GO TO INDEX
Chapter No.4. Data Communication And Computer Network
Text Book Exercise And Activity
Text Book Exercise
B. Respond the following:
1. List the properties of a good communication system. Explain any one.?Ans: Properties of a Good Communication System:
The effectiveness of a data communications system depends on the fundamental characteristics which include:
- Delivery
- Accuracy and
- Timeliness
| S.No. | Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Delivery | Making sure that the data is delivered is the first fundamental characteristic of any communication network. The system must be able to deliver data in correct order to the correct destination. |
| 2. | Accuracy | The system must deliver the data accurately. Data that has been altered during transmission and left uncorrected is not useful. |
| 3. | Timeliness | The data must be delivered in a timely manner. Late delivered data is useless. |
2. Explain different components of a communication system using single example?
Ans: COMPONENTS OF A COMMUNICATION SYSTEM:
A Communication system has following five components:
(i) Message:
It is the information or data to be communicated.
Example: Common forms of information include text, numbers, pictures, audio and video.
(ii) Sender:
It is the device that generates and sends a message.
Example: It can be a computer, telephone handset, etc.
(iii) Receiver:
Any particular digital electronic device which has capability to receive data in form of message. The location of receiving computer is generally different from the sending computer.
Example: Like sender, it can also be a computer, telephone handset, etc.
(iv) Medium:
It is the channel or path through which the message is carried from sender to the receiver.
Example: Some examples include twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, radio waves, etc.
(v) Protocol:
Protocols are the rules and procedures on which computers exchange data on network.
Sender and receiver follow same protocols to communicate with each other.
In other words, a protocol is an agreement between two parties or venders, using communication devices.
Example: FTP, TCP/IP, HTTP etc.
EXAMPLE OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEM:
When a person talk with another person directly, then the speaker is the sender who conveying the message as information in the form of sound waves through a communication channel, the intervening air and listener are the receiver.
If the distance between the speaker and the listener is large sound waves cannot reach from the speaker to the listener directly and communication is not possible. To make communication possible, different communication channel or method is used like microphone and speakers via telephone or internet services etc.
3. Write the function of following network devices.
Amplifiers, Routers, Switch, Hub
Ans: AMPLIFIERS:
Amplifiers are used to overcome attenuation and make signal stronger again. It is measured in decibels.
ROUTERS:
- A Router is a device that connects two or more networks.
- Routers are a combination of hardware and software.
- The main function of a router is to determine the optimal data path and transfer the information through that path, also known as network traffic controller.
SWITCH:
- A switch or network switch is a networking device that connects computers and other devices like printers, scanners and cameras on a network.
- Data cables from all computers and other devices of network are plugged into the switch to enable communication between them.
HUB:
- In a star topology, all the computers are connected to a central device called hub or switch.
- To communicate with any computer, the sender must send information to the hub. Then the hub transmits that information to the destination.
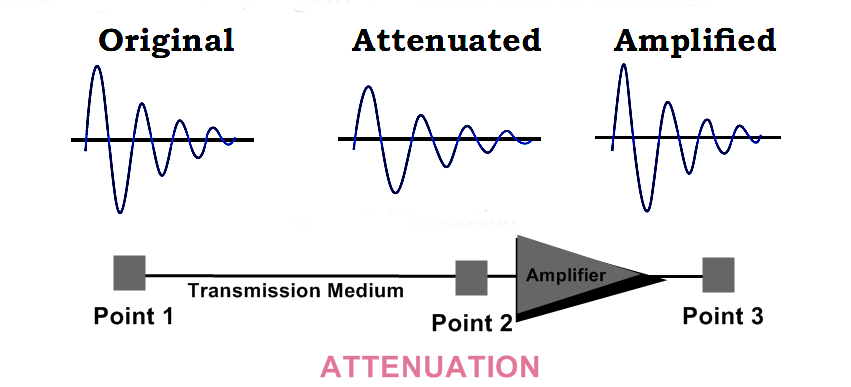
Q.No.4: List the causes of signal impairments. Explain any one.
Ans: TRANSMISSION IMPAIRMENTS OR FLAWS AND FAULTS IN TRANSMISSION SIGNALS:
Sometimes, signals traveling through transmission media lose their quality. This means that received signal is not same as the signal that was sent. This phenomenon is called transmission impairments. Transmission impairments are those defects that occur when data is transmitted.
CAUSES OF SIGNAL IMPAIRMENTS OR TYPES OF FLAWS AND FAULTS IN TRANSMISSION SIGNALS:
There are three causes of impairment i.e.:
- Attenuation
- Distortion and
- Noise
(i) Attenuation:
Attenuation means loss of energy. A signal loses its energy due to the resistance of medium while it is transmitted. Its strength decreases with increase in distance. Amplifiers are used to overcome attenuation and make signal stronger again. It is measured in decibels.
(ii) Distortion:
Distortion means change in the shape of the signal. A composite signal has several frequencies. When it travels through a medium different component of signal may reach at different time at destination because each component has different speed in that medium. This is called distortion. They have different phases at sender and receiver ends.
(iii) Noise:
Unwanted signal that mixes up with the original signal during the transmission of data is called noise. It can be induced noise, crosstalk noise, thermal noise and impulse noise which may damage the signal.
(Note: Explain any one cause as mention in question)
5. What is the difference between radio wave and microwave?
Ans: Difference Between Radio Wave And Microwave:
| S.NO. | Basis | Radio Wave | Micro wave |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Direction | These are omni directional in nature. | These are unidirectional in nature. |
| 2. | Penetration | At low frequency, they can penetrate through solid objects and walls but at high frequency they bounce off the obstacle. | At low frequency, they can penetrate through solid objects and walls but at high they cannot penetrate. |
| 3. | Frequency range | 3 KHz to 1 GHz | 1 GHz to 300 GHz |
| 4. | Security | These offer poor security. | These offer medium security. |
| 5. | Attenuation | High | Variable |
| 6. | Government License | Some frequencies in the radio waves require government license to use these. | Some frequencies in the microwaves require government license to use these. |
| 7. | Usage cost | Setup and usage cost is moderate. | Setup and usage cost is high. |
| 8. | Communication | These are used in long distance communication. | These are used in long distance communication. |
6. Why OSI model is broken up in layers?
Ans: The OSI model is conceptual. It is broken up into layers so a person can visualize network communication from the application to the medium. It works going up the stack at the destination as well. Rather than just "all the magic happens", it is broken down so we can visualize the steps a computer takes when it encapsulates data.
Breaking things down into layers also allows for better troubleshooting. If there is no data being received on our NIC, then we can assume it is a layer 1 or 2 problem.
If we are getting routing errors, then we most likely have a layer 3 problem. It allows an administrator to better pinpoint an issue.
7. Explain the purpose of Standard Organization.
Ans: PURPOSE OF STANDARD ORGANIZATIONS:
- Standard Organization develops, coordinates, revises, amends and reissues technical standards.
- These standards are intended to address the requirements of a group of concerned devices.
- There are several organizations working on standardization of computing equipment to enable the interoperability among different devices manufactured by different companies in different regions.
- Example: ISO, IEEE, IETF, ITU and ANSI are the examples of standard organizations.
8. List one merit and one demerit of each topology.
Ans: (i) BUS TOPOLOGY:
Advantage Or Merit of Bus Topology:
- Simplicity
- Cable required is least compared to other network topology.
- Used in small networks.
- It is cost effective i.e. low cost.
- It is easy to understand.
- Easy expansion of the network i.e. easy to expand joining two cables together.
Disadvantage Or Demerit of Bus Topology:
- A breakdown in the bus cable brings the entire network down.
- If network traffic is heavy or nodes are more the performance of the network decreases.
- Cable has a limited length.
- It is slower than the ring topology.
(ii) RING TOPOLOGY:
Advantage Or Merit of Ring Topology:
- Transmitting network is not affected by high traffic or by adding more nodes, as only the nodes having tokens can transmit data.
- Cheap to install and expand.
Disadvantage Or Demerit of Ring Topology:
- The failure of a link or a computer can make the entire network nonfunctional.
- Troubleshooting is difficult in ring topology.
- Adding or deleting the computers disturbs the network activity.
(iii) STAR TOPOLOGY:
Advantage Or Merit of Star Topology:
- The advantages of star topology are easy to set up and easy expansion of the network.
- Another feature of Star Topology is that if one link to the hub breaks, only the station using that link is affected not the whole network.
- Fast performance with few nodes and low network traffic.
- Hub can be upgraded easily.
- Easy to troubleshoot.
Disadvantages Or Demerits of Star Topology:
- Cost of installation is high.
- Expensive to use.
- If the hub fails then the whole network is stopped because all the nodes depend on the hub.
- Performance is based on the hub that is it depends on its capacity.
9. Give one example of LAN, WAN and MAN.
Ans: Example Of Local Area Network (LAN):
- Networking between two computers.
- Networking in the home, school, library, laboratory, college / university campus or office.
- Wi-Fi which is also known as wireless LAN.
Example Of Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
- Cable TV network
- Telephone networks providing high speed DSL lines.
- IEEE 802. 16 or WiMAX, that provides high-speed broadband access with Internet connectivity to customer premises.
Example Of Wide Area Network (WAN):
- Internet is the example of WAN.
10. How can we measure bit rate and baud rate? Give an example of each.
Ans: Both bit rate and baud rate are generally used in data communication.
Bit rate is the transmission of number of bits per unit of time (second). Bit rate can be ranging from bps (bits per second) for smaller values to kbps (kilo bits per second) and mbps (megabits per second).
For Example:
DSL connection may be able to download data at 10 kbps, means 10,000 bits are transferred within one second.
Baud rate is defined as the number of signal units transmitted per unit of time (second).
For Example:
If a signal changes 1200 times in one second, it would be measured at 1200 baud.
Formula:
We can measure bit rate and baud rate by the following formula, which relate both:
Bit rate = baud rate x the number of bits per signal unit
OR
Baud rate = bit rate / the number of bits per signal unit
Example:
-
When Bit rate and Baud rate are Same:
Assume 9600 bits are transferred per second and 1 bit used to represent signal level i.e either logic 0 or logic 1 then bit rate is 9600 because number of bits transferred per second are 9600 and baud rate is 9600 because number of changes happening per seconds are also the same. - When Bit rate and Baud rate are not same:
If 9600 bits are transferred per second and 2 bits used to represent the signal level then bit rate is 9600 because the number of bits transferred per second are 9600 but baud rate is 4800 because two bits representing signal level.
C. Match the columns:
| S.NO. | A | S.NO. | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (i) | Parts of an IPV4 address | (a) | WAN | (i)-(b) |
| (ii) | Physical address | (b) | Network and Host | (ii)-(e) |
| (iii) | Change in shape of signals | (c) | Transport layer | (iii)-(f) |
| (iv) | A networking connecting two continents | (d) | Data link layer | (iv)-(a) |
| (v) | TCP and UDP are used at | (e) | Cannot be changed | (v)-(c) |
| (vi) | In OSI model the layer responsible to decide the format of data | (f) | Distortion | (vi)-(d) |
Activity
More Short Questions Answers
1. List out the names of standards organizations?Ans: ISO, IEEE, IETF, ITU, ANSI are the examples of standard organizations.



No comments:
Post a Comment