GO TO INDEX
CHAPTER 9: PHARMACOLOGY
Questions And Answers
By Mrs. Ayesha Arif
Vice Principal
(Jauhar Progressive School)
Q.1: What is pharmacology? Pharmacy and pharmacist.Ans: PHARMACOLOGY:
Definition:
"Pharmacology is the branch of biomedical science which is concerned to the uses, effects, and modes of action of drugs. This branch is studied under the discipline of pharmacy."
In other words,
"Pharmacology is the study of drug composition, properties, medical applications and sources of drugs."
PHARMACY:
"Pharmacy is the study of preparation of medicines and drugs."
PHARMACIST:
"One who studies pharmacy responsible for dispensing prescription medications to patients and advising them are called pharmacists."
Q.2: Who is recognized as the founder of modern pharmacology?
Ans: Oswald Schmiedeberg 1838 - 1921) is generally recognised as the founder of modern pharmacology. He studied the pharmacology of chloroform and chloral hydrate.
Q.3: Define Drug. What are its types?
Ans: DRUGS:
"A drug is a chemical substance used to treat, cure, prevent a disease or to promote well-being or artificial pleasure."
OR
"It is defined as any chemical substance used in the diagnosis, cure, treatment or prevention of diseases."OR
"Any substance that is absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal body function is known as a drug."TYPES OF DRUGS:
Drugs can be derived from plants and animals. There are two categories of drugs:
-
Pharmaceutical drug OR Medicinal drug:
are used to treat the diseases and make the patient physically normal. -
Addictive drugs:
which make the person person relaxed by feeling of pleasure, acting on the CNS of the person, finally the person become dependent on it.
Q.4: What are medicinal drugs? Write its sources and also describe main uses of important medicinal drugs?
Ans: MEDICINAL DRUGS:
Medicinal drugs are beneficial for patients as these drugs treat the diseases to prevent them, so many of the diseases can easily be cured.
SOURCES OF MEDICINAL DRUGS:
These beneficial drugs are obtained from various sources. They are as follows:
1. Drugs from Plants:
Many important medicines are obtained from plants . Plants produce special substances in their roots, leaves, flowers or seeds that help to form drugs in laboratory or can be used directly as herbs to treat certain diseases.
Example:
- Cinchona tree contains Quinine in its bark which is used in the prevention and treatment of malaria.
- Opium is used as pain-killer drug extracted from unripe seed pods of the opium poppy.
2. Drugs from microorganisms:
Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi not only produce primary metabolites but are also capable of making secondary metabolites, which constitute half of the pharmaceutical on the market as antibiotics and antifungal drugs.
Example:
- Tetracycline is produced by bacteria.
- Lovastatin are produced by fungi.
3.Drugs obtained from animals:
Certain animal parts and animal products are used as drugs in therapeutics. The major group of animal products used in medicine is hormones, enzymes, animal's extractive, organs and bile acids.
Example:
- Gonadotropin hormone is prepared commercially from either horse serum or from the urine of pregnant woman. They controlled the production of sex hormone in the body.
- Hyaluronidase enzyme is produced by some microorganisms found in the heads of leeches, in snake venom and in mammalian testes.
- Drugs produced by animals are usually their glandular products. Fish liver oil, musk, bees wax, certain hormones and antitoxins are also obtained from animal sources.
- Now a days, scientists are more excited about drugs derived from the sea anemone.
4. Drugs from minerals:
Some of the drugs are synthesized from minerals or can be given with minerals as supplement.
Example:
- Iron is used in treatment of iron deficiency (anemia).
- Zinc is used to make zinc oxide paste which is used in wounds and in eczema.
- Gold salts are used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis etc.
5. Synthetic Drugs:
Synthetic drugs are synthesized in labs by using man-made chemicals rather than natural ingredients. A number of synthetic drugs are available in the market . There are almost 200 identified synthetic drug compounds and more than 90 different synthetic drugs.
Example:
- Synthetic marijuana goes by many names: K2, Spice, fake pot, potpourri, legal weed, and more.
USES OR PRINCIPLE USAGE OF IMPORTANT MEDICINAL DRUGS:
Drugs are classified on the basis of their chemical properties and modes of action. Their uses are as follows:
-
Analgesic (Painkillers):
Reduce pain by acting on CNS.
Example:
Aspirin, Paracetamol and Panadol etc. (A recent study found that aspirin may be most effective when taken at night, rather than in morning.) -
Antibiotics:
Are work against bacterial infections. It either kills or inhibit the bacterial growth.
Example:
Tetracycline, Cephalosporin, Penicillin etc. -
Vaccines:
The vaccine is vital for one's life, vaccines prevent the living body from the microbial diseases by developing in the body.
Example:
Hepatitis vaccine, rabies vaccine, covid-19 vaccine etc. -
Sedatives:
Sedative drugs are helpful for treating anxiety and sleep problem.
Example:
Diazepam (Valium), Alprazolam (Xanax) and Clonazepam( Klonopin).
Q.5: What things must be kept in mind while using medicines? Or What are the side effects or danger zone kept in mind while using medicines?
Ans: While taking medicines we should keep the following things in mind:
- An allergic reaction could happen with any drug. That can range from itching and rash all the way to a life-threatening anaphylactic reaction.
- Overdose of painkillers and sedatives can make a person addictive which on leaving causes severe risk factors.
- One cannot the 'catch' the disease from the vaccines. Some vaccines contain “inactive” virus, and it is impossible to get the disease from them. Other have active but weakened virus designed to prevent the disease.
- The children who are given antibiotics for routine upper respiratory infections are more susceptible to aggressive antibiotic-resistant strains of the bacteria.
- Aggressive antibiotics which are helpful in treating a serious infection, can wipe out many useful gut bacteria.
Q.6: Describe the discovery of antiseptics? OR Who is called as "Father of Antiseptic Surgery" OR Write about the contribution of Joseph Lister in the field of pharmacology.
Ans: Discovery Of Antiseptics OR Contribution of Joseph Lister:
- Joseph Lister is called the “Father of Antiseptic surgery”. Joseph Lister's contribution paved the way to safer medical procedures. His introduction of the antiseptic process dramatically decreased deaths from childbirth and surgery.
- Antiseptics are antimicrobial substances that are applied to living tissues or skin to prevent microbial infections.
- Lister used carbolic acid as disinfectant and used it for washing hands and instruments.
- He also designed spray machine with carbolic acid to kill airborne germs.
Q.7: Who discovered antibiotics and how? OR Write about the contribution of Sir Alexander Fleming in the field of pharmacology.
Ans: Contribution of Alexander Fleming:
- Sir Alexander Fleming, a Scottish researcher, is credited with the discovery of Penicillin in 1928.
- Fleming was experimenting with influenza virus in the Laboratory of the Inoculation Department at St. Mary's Hospital in London.
- After two week vacation when Fleming returned he found a mold had developed on an accidentally contaminated staphylococcus culture plate.
- Upon examination of the mold, he noticed that the culture prevented the growth of staphylococci. This accident led the discovery of antibiotic named as Penicillin.
Ans: Antiseptics are antimicrobial substances that are applied to living tissues or skin to prevent microbial infections.
Q.9: Define addictive drugs and describe their major categories?
Ans: DRUGS ADDICTION:
"One drug often make person dependent on them or addicted. By using such drugs, the person's body become familiar to it and the user cannot function well without it. This is called drug addiction."
Addictive drugs acts on the pleasure center in the brain, causing a shortcut to reward that, when repeated, can change the way person processes information.Drugs' addictive qualities may be enhanced by make a person feel good when using them and they may make user feel bad when they wear off.
TYPES OF ADDICTIVE DRUGS:
The major categories of addictive drugs are as follows:
Sedatives:
Sedative drugs are central nervous system (CNS) depressants. They have following effects:
Effects:
- Slows normal brain function.
- One of the most marked effect of sedatives is their potential for abuse and addiction.
- It can cause drowsiness (dizziness) and sleepiness and are used to reduce anxiety.
- They also reduce heart rate and breathing and can reduce them to the point that death occurs, If there is an overdose.
Narcotics:
Narcotics are also called painkillers. These drugs are often prescribed in conjunction with other less potent pain killers (paracetamol or aspirin). These drugs bind with the pain receptors present in CNS and reduce the pain.
Uses and effects:
- These are used to treat moderate to severe pain that may not respond well to other pain medication such as patients with chronic diseases (cancer).
- These are also used to relieve acute pain after operations.
- The short term effects of opiate use can include feelings of euphoria, pain relief, drowsiness and sedation.
- Narcotics can be dangerous not only because of their potential for abuse and addiction, but also because they can sometimes lead to overdose and death.
The most abused narcotics are the following:
- Heroine:
* Heroine is considered highly addictive.
* Heroine and other opioid drugs interact with dopamine levels in brain, therefore causes burst of pleasure associated with their use.
* Abuse of heroine can lead to drug tolerance, dependence and addiction. - Morphine:
* It is used to relieve moderate to severe pain.
* It remains active in blood stream upto 6 hrs.
* It acts on the CNS and causes relief from pain.
* Overdose can cause many side effects including nausea, vomiting, constipation, lightheadedness, dizziness, drowsiness and sweating.
Hallucinogens:
Hallucinogens are the class of drugs that hallucinations-profound distortion (cause changes) in a person's perception of reality.
Effects:
- Increased breathing rate.
- It affects Sympathetic nervous system.
- It causes dilation of pupils.
- Constriction of some arteries.
- Rise in blood pressure.
- Increased heart rate and irregular heartbeats.
- Palpitations
- Blurred visions.
- Marijuana:
Marijuana (Hashish) is a hallucinogen which is smoked. It is the most commonly used illicit drugs in the world. It is obtained from the flowers, stems and leaves of the marijuana plant (Cannabis indica). People smoke it in hand rolled cigarettes or in pipes.
Effects:- Small doses of marijuana result in a feeling of well-being that lasts two to three hours.
- High doses produce immediate sensations - increased heart rate.
- It weakens the short term memory.
- Reduces coordination and balance.
- Affects brain development.
- Produce a "dreamy" unreal state of mind.
- If teenagers are using marijuana, the drug may impair thinking, memory and learning functions and the affect the brain builds connections between the areas necessary for these functions.
Q.10: What are the symptoms of addiction?
Ans: The following are the signs that can help us identify a addictive person.
- When a person is addicted to a substance, such as a drug, alcohol or nicotine, they are not able to control the use of that substance.
- When body levels of that substance go below a certain level the patient have physical and mood-related symptoms.
- There are cravings for drugs, bouts of moodiness, bad temper, poor focus, a feeling of being depressed and empty, frustration, anger, bitterness and resentment.
- Sometimes the addict may engage in risky activities, such as driving fast.
Q.12: Why addiction is considered as harmful condition? Or What are the problems associated to drug addiction?
Ans: Drug Addiction:
Addiction is considered to be a very harmful condition because addictive drugs act on pleasure center of the brain and therefore affects the way a person processes information.
Drug abusers go through withdrawal of social contact or communication. Many studies by the experts of social sciences prove that there exists a close relationship between drug addiction and crime.
Problems Associated To Drug Addiction:
The problem associated with drug abuse extend beyond immediate personal impact.
- Weakened Immune System & Health Issues:
Due to weakened immune system, addictive people suffer with health issues which increases the risk of illnesses and infection. Such as heart and lung diseases, liver failure, blood vessels infections etc. - Damage Social Life:
Addiction can damage the one's social life. They face social stigma i.e. the society dislikes them because of their unpredictable behaviours. The addictive people are short tempered and mostly their violent acts results in harm to others or society. - Involvement in Crimes:
Addictive people can easily involved in various crimes e.g. Robbery, stealing / snatching, law violator and a criminal. - Brain Damage & Psychic Patients:
Seizures, stroke, mental confusion and brain damage. Problems with memory, attention and decision making, which make daily living more difficult. Drug addicts may become psychic patients also. - Disturbed Family Life:
The family of an addict person is also affected, when the addict does not get its need he become, angry, aggressive, harsh, short temper and does not behave well, ultimately lose relations. - Death Occur:
The most severe effect of drug abuse is death, if overdosed.
Q.13: List some hallucinogens and narcotics obtaining plants found in Pakistan?
Ans: Hallucinogens And Narcotics Obtaining plants found in Pakistan are:
- Salvia divinorum
- Datura
- Opium poppy
- Willow Bark (Salix)
- Cannabis
- Psilocybin mushroom
Q.14: What are antibiotics? How do they work OR Discuss their uses and misuses?
Ans: ANTIBIOTICS:
Antibiotics are chemical substances mostly used to fight infections caused by bacteria. They treat infections by killing or decreasing the growth of bacteria. They are the chemicals can be produced naturally by microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) or can be derived by microorganisms in laboratory or can be synthesized in labs.
Antibiotics are used to treat only bacterial infections. They can treat viral or fungal infections.
TYPES OF ANTIBIOTICS:
There are two types of antibiotics:
-
Bacteriostatic Antibiotics:
which means they inhibit (work by stopping) the bacterial growth. -
Bactericidal Antibiotics:
Some antibiotics are "bactericidal", which means these can kill bacterial cell.
Antibiotics can cause side effects based on they work. Antibiotics are prescribed for a particular infection, but can harm to normal flora which is beneficial to our body. Some of the harmful side effects are as follows:
- Antibiotic resistance
- Diarrhea
- Upset stomach
- Thrush, which is a fungal infection that can affect the mouth or digestive tract.
- Vaginal yeast infection caused by Candidia albican (discharge, burning, pain, itchiness).
- Can cause yellowing of teeth.
Q.15: How bacteria produce antibiotics resistance?
Ans: ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE:
Antibiotics are most important in medicine but overuse of antibiotics can cause antibiotic resistance. Unfortunately bacteria are capable of developing resistance to them. Such bacteria are not affected by commonly used antibiotics; this condition is called antibiotic resistance.
Ways Of Resistance:
Bacteria have number of ways of developing resistance.
- Sometimes bacteria become habitual for that antibiotic or alter strategy to hinder the effect of antibiotic.
- The change either protects the bacterium from the action of the medication or neutralized the medication.
- They can acquire resistance by getting a resistance gene encoded to its chromosomes.
- Another cause of antibiotic resistance is their use in diseases in which they have no effect (e.g. antibiotics are not effective against infections caused by viruses).
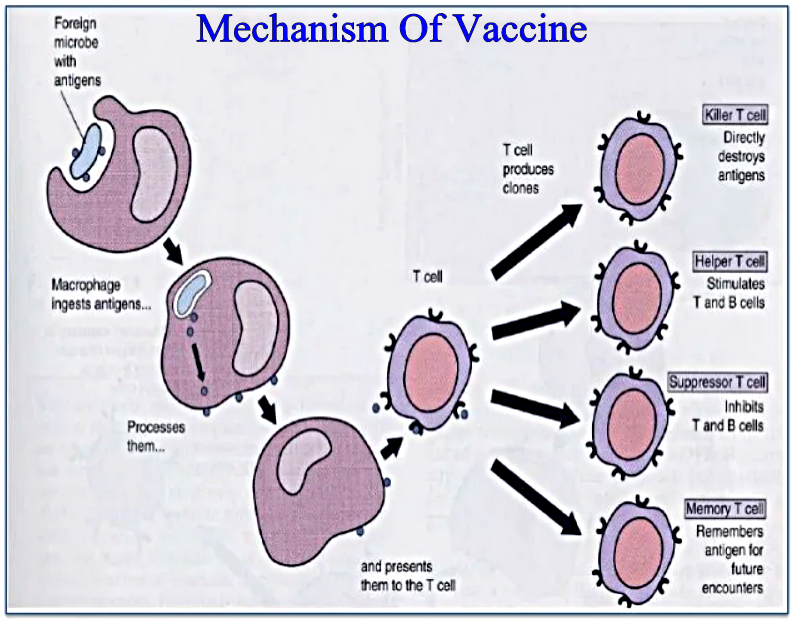
Q.16: What are vaccines? Illustrate mechanism of vaccination?
Ans: VACCINE:
A vaccine is a biological preparation that improve immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins on one of its surface proteins. A vaccine can confer active immunity against a specific harmful agent by stimulating the immune system to attack the agent.
MECHANISM OR WORKING OF VACCINATION:
- Antigens: Pathogens contain special proteins called antigens.
- Antibodies: When pathogens enter the body (blood) of host, these proteins stimulate the immune response in host i.e. synthesis of antibodies. Antibodies bind to pathogens and destroy them.
- Memory cells: These cells are produced which remain in blood and provide protection against future infections with the same pathogen.
Q.17: Who introduced world's first vaccination?
Ans: World's First vaccination.
The first vaccine was introduced by British physician, Edward Jenner, who in 1796 used the cowpox virus (vaccinia), to confer protection against smallpox, a related virus in human. This method was named vaccination and the substance used to vaccinate is called a "vaccine".
Q.18: Define Immunization?
Ans: IMMUNIZATION:
Immunization is the process in which a person is made immune or resistant to an infectious disease by administering a vaccine.
Source: Special Thanks To Sir Syed Arif Ali
thanx
ReplyDeleteJAZAKALLAH
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteI really liked how the article highlighted both the benefits and risks of antibiotics. It made me think about women’s health too—sometimes people wonder, will a yeast infection cause spotting? It’s surprising how interconnected everything is.
ReplyDeleteThank you
Delete