Go To Index
Physics For Class IX (Science Group)
SCIENTIFIC REASONS
UNIT 1: PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AND MEASUREMENT
1. Fill a tub with water to certain level and mark.
Put some ice in it and observe the water level carefully as well as floating or sinking. Remove the ice from the tub without being melt and put a balloon in it and then observe. Likewise, put a spoon in that tub and observe. Again put an empty can of coke and observe. Can you tell which of all four has more density? And which has more volume?
Reason:
When we put a spoon in that tub it sinks into water, while rest are float on the surface of water. Thus spoon is much denser than rest object and has more density.
Similarly Balloon occupies more space than ice, spoon or empty can of coke. Thus balloon has more volume than rest objects.
2. Why large weight woods floating on the surface of water and iron needle sinks into the water?
Reason:
Iron is “denser” than wood and have more density that is why iron needle sink into water and large weight woods floating on the surface of water.
3. Why the humans in 'Dead Sea' situated in Jordan does not sink while swimming?
REASON:
The humans in that sea while swimming does not sink! This is because the water of sea is much more salty than normal, which raises the density of water.
4. The large weight woods floating on the surface of water. However, an iron needle sinks into the water.
REASON:
Iron is “denser” than wood and water, where as wood is less dense than water that is why needle sinks into water while the large weight woods floating on the surface of water.
5. Why ice floats while a coin sinks in the water?
REASON:
Solid objects are denser and have more weight than liquids. Although ice is a solid but the water is heavier than ice, it displaces the lighter ice, causing the ice to float to the top.
While the coin have more density than the water, and so the coin sink. So anything with more density than water will sink in water, but other objects that have less density than water will float.
6. Which is more accurate Vernier Caliper or a Screw Gauge and why?
Ans: Screw Gauge is more accurate than Vernier Caliper:
REASON: As compare to Vernier calipers, screw gauge is more accurate and precise because a screw gauge can even measure dimensions smaller (such as the diameter of a wire or sphere) than those measured by a Vernier Caliper. The least count of Vernier calipers is 0.1 mm and for screw gauge it is 0.01 mm. So, a screw gauge can measure accurately up to one hundredth part of a millimeter and more accurate than a Vernier caliper.
UNIT 2: KINEMATICS
Ans: Gravitational acceleration or gravity is taken negative for objects moving upward direction. Because if a body moving upwards, the acceleration due to gravity is downward and hence, it acts in opposite direction of the velocity. So it is considered negative.
UNIT 3: DYNAMICS
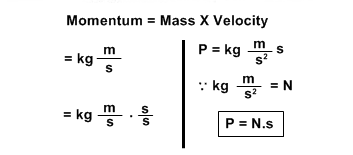
Ans: We know that momentum is P = mv.
If a body comes to rest, it means its velocity, v = 0, therefore its momentum becomes:
P = mv
P = m(0)
P = 0
So, when a body comes to rest its momentum is considered equal to zero.Q.2: Why do you pull your hands while catching a fast moving ball?
Ans: A fast-moving ball tends to keep moving due to inertia. According to Newton's second law, the force with which a ball is moving is equal to its mass multiplied by its acceleration. When we catch a ball, the momentum of the ball is transferred from ball to hand. If we keep our hands stationary, the force with which momentum is transferred might hurt our hands. But as soon as we pull our hands back, it increases the time during which the high velocity of the moving ball decrease to zero and net momentum is decreased, thus reducing the force with which the ball makes an impact with our hands.
Q.3: What is reason that you experience a jerk whenever the school bus stops all of sudden?
Ans: When the school bus stops suddenly, we tend to fall forward because due to our inertia we tend to remain in a state of motion even though the bus has come to rest.
Q.4: Why it is dangerous to jump from a moving bus?
Ans: A man jumping out from a moving bus holds the inertia of motion. As the man lands on the ground, his feet come to rest instantly while the upper part of the body continues to move due to inertia of motion. Therefore, the person may fall forward. So, it is very dangerous to jump out of a moving bus.
Q.5: What is the role of force according to Newton's second law of motion?
Ans: According to Newton's second law of motion,
"A force is a vector that causes an object with mass to accelerate. Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object depends upon two variables:
- The net force acting on the object and
- The mass of the object"
Q.6(a): What happens according to Newton's third law, while you pull a catapult?
Ans: Newton's Third-law of motion states that:
"For every action force, there is a reaction force that is equal in strength and opposite in direction."
Newton's Third-law is without a doubt the law that is seen most in the launch of the catapult. It is displayed countless moments in the experiment. This law applies a pushing force as well as pulling force too.- "Pulling back the lever is the action, and flinging forward the marshmallow is the reaction."
- Similarly as the rubber bands of catapult are pulling on the hook forcefully, the hooks are pulling on the rubber bands with just as much force in the opposite direction.
- Also, when the key of the catapult is being pulled out of the key post, the key is pulling the string with the same amount of force that the string is pulling the key. These forces are just going in the opposite direction.
Q.6(b): What happens according to Newton's first law, while you pull a catapult?
Ans: According to Newton's first law of motion:
"An object at rest stays at rest until a force is applied, and an object in motion stays in motion, at the same speed, until a force acts upon it".
An object at rest stays at rest- this means that the projectile will always sit in the cap if we don't apply a force to it. Until a force is applied- the force we applied was the arm of the catapult. When we pull back the arm it stores up a lot of energy, but when we let go of the arm it changed the form of energy and applied a force to the projectile. This change in the energy created
a force that launched the projectile forward.Q.7: Why mass does not differ, while weight differs from place to place?
Ans: Weight of a body is the gravitational force on it and mass is the amount of matter in the body. Thus, weight is dependent on gravitational acceleration, g but mass does not depend on the value of g. Hence, the weight of a body will change from one place to another place because the value of g is different in different places. For example, the value of g on the moon is 1 /6 times the value of g on earth. As mass is independent of g, so it will not change from place to place.
Q.8: Why do we feel pushed outward while a car turns on a curved road?
Ans: The force that pulls out from the center on a body in circular motion is called centrifugal force and it increases with acceleration. Centrifugal force results in a strong outward pull on our vehicle. That's why we feel pushed outward while a car turns on a curved road. So we need to slow down a car before entering a curve.
Q.9: Which force prevents a passenger from falling down a roller coaster while it turns the riders into upside-down position?
Ans: This force is inertia which prevents us from falling down or out in a a roller coaster because inertia is a resistance against a change in direction. It keeps us pressed against the bottom of the car with a force stronger than gravity.
Q.10: Why it is easier to walk wearing flat slippers than the high heel sandals?
Ans: Wearing flat slippers will likely be far more comfortable than high heel sandals. This is because the whole of the foot and arch are fully protected without putting too much pressure on sensitive areas such as the toes and heel. Flat slippers have a greater area in contact with the soft sand as compared to high heel sandals. Due to this, there is less pressure on the surface area and less reaction force and it is easy to walk on it.
Q.11: Why leather sheet is used in brake drums of motor bike?
Ans: A drum brake is a brake that uses friction caused by a set of shoes or pads that press outward against a rotating cylinder-shaped part called a brake drum. The leather sheet is used in brake drums because it provides high friction to stop the motorbike.
Q.12: When a free falling object moves towards earth due to pull of earth on it. Does earth also move towards that object due to reaction? Explain.
Ans: Yes, when a free falling object moves towards earth due to pull of earth on it. Earth also move towards that object due to reaction, but the acceleration produced by the earth towards the object is negligible.
This can be easily explained by the equation of Newton's second law of motion F = ma.
Earth and any free falling object pull each other towards them. The force applied on both of them remaining the same, but the changes in the position of an object are determined by its mass and acceleration.
According to the universal law of gravitation, two bodies attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them. So, theoretically, a free-falling object also pulls the earth in the same way the earth does. But comparing to the mass of the earth, the mass of the free-falling object is negligible. Hence the motion of Earth in not noticed because the acceleration produced in Earth is negligible small, due to large mas of the Earth. So we can say the earth does not move toward the falling object.
Q.13: Why a wire fence is designed in the helmet of batsman?
Ans: When a helmet breaks, it's absorbing that's called "impulse" - a secondary effect of an initial force. Impulse, which gives objects momentum, is what transmits kinetic energy through a system. It takes into account not just force, but also how long that force was applied.
A wire fence is designed in the helmet of batsman aims to reduce the risk of serious jaw and teeth injuries by reducing the impact of a force or collision to the face.
Q.14: How does it (helmet) prevent from injuries?
Ans: When a bike helmet breaks, it's absorbing that's called "impulse" - a secondary effect of an initial force. Impulse, which gives objects momentum, is what transmits kinetic energy through a system. It takes into account not just force, but also how long that force was applied. A helmet aims to reduce the risk of serious head and brain injuries by reducing the impact of a force or collision on the head. A helmet works in three ways: It reduces the deceleration of the skull, and hence the brain movement, by managing the impact.
Q.15: Riding a bicycle needs continuous paddling.
Ans: Riding a bicycle needs continuous pedaling because When the rider stops pedaling the bicycle, the force of friction between the tyres of the bicycle and the road acting in the direction opposite to the direction of motion of the bicycle, opposes the motion of the bicycle and this force is now unbalanced, thus slowing down the bicycle.
Q.16: You always feel a pullback whenever you pull on your school bag or some heavier object.
Ans: By putting a heavyweight on our shoulders in the wrong way, the weight's force can pull us backwards. So people who carry heavy backpacks sometimes lean forward.
Q.17: Why do we use ball bearings in vehicles and other things?
Ans: In the case of rolling friction the contact area between two surfaces is lesser than the contact area in the case of sliding bodies. Therefore ball bearings are used in vehicles that reduce the contact area as compared to the contact area of axle and bush.
Similarly a pedestal fan with a ball bearing saves a lot of electricity therefore the customers always select a fan with a ball bearing rather than one with a bush and axle.
UNIT 4: TURNING EFFECT OF FORCES
Q.18: Why a body in unstable equilibrium does not return back to it original position when given a small tilt?
Ans: The center of gravity of the body is at its highest position in a state of unstable equilibrium. As the body topples over about its base (tip), its center of gravity moves towards its lower position and does not return back to its previous or original position.
Q.19: Why racing cars are made heavy at bottom?
Ans: The sports cars are made heavy at bottom which increases the base area of the car and lowers the center of mass and hence increases the stability.
Q.20: Why the base area of Bunsen burner is made large?
Ans: The base area of Bunsen burner is made large because having a large base ensures that the vertical line through the center of gravity of the object will lie within the base of the object when it is tilted. While having a heavy base ensures that the center of gravity is low. therefore the Bunsen burner will be very stable.
This is also reduce the chances of the burner accidentally tipping over, knocking over a lit Bunsen burner could have very bad result.
Q.22: Why does a man carry a long beam, while walking on tight rope?
Ans: A man walking on tight rope carries a long beam which helps him to maintain balance by increasing their torque or moment of inertia and lowering his center of mass or the center of gravity. This help in maintaining stability and resist to rotating and falling while walking over the narrow rope.
UNIT 5: FORCES AND MATTER
23. Why an acrobat does not hurt when he lied down on the bed of nails?
Ans: There is no miracle in this trick. We know that pressure is defined as force per unit area. If we step up on a nail, the entire body weight exerts more pressure because the area of nail tip is very small. In case of bed nails, the pressure exerted by weight of body is distributed on the hundreds or thousands of nails lying close to each other. Thus, net pressure on a nail is very small. Hence, an acrobat does not hurt when he lied down on the bed of nails.
24. Explain why foot ball shoes have spikes or studs?
Ans: The pressure under the studs on the soles of football shoes is high enough to sink into the ground, which gives extra grip. Therefore, studs prevent a player from slipping on the grass and help to run faster and change direction quickly without slipping.
25. Why do ice skates have blades?
Ans: Ice skates have blades in the part that is in contact with ice. Therefore the skater's weight is concentrated on a small area. The effect of this high pressure melts ice just below the blades. This gives the thin film of water, which provide lubrication for the skate to skim over the ice. As the skate moves on, the water re-freezes. On very cold days, the pressure may not be enough to melt the ice, and skating is impossible.
26. Why do elephants have broad soles?
Ans: An elephant has broad soles to reduce the pressure exerted on the ground. They have broad feet in proportion to their size, to distribute the weight better.
27. Why does the school bag have broad shoulder straps/pads?
Ans: Wide shoulder pads of school bag reduce pressure on the student's shoulder. These broad shoulder straps are more helpful to distribute the weight of the bag across all over the shoulders. It avoids the weight of concentrating on a particular area.
Use the idea of pressure to explain the following:
-
Q.28: Sharks and crocodiles have sharp teeth.
Ans: Sharks and crocodiles have sharp teeth because they have evolved successfully as carnivorous creatures. Most carnivores have long, sharp teeth adapted to ripping, tearing or cutting flesh. Sharp teeth are required to effectively grab and tear away chunks of tissue by applying high pressure. - Q.29: Camels have wide, flatted feet.
Ans: Camels have to walk on sand, and to walk fast, their feet should not sink in the sand. The feet area is broad to exert less pressure which makes the feet sink less in the sand. - Q.30: If you walk on wooden floor wearing shoes with very narrow heels, you will damage the floor.
Ans: If we walk on wooden floor wearing shoes with very narrow heels, we will damage the floor because of the smaller surface area of a heel there is a greater force per square inch that is produced against the floor.
Q.31: Dam holds water at high altitude. The walls of the dam are made wider at the base. Explain why?
Ans: The walls of dam is made much thicker at the bottom than it is at the top because pressure exerted by a liquid increases with Depth. Thus as depth increases more and more pressure is exerted by water on the walls of dam. A dam needs the thicker wall to withstand this large pressure, therefore, the wall of the dam is made wider and thickness increasing towards the base.
In other words,
A dam has broader walls at the bottom than at the top to withstand the great pressure of water which increases with an increase in depth.
Q.32: Why does pressure increases as you dig deeper; Explain in detail.
Ans: Pressure Increases As We Dig Deeper:
Pressure is force per unit area and pressure and depth have a directly proportional relationship.
In this case, the force is primarily the weight of the overlying rock. So, in very simple terms, the deeper we go the more rock must be supported so the more force is required and the pressure goes up. It is the same thing that happens in the ocean and the atmosphere. The deeper we go in the ocean the higher the pressure. And in the atmosphere the density of air becomes heavier near the surface of the earth (due to gravity). Thus, the atmospheric pressure is high at lower altitudes, the density being higher.
UNIT 6: GRAVITATION
Ans: An object's weight is dependent on its mass and the strong gravitational pull of the planet on which it is standing on. In other words, Every object in the universe with mass attracts every other object with mass. Mass of an object only depends on the constituent matter of an object and is independent of other factors. The mass of an object will always be a non-zero value.
While the acceleration due to gravity of planet (or any other object’s) is caused due to the gravitational pull of that planet and depends on its size, mass, and density. It has different values at different places.
Therefore, The weight of the same object is different on different planets because weight depends on the gravitational force of the planet and gravitational force on every planet is different so the weight also differs from planet to planet. the higher the gravity the higher our weight.
Q.34: If you go on a diet and lose weight, will you also lose mass? Explain.
Ans: Let us imagine a surface that just barely surrounds our body as if we shrink-wrapped a body in plastic, by the law of conservation of mass the only way our body can lose any amount of mass is for that amount of mass to pass out through the surface. So we just have to consider what bodily functions cause that to happen:
- Exhaling
- Sweating
- Excretion (in the non-technical sense of, roughly, things we do in the bathroom)
- Eating and drinking: solids and liquids through the esophagus and gastrointestinal tract.
- Inhaling gas through the trachea and lungs.
Q.35: Why the two satellites of different masses have same speed in the same orbit?
Ans: We know that the velocity that a satellite must possess when orbiting around the Earth in an orbit of radius (r = R + h) is:
This shows that the speed of the satellite is independent of its mass. Hence every satellite whether it is very massive (large) or very light (small) has the same speed in the orbit. Hence, the two satellites of different masses have the same speed in the same orbit.
Q.36: Why we do not feel the gravitational force of attraction from the objects around us?
Ans: We do not feel the gravitational force of attraction between objects around us due to the very small value of `G'. But it exists everywhere in the universe. Gravitational force is a weak force unless large masses are involved. The masses of humans are quite small and thus the magnitude of gravitational force is also very small and negligible as compared to that shown by the Earth. Thus, gravitational force exists between two people sitting close by but it is negligible and cannot be felt.
Q.37: Why weight of an object does not remain same every where on Earth?
Ans: The weight of a body is the gravitational force on it.
Mathematically, W = mg.
Thus, weight is dependent on gravitational acceleration, g or gravity. Hence, the weight of a body will change from one place to another place because the value of g is different in different places. GraVity is often assumed to be the same everywhere on Earth, but it varies because the planet is not perfectly spherical or uniformly dense. Earth's gravity is weaker at the equator due to centrifugal forces produced by the planet's rotation. It's also weaker at higher altitudes, further from the planet's centre. Therefore, the weight of an object does not remain the same everywhere on the Earth.Q.38: Why the unit of weight is Newton? Explain.
Ans: The weight of an object is the force of gravity on the object and may be defined as the mass times the acceleration of gravity, i.e. w = mg. Since the weight is a force, its SI unit is the newton.
Q.39: Your weight decreases as you go up at high altitudes, without dieting. Explain.
Ans: A we know that weight is equal to mass times gravitational acceleration. If we move up to higher altitude the distance between us and the earth increases. Since the gravitational force is inversely proportional to distance, thus the gravitational force exerted on our body decreases as we go up at high altitudes, without dieting and so our weight also decreases.
Q.40: If you step on a scale and it gives reading 55 kg, is that a measure of your weight. If not then which physical quantity it shows?
Ans: The terms "balance" and "scale" are often used interchangeably, and most of us would have a bit of trouble nailing down the characteristics of each. There are technical and practical differences between the two, including exactly the quantity is being measured and the types of applications are used for. Although the terms "balance" and "scale" are used interchangeably, technically they measure different things.
Balances Measure Mass: Balances are instruments that measure mass (basically the amount of matter in something). A true balance measures mass directly by comparing the unknown mass to a known mass, a process that is not affected by changes in gravity. A balance of this sort will give the same reading irrespective of location because gravity will act on both sides of the balance equally.
Scales Measure Weight: Scales measure weight, which is the force acting on a mass that is equal to the object's mass times its acceleration due to gravity. A scale can't measure mass directly, because the weighing mechanism and the weight of any given object are dependent on local gravity. On the Earth, gravitational acceleration can vary by as much as 0.5%, changing with distance from the Earth's core, as well as the latitudinal way. From a practical viewpoint, once a scale has been calibrated at its location, gravity is assumed or ignored. Therefore, weights are reported in mass units like kilograms, even though weight is a measurement of force using the newton. This also allows for the use of the terms "weight" to refer to both weight and mass, and "weigh" can be the process of determining either.
UNIT 7: PROPERTIES OF MATTER
Ans: The measurement of volume of a given liquid remains same, because, the forces of attraction between particles are strong and the particles are free to move about within the liquid. Due to these features liquids have fixed volumes, but they take the shape of the container, so it is measured by measuring cylinders of different shapes and sizes.
Q.42: Why Tungsten melts at a much higher temperature than iron?
Ans: Tungsten melts at a much higher temperature than iron because of its heaviness and covalent bond between the atoms. It is well known that elements with a higher atomic mass have higher melting points. For Tungsten there is the added indication that some of its valence electrons (the 5d electrons) are making covalent bonds between neighbouring atoms in the crystal structure. In general, the greater the number of valence electrons, the stronger is the resultant bonding. Tungsten has the maximum number of unpaired electrons and therefore, it is one of the very hard metals and has maximum enthalpies of atomization. So tungsten has a very melting point.
Q.43: Why the kinetic model of matter is called kinetic?
Ans: Any matter that is moving has energy just because it's moving. The energy of moving matter is called kinetic energy. Scientists think that the particles of all matter are in constant motion. In other words, the particles of matter have kinetic energy. The theory that all matter consists of constantly moving particles is called the kinetic theory of matter or Kinetic model of matter.
Q.44 By using kinetic molecular theory explain why we can walk through air, swim through water but can not walk through a solid wall.
Ans: According to kinetic molecular theory, there is not a little space between the particles of solids as compared to liquids and gases. The forces of attraction between these particles are so strong that we cannot pass through solid objects, such as walls.
Q.45: A balloon kept under sunlight shattered, why?
When the balloon is kept in the sun, due to Sun's heat, the kinetic energy of gaseous particles inside the balloons also gets increased and the balloon expands. This will increase the pressure on the walls of the balloon. It continues to expand and comes to a stage when the balloon bursts.
Q.46: Why a hot coffee or tea in a cup became cold as the time passes?
The heat from the tea is transferred to the surroundings through a process called convection. The nearby air molecules will collide with the tea in the cup and take away its heat energy and transfer it through the surrounding air. This is the reason hot tea becomes cold after some time.
Q.47: Clothes dry up quickly under sunlight?
Warm water evaporates much faster than cool water. So, the heat from the sun dries the clothes quickly.
Q.48: Honey is thicker than water, why?
In water, only water molecules are there. So, the attraction between the molecules (inter-molecular force) is not much high. Honey contains many types of molecules. Therefore they have more inter-molecular forces between the molecules, so that the layers of liquid cannot move freely upon the other layers. That results in the resistance to the deformation in the fluid. So, we can say that due to more inter-molecular forces, honey is more thicker than water.
Q.49: Why do water and milk or other liquids boil at different temperatures?
Different liquids have different boiling points depending on the strength of bonding between the particles and the mass of the particles. The heavier the particles in the liquid, and the stronger the bonding, the higher the boiling point will be. This is the reason water and milk or other liquids boil at different temperatures.
Q.50: Why do water and milk take the shapes of the container in which they are poured? OR Why do different substances boil and melt at different temperatures?
water and milk are liquid state of matter. As the particles in a liquid are close together, but they are not bound to fixed positions; they can slide past and around each other. This enables liquids to take the shape of their container and to flow when they are poured.
Q.51: Why liquids and gases take the shapes of their containers while solids have definite shapes?
In liquids, the forces of attraction between particles are strong and these particles are free to move about within the liquid. So, the liquids have fixed volumes, but take the shape of the container. Similarly in gases, the forces of attraction between particles are negligible and these particles are able to move freely in random directions at very high speeds. thus particles occupy any available space.
But in solids, the forces of attraction between particles are very strong. and they are not able to change positions. Their particles vibrate about fixed positions thus are not entirely stationary. That's why solids have fixed shapes and volumes.
Q.52: Explain why:
(i) Solids have the highest densities.
Ans: There are a large number of particles per unit volume. That is why solids have the highest densities.
(ii) Solids have fixed shapes and volume.
Ans: in solids, the forces of attraction between particles are very strong. and they are not able to change positions. Their particles vibrate about fixed positions thus are not entirely stationary. That's why solids have fixed shapes and volumes.
(iii) Liquids have relatively high densities.
Ans: There is slightly less number of particles per unit volume compared to solids. This is why liquids have relatively high densities.
Q.53: Why dose a gas has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume?
Ans: The molecules of a gas keep moving very fast in all directions. They are far from one another. Thus the cohesive forces are insignificant and the gases do not have a fixed shape or a fixed volume. They occupy all the space available to them.
Q.54: Its is easy to compress air as compared to water. Why?
In gases the molecules are far apart from each other. There are a lot of empty spaces between gas molecules. As air is a mixture gases so it can be compressed quite easily . Whereas water, is a liquid and its molecules are closer then air. Liquid are incompressible. That is why it is easy to compressed air as compared to water.
Q.55: Why can gases be compressed easily while solids and liquids?
In gases the molecules are far apart from each other. There are a lot of empty spaces between gas molecules. So it can be compressed quite easily. While solids and liquids,have high force of attraction among molecules so they are closer then gas molecules and incompressible. That is why it is easy to compressed gas as compared to solids and liquids.
Q.56: Why did the smell of perfume quickly spread through the room.
Ans: The smell of perfume quickly spreads through the room as soon we spray it at our body or clothes because the molecules move freely and randomly at high speeds throughout the room.
UNIT 8: ENERGY SOURCES AND TRANSFER OF ENERGY
Ans: In Physics, work is defined as the measure of the displacement of an object or a point. In this case, Urwa made an assignment on her laptop in three hours but she did not cover any distance in the direction of force, she was sitting in one place. Therefore, according to the definition of work in physics, Urwa did not perform any work.