GO TO INDEX
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY
Text Book Exercise
1. Encircle the correct answer:(i) A localized group of organisms that belong to the same species is called a:_______.
(a) Biosphere
(b) Community
(c) Ecosystem
(d) Population
2. Increased quantity and quality of fish production:_______.
(a) Fisheries
(b) Farming
(c) Animal husbandry
(d) Forestry
3. Study of remote past organic life, with the help of fossils:______.
(a) Entomology
(b) Paleontology
(c) Taxonomy
(d) Histology
4. Laws and techniques of physics are applied to explain the living processes of life:________.
(a) Biometry
(b) Biostatistics
(c) Biophysics
(d) Bio-economics
5. Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Six elements such as C, H, O, N, S and P are called basic elements of life.
(b) Foundation of life based on chemicals.
(c) Members of different species form population.
(d) Part of earth where life exists is called biosphere.
6. Science of diagnosis and treatment of diseases:_____.
(a) Agriculture
(b) Medicine
(c) Surgery
(d) Both B and C
7. Similar cells combine together to form:_______.
a) Organs
(b) System
(c) Tissue
(d) Body
8. Scientific name of frog is: _______.
(a) Palaeon
(b) Rana tigrina
(c) Periplaneta
(d) Pheretima
9. Select the correct sequence of biological organization:
(a) Atom → Cell → Tissue → Molecule → Organ
(b) Atom → Tissue → Cell → Molecule → Organ
(c) Atom → Molecule → Cell → Tissue → Organ
(d) Atom → Cell → Molecule →Tissue → Organ
10. Volvox is a polyphyletic genus of:______.
(a) Green algae
(b) Red algae
(c) Brown algae
(d) None of these
2. Fill in the blanks:
(i) Techniques for manipulation of gene to achieve desirable characters are called biotechnology.
(ii) Distribution of different living organisms in different regions of the world biogeography.
(iii) Part of agriculture for the development of new varieties of plant, and their fruit is horticulture.
(iv) Bio elements considered as vital for life are 16 in members.
(v) Members of different species living in specific habitat are called Community.
(vi) The Muslim scientists who identified many diseases like tuberculosis, meningitis and other such inflammations was Bu Ali Sina.
(vii) Part of earth where life exists is called Biosphere.
(viii) Foundation of life based on chemical foundation.
(ix) Fish is one of the best source of protein.
(x) Radio labeling and carbon dating also show some uses of radioactive isotopes in determining the age of fossils.
Q.3: Define the following terms:
- Anatomy
- Histology
- Immunology
- Pharmacology
- Entomology
- Biometry
- Biogeography
- Surgery
- Animal husbandry
- Bioelements
The study of internal parts of body of living organisms by cutting them open.
(ii) Histology (Gr. histos: tissue; logos, discourse):
The study of structure of tissues of plant and animals.
(iii) Immunology:
The branch of Biology that deals with the study of immune system of animals, which defends the body against invading harmful microbes (micro organism) is called immunology.
(iv) Pharmacology (Gr. pharmakon, drug;):
The study about action and effects of drugs.
(v) Entomology:
The branch of zoology deals with the scientific study of insects is called entomology.
(vi) Biomathematics / Biometry:
The branch of mathematics which collects data of living organisms using mathematical techniques and tools is called Biometry or Biomathematics. It plays very important role in research.
(vii) Biogeography:
It deals with the distribution of different living organisms in different geographical regions of the world.
Many living organisms are restricted to particular geographical regions due to environmental conditions.
(viii) Surgery:
The profession of medicine deals with repair, replacement or removal the affected organ is called Surgery.
OR
The branch of medicine that employs operations in the treatment of disease or injury.(ix) Animal husbandry:
This profession is part of agriculture science. It deals with the care and breeding of animals which are beneficial for man.
(x) Bio-elements:
Chemical elements which are found in the molecules and compounds that make up a living organism are called bio-elements. There are more than 100 kinds of elements in nature and among these 16 elements are called as bio-elements, which are vital for life. Only six elements such as C, H, O, N, S and P are called basic elements of life.
OR
Any of the chemical elements which are component of living organism and are required for their survival and growth are called bio-elements. In human body the most common bio elements are oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium and phosphorous.Q.2: Distinguish between the following in tabulated form
(i) Colonial organization and multicellular organization
(ii) Agriculture and horticulture
(iii) Unicellular Organism and Multicellular Organism
Ans: (i) Difference between Colonial organization and multicellular organization
| S.NO. | Colonial organization | Multicellular organization |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Unicellular organisms who lives in colonies are included in Colonial organisms. | Multicellular organism are composed of more than one cell and refer to form tissues and organs in multicellular organism. |
| 2. | If all members of an aggregation can perform all the basic functions of life for themselves, so none of them depends on others to do things they can not, then the aggregation is the colony. | If some members of the aggregation carry out function that others can not, so their respective contributory functions are each necessary to the survival of the whole then it is a multicellular organism. |
| 3. | The cells are not dependent on each other. | The cells are dependent on each other. |
| 4. | A colonial organism is the individual organisms that form a colony, and can survive on their own, if separated. | Cells from a multicellular organism (e.g., liver cells), if separated can not survive on their own. |
| 5. | There is no separation in somatic cells and gametes. All cells can have offspring, which contribute to the formation of daughter-colonies | In multicellular organisms,cells are differentiate as somatic cells which form tissues and organs etc., while gametes contribute to the formation of next generation, |
| 6. | example: Volvox | example: Mustard plant, Frog |
(ii) Difference between Agriculture and horticulture
| S.NO. | Agriculture | Horticulture |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Agriculture is a broad term that cover forestry, agronomy, animal husbandry, aquaculture and horticulture. | Horticulture is a branch or sub-group of agriculture. |
| 2. | Agriculture is conducted on wider area, infield and farms. | Horticulture is conducted on smaller area. |
| 3. | Agriculture includes cultivating crops (plants), animal husbandry (raising animals for food and other human necessities) and fungi. | Horticulture is mainly crop (plant) cultivation. It focuses on cultivation, marketing, improving and technology of plants for food and human necessities. |
| 4. | Agriculture uses more chemicals | Horticulture uses lesser chemicals |
| 5. | Agriculture has an adverse effect on biological diversity | Horticulture has lesser impact on biological diversity |
| 6. | Agriculture dates its origin to much older times i.e., immediately after old stone-age. | Horticulture is a division of agriculture finding its origin much later. |
| 7. | It is expensive. | It is less expensive. |
| 8. | It has large output. | It has less output. |
| 9. | Sometimes called "farming". | Sometimes called "gardening". |
(iii) Difference between unicellular Organisms and multicellular Organisms
| S.NO. | Unicellular Organisms | Multicellular organization |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Unicellular organisms are composed of a single cell. | Multicellular organisms are composed of more than one cell. |
| 2. | Simple body organization. | Complex body organization. |
| 3. | A single cell carries out all necessary life processes. | Multiple cells perform different functions. |
| 4. | The total cell body is exposed to the environment. | Only the outer cells are exposed to the environment. |
| 5. | Division of labour is at the organelle level. | Division of labour is at cellular, tissue, organs and organ system level. |
| 6. | Includes both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. | Includes only eukaryotes. |
| 7. | A lifespan of a unicellular organism is usually short. | A lifespan of a unicellular organism is usually short. |
| 8. | Injury to the cell leads to the death of the organism. | Injury to a cell does not cause the death of the multicellular organism. |
| 9. | Asexual reproduction is predominant, however, sexual reproduction is also seen (conjugation). | Reproduction happens sexually as well as asexually. |
| 10. | Cell differentiation is absent. | Cell differentiation is present. |
| 11. | They can be autotrophs or heterotrophs. | They include both autotrophs and heterotrophs. |
| 12. | They are microscopic in nature. | Most organisms can be seen with naked eyes. |
| 13. | Bacteria, Amoeba, Paramecium, and yeast are examples of unicellular organisms | Humans, animals, plants, birds and insects, are examples of multicellular organisms |
Q.3: Write short answers of following questions.
(i) Why subject biology is named as multidimensional subject?
Ans: Biology is named as multidimensional subject because it links with other sciences. For example, the movement of animals follows the laws of motion in physics. Biology is considered as interdisciplinary science, which is related with other sciences.
(ii) How farming profession helps mankind?
Ans: In this profession, the development and maintenance of different kinds of farms takes place.
Farming profession helps mankind as:
- In cattle farms, new technologies are used for the production of animals as source of meat and milk, leather, wool, etc.
- In poultry farm, chicken and eggs are produced.
- Other farms are fish farm and fruit farms etc.
OR
Farming is the science of developing and maintaining farm. With the advancement of farming techniques, man improves the quality and yield of the existing varieties and produces certain new varieties of crops. This helps to overcome the problems of food shortage, incidence of famine declines and economic conditions of mankind are improving.OR
When farmers prioritize biodiversity on their land, it benefits the earth. Having more biodiversity results in healthier soil, less erosion, better water conservation, and healthier pollinators. This is all good news for the environment as a whole, making agriculture an important part of the cycle of life.(iii) Why species is called as smallest taxonomic level?
Ans: Species is called as smallest taxonomic level because it is the smallest and basic unit of classification. Taxonomic studies consider a group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities as a species. Thus all the individual members belonging to particular species show all similar characters and can breed among themselves to produce a similar type of organism.
(iv) How population is different from community?
Ans:Difference between population and community
| S.NO. | Population | Community |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | All the members of a same species, living in specific habitat are called Population. | The members of different species living in specific habitat are called as Community. |
| 2. | A Population is group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time and sharing a common gene pool. | The term Community refers to the populations of animals and plants that live within a specific region under similar environmental conditions. |
| 3. | A group of parrots living on tree, is called parrot population. | A group of different kind of birds, living on tree, is called as bird community. |
(v) How new varieties of plant are produced?
Ans: Horticulture is a part of agriculture, in which work is carried out for the development of new varieties of plants and their products. In other words, the new plant varieties are produced by selection and hybridization.
Selection is a non-random process which leads to individuals of different genotypes being represented unequally in their progeny in later generations of a population of self-propagation units. Selection can be natural or artificial.
Hybridization is the crossing of two varieties, species or genera having desired genes by bringing together the useful characters of these into one progeny.
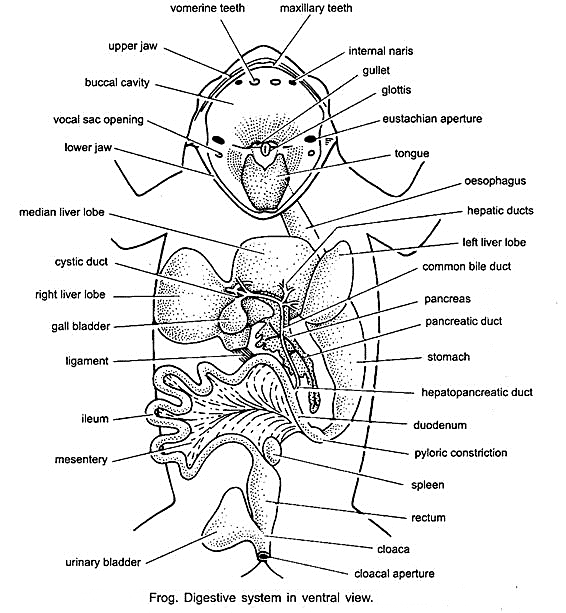
(vi) Draw a labeled diagram of frog’s digestive system.
Digestive System Of Frog
OR
6. Write detailed answers of the following questions.
(i) Describe the role of Muslim scientists in the field of biology.
Ans: Contribution of Muslim Scientists:
The Muslim scientists have played great role in the development of biological science. They began experiments and observations from the first Century of Hijra. Following are some details about the important Muslim scientists, who made significant contribution towards the development of biology.
1. Jabir Bin Hayan:
- Period: He was born 722 and died in 817 A.D.
- Birth Place: He was born in Iran
- Contribution: He worked in the field of chemistry.
- Famous Books: He also wrote a number of books on plants and animals. Like:
(i) “Al-Nabatiat” on plants.
(ii) “Al Haywan” on animals.
2. Abdul Malik Asmai:
- Period: He was born 741 and died in 828 A.D.
- Contribution: He was great zoologist.
- Famous Books: He wrote many books on animals. Like:
(i) “Al Kheil” on horse.
(ii)“Al-Ibil” on camels.
(iii)“Al-Shat” on sheep.
(iv) “Al-Wahoosh” on wild animals and
(v)“Khalqul Insan” on the different parts of human body and their functions.
3. Bu Ali Sina :
- Period: He was born 980 and died in 1037 A.D.
- Founder of Medicine: He was greatest of all the Muslim scientists and considered as the founder of medicine. He is called as Avicenna in the west.
- Contribution: He identified many diseases like tuberculosis, meningitis and other such inflammations.
He also worked in the field of mathematics, astronomy, physics, paleontology and music. - Famous Books: He wrote books like:
(i) “Al-Qanoon” and
(ii) “Fil Tib Al-Shafa”.
(ii) Describe the relationships of biology to other sciences.
Ans: Relationship Of Biology To Other Sciences:
Biology is a multidimensional subject and linked with other sciences. For example, the movement of animals follows the laws of motion in physics. Biology is considered as interdisciplinary science, which is related with other sciences. Some of these are mentioned below:
Biophysics:
It is a branch of physics, in which laws and techniques of physics are applied to explain the processes of life.
Example:
- The radio-physics branch where radioactive isotopes are used to trace the translocation of different materials within the organisms.
- Radio-labeling and carbon-dating also show some uses of radioactive isotopes in determining the age of fossils.
- Uses of sound waves as ultrasound and laser technology show relation of physics with biology.
- Biomathematics / Biometry:
The branch of mathematics which collects data of living organisms using mathematical techniques and tools is called Biometry or Biomathematics.
Example: It plays very important role in research. - Biochemistry:
It is branch of biology which deals with the study of molecules which form living organisms or cell and requires authentic knowledge about biology and chemistry to explain the synthesis of biomolecules and function of different molecules in the body of an organism.
Example: The study of basic metabolism of photosynthesis and respiration involves the knowledge of chemistry. - Biogeography:
It deals with the distribution of different living organisms in different geographical regions of the world.
Example: Many living organisms are restricted to particular geographical regions due to environmental conditions. - Bio-economics:
This deals with the economically important organisms involved in production.
Example: meat production, etc. are calculated for cost value and profit value.
(iii) Describe the level of organization.
Ans: Level Of Organization
The levels of organization in living world are based on chemical foundation. All the living organisms are made up of cells and the protoplasm of cell is the physical as well as chemical basis of life. These levels are as follows:
1. Atomic level of organization:
- All the matter is made up of elements, which is composed of atom (a: not, tom: cut).
- Each atom is made up of sub-atomic particles, such as electrons, protons and neutrons.
- In nature, there are more than 100 kinds of elements and among these 16 elements are called as bio-elements, which are vital for life.
- Only six elements such as C, H, O, N, S and P are called basic elements of life.
2. Molecular level of organization:
- Molecules are formed by the binding of atoms.
- These organic molecules of cells are called as bio-molecules.
- These are constructed in great variety and complexity.
- They are classified as micro-molecules and macro molecules.
- Glucose, amino acid and fatty acids are micro-molecules.
- Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids are macro-molecules.
- The units of micro-molecules combine together to form macro-molecules.
3. Cellular level of organization:
- The bio-molecules when work together in the form of suspension, It is called Protoplasm.
- Protoplasm is the combination of organic and specific inorganic substances.
- When protoplasm work in the form of a unit, this is called Cell.
- Cell is the basic unit of living organisms.
- When similar type of cells organize together in a group, called tissues.
- The different types of tissues arranged in a particular manner to work together are called Organs.
- Organs of different types work in a co-ordinated manner to perform a function are called Organ-system.
- When different organ-system function in co-ordination in as a unit, they form a body or Multicellular Organism.
4. Taxonomic level:
- Taxonomic level is another level of organization which is related with living organisms.
- The Species is the smallest unit of taxonomic level of organization, which includes morphologically similar living organisms which inter-breed and produce fertile offspring.
5. Population level:
- All the members of a species, living in specific habitat are called Population.
- For example, A group of parrots living on tree, is called parrot population.
6. Community level:
- The members of different species living in specific habitat are called as Community.
- For example, A group of different kind of birds, living on tree, is called as bird community.
7. Ecological system:
- Communities always depend upon their non-living environment in a reciprocal interaction for their survival.
- For example, oxygen for respiration is obtained from environment and in turn given out CO2 .
- This interaction of living organisms with each other and with non-living of the environment is called Ecosystem or Ecological system.
8. Biosphere level:
- The part of earth where life exists is called biosphere.
- It consists of different kinds of Eco-systems.
Graphical Representation Of Level Of Organisations: