans: Difference Between Analog Signals and Digital signals
| S.No. | Analog Signals | Digital signals |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | An analog signal is a continuous wave that changes by time period. | A digital signal is a discrete wave that carries information in binary form. |
| 2. | Analog signal has no fixed range. | Digital signal has a finite number i.e. 0 and 1. |
| 3. | An analog signal can easily be disturbed by other signals or waves. | A digital signal is less prone to other signals disturbance. |
| 4. | The human voice is example of an analog signal. | Signals used by computer are the digital signal. |
| 5. | An analog signal is represented by a sine wave. | A digital signal is represented by square waves. |
| 6. | Analog signals are long term waves need to be boosting. | Digital signals are short term signals remain within digital devices / electronic. |
(Note: Do any three as mentioned in question)
SECTION "C"
(DESCRIPTIVE - ANSWER QUESTIONS) (12 Marks)
Note: Answer any Two (2) questions from this section. All questions carry equal marks.(DESCRIPTIVE - ANSWER QUESTIONS) (12 Marks)
Q.11: Define CPU and Microprocessor and their major parts.
Ans: Microprocessor (CPU):
Definition:
Microprocessor is also called (CPU ) Central Processing Unit. CPU or microprocessor is the brain of computer. The microprocessor or CPU is a chip which is made up of silicon and containing millions of tiny transistors. These transistors manipulate data. The CPU is housed in the computer's mother board.
Microprocessor performs all the calculations necessary to make the computer work. Thee microprocessor fetches, decodes, executes and stores all the instructions given by the user or any other device. The speed of computer mainly depends upon the speed of microprocessor. It interprets the data and instructions. It generates control signals. It also produce the address bit needed by memory.
Components Or Parts Of Microprocessor:or CPU
There are typically five components of a microprocessor.
(a) Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):
(b) Control Unit (CU):
(c) Clock:
(d) Registers:
(e) Cache:
Q.12: Define Topology. Explain its type?
Ans: Definition Of Topology:
The physical layout in which computers are connected is called topology. The topology of network describes the way computers are connected. Topology is a major design consideration for computer networking.
Types Of Topology:
(i) Bus Topology:
In Bus Topology computers and other devices are connected with a single cable. The central cable is the backbone of the network and every device communicates with the other device through this bus.
The advantages of Bus Topology are simplicity, low cost and easy expansion of the network. The disadvantage of the Bus Topology is that a breakdown in the bus cable brings the entire network down.
(ii) Ring Topology:
In Ring Topology, computers are connected in a ring or circle shape. The signal travels around the loop in one direction and passes through each computer. The recipient of the message receives the message while another computer acts like a repeater to send it to the next computer.
The failure of a link or a computer can make the entire network nonfunctional.
(iii) Star Topology:
In a star topology, all the computers are connected to a central device called hub or switch. To communicate with any computer, the sender must send information to the hub. Then the hub transmits that information to the destination.
The advantages of star topology are easy to set up and easy expansion of the network. Another feature of Star Topology is that if one link to the hub breaks, only the station using that link is affected not the whole network.
Q.13: Explain the basic components of DBMS?
Ans: BASIC COMPONENTS OF DBMS
The basic components of DBMS are:
(i) Table:
(ii) Field:
(iii) Record:
(iv) Data Types:
For example:
(v) Views:
Q.14: What are the properties of a Good Communication System?
Ans: Properties of a Good Communication System:
The effectiveness of a data communications system depends on the fundamental characteristics which include delivery, accuracy and timeliness.
Components Or Parts Of Microprocessor:or CPU
There are typically five components of a microprocessor.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
- Control Unit (CU)
- Clock
- Registers
- Cache
(a) Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):
- ALU performs all the actual calculations like arithmetic operations and logical comparisons.
- Arithmetic operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication and division while logical comparisons include comparing, selecting and matching of data.
(b) Control Unit (CU):
- Control Unit is responsible for controlling the transfer of data and instructions among other units of a computer.
- This unit controls the operations of all parts of the computer but does not carry out any actual data processing operations.
- CU functions just like a traffic policeman.
- It manages and coordinates all the units of the computer.
(c) Clock:
- Clock generates pulses and instructions are executed on the basis of pulses.
- Clock speed is measure in MHz and GHz.
(d) Registers:
- It is a temporary storage area that holds the data that is being processed.
- It is also known as programming model which may be of 8 bits, 16 bits, 32 bits or 64 bits.
(e) Cache:
- Cache is an intermediate storage area, which is available inside microprocessor.
- The immediate processed information is stored in cache.
- The cache inside the microprocessor is called internal cache and outside is called external cache.
Q.12: Define Topology. Explain its type?
Ans: Definition Of Topology:
The physical layout in which computers are connected is called topology. The topology of network describes the way computers are connected. Topology is a major design consideration for computer networking.
Types Of Topology:
(i) Bus Topology:
In Bus Topology computers and other devices are connected with a single cable. The central cable is the backbone of the network and every device communicates with the other device through this bus.
The advantages of Bus Topology are simplicity, low cost and easy expansion of the network. The disadvantage of the Bus Topology is that a breakdown in the bus cable brings the entire network down.
(ii) Ring Topology:
In Ring Topology, computers are connected in a ring or circle shape. The signal travels around the loop in one direction and passes through each computer. The recipient of the message receives the message while another computer acts like a repeater to send it to the next computer.
The failure of a link or a computer can make the entire network nonfunctional.
(iii) Star Topology:
In a star topology, all the computers are connected to a central device called hub or switch. To communicate with any computer, the sender must send information to the hub. Then the hub transmits that information to the destination.
The advantages of star topology are easy to set up and easy expansion of the network. Another feature of Star Topology is that if one link to the hub breaks, only the station using that link is affected not the whole network.
Q.13: Explain the basic components of DBMS?
Ans: BASIC COMPONENTS OF DBMS
The basic components of DBMS are:
- Table
- Field
- Record
- Data Types
- Views
(i) Table:
- It is a collection of data elements organized in shape of rows and columns.
-
Example:
(i) A contact list may be one of the simplest examples of a table.
(ii) The marks record prepared by a class teacher is also an example of a table.
(ii) Field:
- It is the smallest component in a database.
- It is where the actual data is stored during data entry.
- All data fields in the same table, have unique names.
- Fields are also called attributes or columns.
- Multiple fields make up a data record, several data records make up a data table, and several data tables make up a database.
(iii) Record:
- A single entry in a table is called a record.
- Records are also referred as tuples or rows.
- A record is made up of two or several data items which are also called tuples in a table representing a set of related data.
- For example, the illustrated Student table has 4 tuples /records/rows.
Components Of Tables
(iv) Data Types:
- All fields in a table must have some data type.
- Data type is a data storage format that can contain a specific type or range of values.
- The data type of a field is a property that tells what kind of data that eld can hold.
- Different DBMSs offer different range of data types to be stored.
- Here are some basic data types:
| Data Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Integer | Holds only whole numbers. | 145, -35, 74586 |
| Floating Point | Holds numbers with decimal points. | 5.6, 3.14, 554.9 |
| Character | Stores only one character. | A, B, c, d |
| String | Can store a combination of numbers, letters and special characters. | Pakistan, Computer, @admin |
| Boolean | Can hold only Boolean values i.e. true or false. | 1,0 |
| Date And Time | Stores date and time in specified format. | 01-01-2020 11:30 |
For example:
- MS Access allows a range of whole numbers from -32768 to 32767 for an “Integer”.
- In modern DBMS, choosing proper data type is important to make sure that database runs faster.
(v) Views:
- In a database the data is stored in tables. However, we can see that data through views.
- Views do not store data and just show the information virtually.
- They have the ability to fetch data from different tables.
- Views maintain the security of data and ensure that no changes occur in the original data.
Q.14: What are the properties of a Good Communication System?
Ans: Properties of a Good Communication System:
The effectiveness of a data communications system depends on the fundamental characteristics which include delivery, accuracy and timeliness.
| S.No. | Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Delivery | Making sure that the data is delivered is the first fundamental characteristic of any communication network. The system must be able to deliver data in correct order to the correct destination. |
| 2. | Accuracy | The system must deliver the data accurately. Data that has been altered during transmission and left uncorrected is not useful. |
| 3. | Timeliness | The data must be delivered in a timely manner. Late delivered data is useless. |
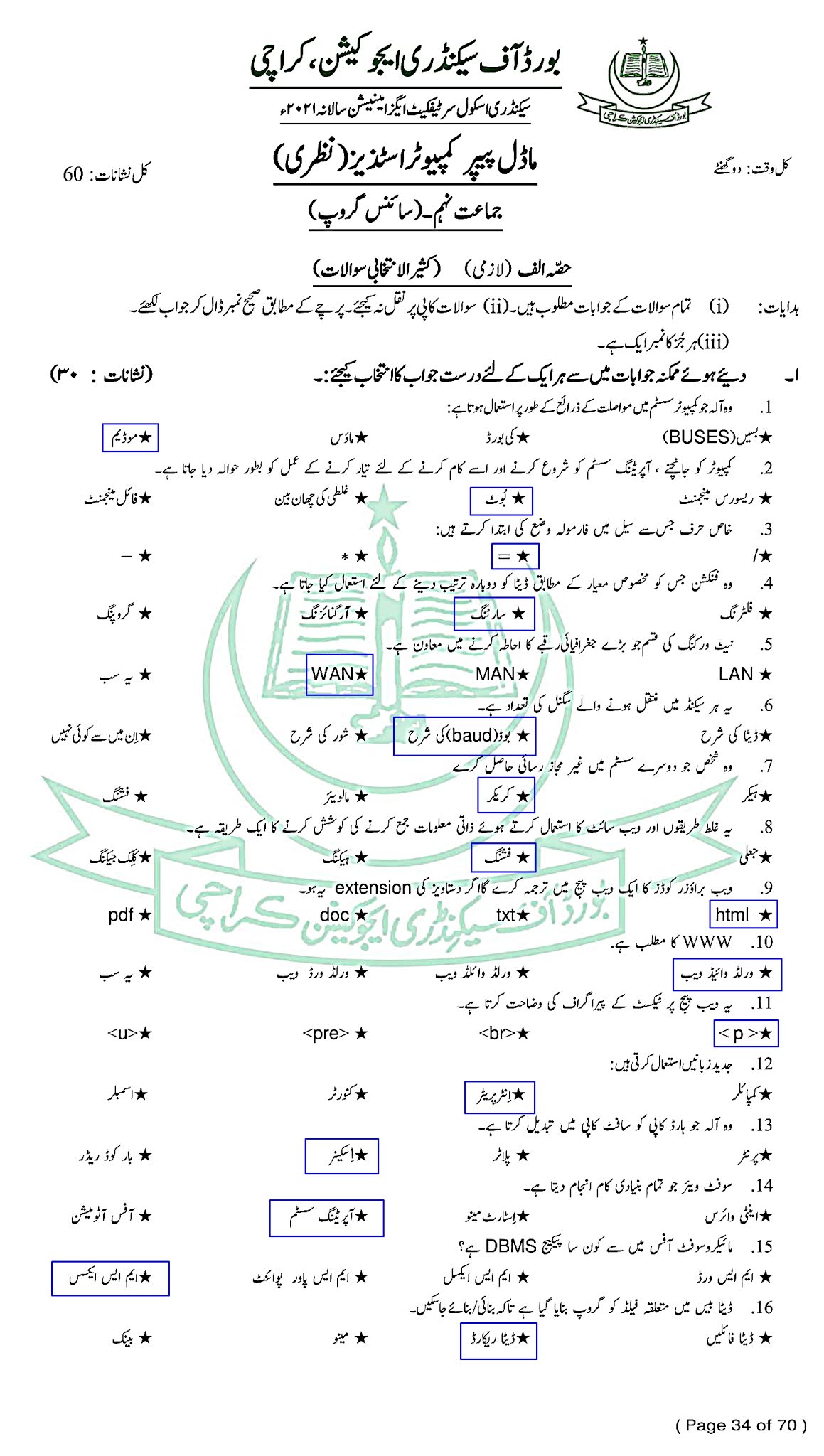
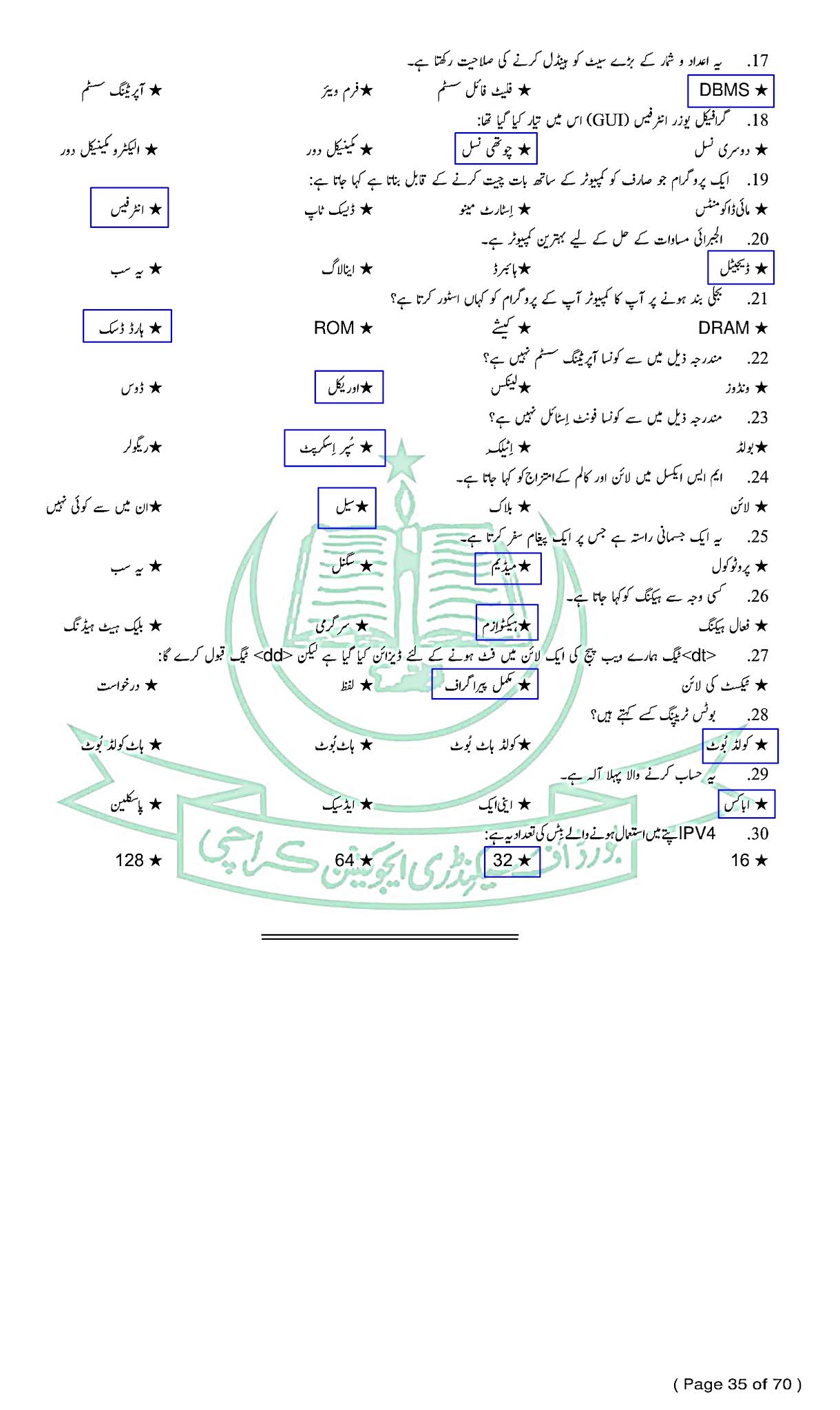
Computer Studies (Urdu) - کمپیوٹر اسٹڈیز - For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Group) - Solved Model papers 2020 -2021- AS PER CONDENSED SYLLABUS
GO TO INDEX
Computer Studies - کمپیوٹر اسٹڈیز - ((Urdu)
For Class SSC - Part 1 (Science Groups)
Solved Model papers 2020 -2021
As Per condensed Syllabus
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)