GO TO INDEX
CHAPTER 4: SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT
QUESTIONS ANSWERS
By Mrs. Ayesha Arif
Vice Principal
(Jauhar Progressive School)
Q.1: Define irritability and stimulus?Ans: IRRITIABILITY:
The cells of an organism have a living material, protoplasm, which is sensitive, due to its sensitive nature it possess special property called irritability.
STIMULUS (pl. STIMULI):
The change in environment takes place due to some factors. these factors are called stimulus. OR It refers to any factor which causes change either in internal or external environment of the organism.
In other words, A stimulus is a change in the environment that can be detected by a sense organ and bring about a response.
Q.2: Define movement. Describe types of movement on the basis of stimuli and responses?
Ans: MOVEMENT:
Definitions:
(i) "Living organisms show responses towards stimuli are called Movement."
(ii) "Any action taken by living organs to reduce its irritability produce by stimuli are called Movement."
(iii) "Protoplasm of a living cell irritates when there is a change in its environment. Due to this irritability the living organism take some action to reduce its irritation these actions called movement."
TYPES OF MOVEMENT:
All living organism have property of locomotion due to nutrients, shelter and reproduction mainly plants are sessile (do not move from one place to another) while animals are usually motile therefore they respond to stimuli in different ways.
Types Of Movement On The Basis Of Stimuli:
On the basis of stimuli there are two type of movement.
- Autonomic Or Spontaneous Movement:
Movement which occurs due to internal stimuli are called Autonomic or spontaneous movement.
Examples: Cramps due to involuntary release of Ca++ ions. - Paratonic Or Induce Movement:
The movement occurs due to external stimuli are called paratonic or Induce Movement.
Examples Reflex action.
OR
Types of Movement on the basis of responses:
There are three type of movement on the basis of responses.
- Locomotory or Taxis or Tactic Movement:
These are types of movement where organism changes its place either toward or away from stimulus.
Example: Usually found in animals, bacteria and protozoa. - Tropic Movement:
It is a type of growth movement in which organism move towards or away by growing their organs.
Like growth of root towards water and minerals while growth of stem towards light.
Example: Usually this movement is seen in plants, fungi or in bacterial colony etc. - Nastic Movement:
This is the type of movement where change in osmotic water occur due to stimuli.
Example: It is purely found in plants like touch me not (which close leave when touch) etc.
OR
Q.3: Define movement in plants? OR How do plants respond to stimuli?
Ans: Movement in Plant:
All living organism have property of locomotion due to nutrients, shelter and reproduction but plants are sessile (do not move from one place to another) therefore they respond to stimuli in different ways.
Plant responds to stimuli by adjusting the rate of growth and osmotic condition. While respond to these stimuli by changing their position either towards or away from stimuli.
Q.4: Give an example of movement at the cellular level?
Ans: The movement can also occur at cellular level, like cyclosis in cell or the movement of chromosomes towards their respective poles during cell division etc.
Q.5: Differentiate between movement and locomotion? OR Is movement and locomotion are same phenomena?
Ans: Difference Between Movement And Locomotion
| S.NO. | Locomotion | Movement |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Locomotion is a type of movement and define as the movement of an organism from one place to another is known as locomotion. | Movement is generally defined as a state of changing the position from rest to motion or vice-versa |
| 2. | It takes place either towards or away from the stimuli. An organism move to change its place from original position in locomotion. | If an organism show response towards stimuli but does not change its place it may be any type of movement but not locomotion. |
| 3. | It is always voluntary. | It can either be voluntary or involuntary. |
| 4. | Locomotion takes place at the organism level. | A movement takes place at the biological level. |
| 5. | Locomotion doesn’t necessarily require energy. | Movement requires energy. |
Q.6: What is skeleton? Define its main functions?
Ans: SKELETON:
For locomotion animal body want support to change its place in a balanced and well-coordinated manner. For support animal have skeletal system. Skeleton are the frame work which gives shape to any structure.
FUNCTIONS:
The skeleton performs three main functions:
- Provide shape to organs.
- Provide support to organs during movement.
- Provide protection to soft, vital organs.
Q.7: Explain the types of skeleton.
Ans: TYPES OF SKELETONS
There are three main types of skeleton in animals.
- Hydrostatic Skeleton
- Exoskeleton
- Endoskeleton
1. Hydrostatic Skeleton (Hydro = water, static = to stay):
- Skeleton is made up of fluid filled cavity is called hydrostatic skeleton.
- Found in soft bodied animal.
- It is the simplest type of skeleton.
- It helps in extension or withdrawal of body or its organs.
- Example:
* Hydrostatic skeleton is found in annelids and other soft bodies invertebrate.
* In jelly Fish, helps in propulsion by water.
* In earthworm coelomic fluid acts as Hydrostatic skeleton.
2. Exoskeleton (Exo = Outer):
- The skeleton deposit (present) outside the body or organs are called Exoskeleton.
- It provides support and protection.
- It is non living in nature.
- In high animals made up of proteins.
- Example:
* It is found in arthropods ,Mollusca and higher animals.
* The exoskeleton of arthropods is made up of hard, non living substance called chitin.
* In Mollusca made up of calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
3. Endoskeleton (Endo = Inner):
- It is the skeleton present inside the body.
- It provides shape support and protection.
- It is living in nature and made up of cells.
- Two types of endoskeleton i.e. cartilage and bones.
- Cartilages are made up of chondreocyte and bones are made up of osteocytes.
- Example:
It is found in high animals.
Q.8: Differentiate between hydrostatic skeleton, exoskeleton and endo skeleton?
Ans: Difference Between Hydrostatic Skeleton, Exoskeleton And Endoskeleton:
| Hydrostatic Skeleton | Exoskeleton | Endoskeleton |
|---|---|---|
| Hydro means water and static means to stay. So this skeleton is made up of fluid. | Exo means outer. So this skeleton deposit (present) outside the body or organs. | Endo means inner. So this skeleton is developed inside the body. |
| Found in soft bodied animal. | Found in Arthropods, Mollusca and higher animals. | Found in higher animals. |
| Simplest type of skeleton. | It provides support and protection. | Provides shape support and protection. |
| Helps in extension or withdrawal of body or its organs. | Non living in nature. | Living in nature and made up of cells. |
| In jelly Fish, helps in propulsion by water. In earthworm coelomic fluid acts as Hydrostatic skeleton. | In arthropods made up of chitin. In Mollusca made up of CaCO3. In high animals made up of proteins. | Two types of endoskeleton i.e. cartilage made up of chondreocyte and bones are made up of osteocytes. |
OR
Q.9: Define types of skeletal system in human?
Ans: The skeletal system of human is basically made up of two types of skeletons.
- Cartilage
- Bones
Q.10: Differentiate between cartilage and bone?
Ans: Difference Between Cartilage And Bone:
| S.NO. | Cartilage | Bones |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Type of skeleton which is flexible. | Type of skeleton which is harder. |
| 2. | It is made up of cells called chondrocytes embedded in a matrix of protein called collagen. | It is made up of cell called osteocytes embedded in a matrix of protein called collagen. |
| 3. | It is much softer than bones as well as flexible. | It is harder due to the deposition of calcium phosphate, process is called calcification. |
| 4. | Calcification does not takes place. | Calcification takes place. |
| 5. | It covers ends of the bones and joints. | It support the organ consists of an outer shell of compact bone. |
| 6. | No blood vessel penetrate into cartilage. | Blood vessels can penetrate into bone especially in spongy bones. |
Q.11: Prove that skeleton provide support and movement?
Ans: Skeleton Provide Support and Movement:
Person Stand Straight:
Skeleton provides support to the body, especially limbs. i.e: Hind Limbs and pelvic girdle provide support to the human body to be a bipedal animal, with these limbs the complete vertebrae of vertebral column provide support to stand straight.
Cartilage Gives Support And Proper Shape To Organs As:
- Cartilage of external pinna and nose support the organs to make their proper shape.
- Cartilages also support larynx, trachea and bronchi of respiratory system.
- It forms tough pads which acts as shock absorbers found in knee joints and also form intervertebral discs between vertebrae of backbone.
Q.12: Prove that the skeletal system is s dynamic system?
Ans: The skeletal system is a dynamic system . it possesses the following qualities:
- It is made up of living tissues.
- It is capable of quick growth.
- It can adapt to stress and can repair itself after damage (injury).
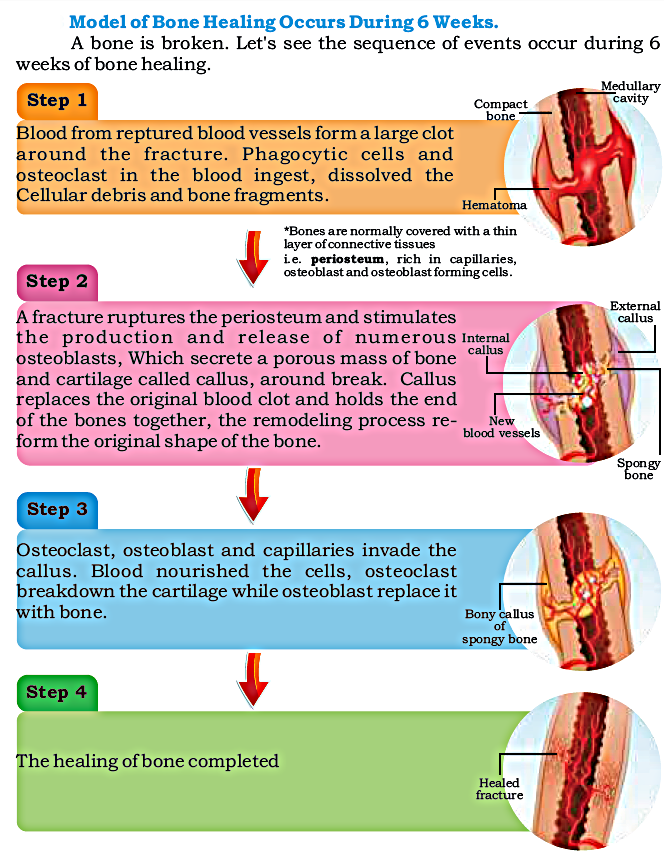
- 5% to 10% of our bones dissolve away annually and are replaced by a new one. This process is called remodelling while in the growing age our bones enlarge with the growth of the body.
Q.13: Define remodeling? Also name the cells associated with bones?
Ans: Remodelling
5% to 10% of our bones dissolve away annually and are replaced by new ones. This process is called remodeling.
The remodeling system allows a skeleton to alter the shape and size of skeleton in response to demands. e.g. the bones carry heavy loads or subjected to extreme stress become thicker to provide more strength and support. Normal stresses are major factors in maintaining bone strength.
Bone remodeling is the result of coordinated activity of osteoclast and osteoblast. This coordination can be seen clearly at the time of repair of broken bone.
Cells Associated With Bones:
There are three types of cells associated with bones i.e.:
- Bones forming cells (osteoblast).
- Mature bone cell (osteocyte).
- Bone dissolving cells (osteoclast).
Q.14: Describe the process of remodelling OR Describe the model of bone healing occurs during 6 weeks?
Ans: Process Of Remodeling: OR
Q.15: Draw a well labelled diagram of human skeleton?
Ans: HUMAN SKELETON:
Q.16: Define skeleton? Describe human skeleton OR Categorize human skeleton as bone skeleton.
Ans: SKELETON:
The tough hard and rigid framework of the body which gives particular shape and support to animal body are called Skeleton.
Human Skeleton:
Human skeleton is the Endoskeleton present inside the human body. In human skeleton 206 bones are present which can be divided (categorized) into two groups.
- The axial skeleton
- The appendicular skeleton
1. Axial Skeleton:
The axial skeleton forms the main axis of the human body.
It includes:
- Bones of head (skull 22 bones).
- Vertebral column (26 vertebrae).
- Rib cage: (Ribs 12 pairs and sternum).
Sternum: It is also known as breast bone. It is only one bone.
The appendicular skeleton system forms the appendages (Limbs) and their attachment to the axial skeleton includes pectoral (shoulder) and pelvis (hip) girdles.
-
Pectoral Girdle:
The girdle present in shoulder region and attach the arm to the trunk are called Pectoral Girdle.
It consist of two bones
1. Scapula: broad part
2. Clavicle: Collar bone which connects scapula with sternum.
Fore Limb
* The Fore Limb consist of:
* Humerus (1)
* Radius (1)
* Ulna (1)
* Carpals (8)
* Meta Carpals (5) and
* Phalanges (14) - Pelvic Girdle:
The girdle present in lower region (hip region) and attached the hind limbs (legs) to the vertebral column are called Pelvic gridle.
Each pelvic girdle consist of three bones called:
1. Illium
2. Ischium and
3. Pubis.
Hind Limbs
The hind limbs consist of:
* Femur (1)
* Tibia (1) + Patella (1)
* Fibula (1)
* Tarsals (7)
* Meta tarsals (5) and
* Phalanges (14)
Q.17(a): Define a joint. How many types of joints are there in human skeleton? OR Write a detailed note on joints.
Ans: JOINTS:
The junction of two bones is called joint. They help in motility of skeleton.
Types of Joint:
Joints are classified on the basis of the amount of movement allowed by them, into two categories.
- Immovable or fixed joints
- Freely or Slightly Movable Joints
i. Immovable Joints
Joints where bones are fixed tightly like puzzle pieces and do not allow to movement are called immoveable joints or fixed joints.
Example
- 8 bones of skull (Skull sutures)
- The articulation between the teeth and the mandible
- The joint found between the first pair of ribs and the sternum.
- 3 bones of pelvic girdle
ii. Moveable Joints
Joints where bones are allowed to move freely or partially are called moveable joints.
Types Of Movable Joints:
There are two types of moveable joints i.e.:
- Freely moveable such as.:
* hinge joint (e.g. elbow, knee, phalanges.
* ball and socket joint (e.g. hip joint, shoulder joint)
* pivot joint (e.g. elbow joint)
* gliding joint, (e.g. vertebrae)
* sliding joint (e.g. wrist joint) - Partially moveable (e.g. sternum and ribs)
Q.17(b): Draw neat and labelled diagram of: Immovable Joint, Hinge joint, Ball & socket joint, Pivot joint, Sliding joint, Gliding joint and partially moveable joint?
Ans: JOINTS
Q.18: Describe the movement and location of hinge joint and ball & socket joint? Also draw neat and well labelled diagram.
Ans: Hinge Joint:
Movement: The joints that allow the movement in one plane only i.e. in two direction, move back and forth like a hinge on a door are called hinge joint.
Location: Joint of fingers (Phalanges), elbow and knee are hinge joints.
Ball and Socket Joint:
Movement: The joints which allow the movement in many planes in all directions (such as forward, backward and sideways) even in a circle are called ball and socket joint.
In this joint ball like head of the long bone of leg and upper are fit into a cup like socket of girdle.
Location: Joint of hips and shoulder are ball & socket joints.
Q.19: Define ligament and tendon and their role in movement?
Ans: Ligament:
Ans: The band of fibrous connective tissues by which bones are joined to one another at joints called ligament.
Role in Movement:
- It works as strong firmly attached ropes.
- It stabilizes the joint or hold the ends of two bones together.
- The strong connective tissue in the ligaments protects these structures and prevents them from bending twisting or tearing.
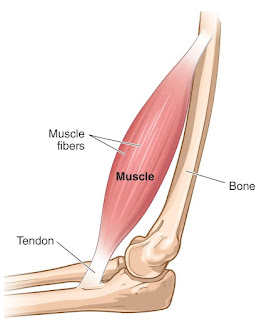
Tendon:
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones on either side of the joint by bands of tough, fibrous connective tissues called tendons.
Role in Movement:
- They are tougher and less elastic than ligaments.
- Tendon transfers the mechanical force of muscle contraction to the bones.
- It is strongly connected to muscles fiber at one end and to components of the bones at its other end. They are very strong, highly tensile.
Q.20: Define Muscles and their kinds?
Ans: Muscular System
Muscles are connective tissues consist of fibrous cells. These tissues have a tendency to contract and relax. Movement of arms and legs are brought about by he contraction of muscles attached to bones.
Kinds (types) of Muscles
The vertebrate possess three kinds of muscles.
- Skeleton Muscles
- Smooth Muscles
- Cardiac Muscles
i. Skeleton Muscles:
The muscles which are attached to the skeleton called skeletal muscles. They are associated with the movement of bones
Characteristics
- These muscles are voluntary in nature .
- They are also called striped or stride muscles because they have alternate thick and thin means dark and light band.
ii. Cardiac Muscles:
These are the muscles which build the walls of heart so they are called Cardiac Muscles.
Characteristics:
- These are also striated muscles but unlike skeletal muscles they are branched in nature and arranging mash work.
- They are involuntary in nature, work under the control of SAN (Sino auricular node).
iii. Smooth Muscles:
Smooth muscles are the earliest form of muscles from evolutionary point of view. They are made up of long and spindle shaped cells, each cell contain single nucleus.
Characteristics:
- They have no striations or stripes.
- They are involuntary in nature.
- These muscles are found in blood vessels, digestive tract and many other internal organs.
Q.21: Prove that support and locomotion is due to skeletal system and skeletal muscle system?
What do you mean by antagonism and antagonistic muscles? Also describe the Flexon and extension in human arm.
Ans: Support and locomotion is mainly due to skeletal system and skeletal muscle system. The contraction and relaxation of the skeletal muscles allows the bones to move. The muscles which are attached with bones are called skeletal muscles.
Antagonism:
The skeletal muscles only exert a pulling force. When skeletal muscles relax, they are stretched by the contraction of another muscles. It shows that muscles are always found in pairs. The one muscle of this pair when contracted other muscle will relaxes .This type of working of two muscles against each other called antagonism.
Antagonistic Muscles
The pair of skeletal muscle which work against each other are called Antagonistic pair. The action of biceps and triceps muscles of arm is a good example of an antagonistic pair.
Biceps: The bicep muscle is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and elbow. It has two heads or origin. The biceps are the flexor muscle
Triceps: The triceps is also a large muscle on the back of arm. It is three headed or origin. The tricep is the extensor muscle.
Movement Of Human Arm:
Flexon: When the biceps muscle contracts it pulls upon the radius bone of lower arm, which bend the arm at elbow, this bending process is called flexon.
Extensions: On the other side when triceps muscle contracts it pull on the ulna which straightens or extends the arm. The straighten process is called extension.
The triceps serve as an antagonist, or opposing, muscle of the biceps. When the biceps contracts the triceps relaxes and vice versa.
Q.22: Describe different disorders of bones OR Skeleton system?
Ans: Effect Of Calcium Deficiency On Bone:
Hypocalcemia:
The bones are hardened due to the deposition of calcium and phosphate. This process is called calcification.
If Ca++ deficiency occurs in body or blood, ultimately it occurs in bones as well . This deficiency of Ca in bone is called hypocalcemia known as calcium deficiency disease. A long term calcium deficiency can lead to dental weakness, osteoporosis, in childhood rickets.
Osteoporosis:
It is a disorder related to the aging process. In this condition the bones become porous or more spongy, thinner and weaker so that they become fragile, in this condition a slight injury break the bone. Osteoporosis is more common in female than male.
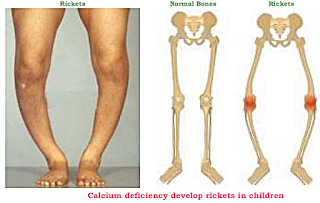
Ricket:
Rickets is a skeletal disorder which is most common in children. It results in bowed legs and deformed pelvis. It includes the softening and weakening of bones.
Causes:
It is caused by deficiency of calcium in diet or an extreme and prolonged vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D plays vital role in the absorption of Ca++, deficiency of vitamin D leads to deficiency of Ca++ in bone.
Q.23: What is arthritis? Describe main causes and the common types of arthritis? Also explain the rate of obesity in arthritis? OR Write a note on disease arthritis?
Ans: Arthritis:
It is the painful condition of joints due to swelling and tenderness of joint.
Symptoms:
The main symptom of arthritis are:
- Joint pain
- Tenderness and stiffness
- Inflammation in and around the joint
- Restricted movement of joint
- Warm red skin over the affected joint
- Trouble dressing, combing, gripping, bending over squatty or climbing stair.
Causes:
The following factors are the causes of arthritis.
- Injury
- Abnormal metabolism
- Infection
- Auto immune system
- Genetic makeup
- Reduction in the normal amount of cartilage or synovial fluid
Common Types:
-
Osteoarthritis:
It is a “wear and tear” type of disease.
Cause: It is caused due to the overuse of joints, age, joint injury and obesity. Joints that bear weight, like knees, hips, feet and spine. - Rheumatoid Arthritis:
It is due to immune system i.e. autoimmune disorder.
Cause: In this disorder immune system attacks on joints. - Psoriatic Arthritis:
In this disorder joints and skin affects.
OR
Role of obesity in Arthritis:
Obesity puts stress on joints, especially on knee, causing pain and develop worse condition in arthritis damage. The rheumatologist states that just 10 pound overweight increases force of 20 to 40 pound on knees at each step during walk.
The excessive fats tissues release high levels of cytokines proteins that can cause inflammation throughout body. The same protein produced by joints during rheumatoid arthritis . It makes existing joint inflammation more worse.
Source: Special Thanks To Sir Syed Arif Ali


















No comments:
Post a Comment