GO TO INDEX
CHAPTER 9: PHARMACOLOGY
Review Textbook Exercise
By Mrs. Ayesha Arif Vice Principal
(Jauhar Progressive School)
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer:1. Who is called father of antiseptic?
a) Alexander fleming
b) Edward Jenner
c) Lister ✓
d) Oswald Schmiedeberg
2. Drugs for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis can be obtained from:
a) Animals
b) Minerals ✓
c) Plants
d) Micro organisms
3. Drugs that slow normal brain functioning are categorized as:
(a) Narcotics
(b) Hallucinogen
(c) Marijuana
(d) Sedatives ✓
4. Vaccination can be administered:
(a) After infection
(b) Before infection
(c) During infection
(d) All are Correct ✓
5. The substance which inhibit the growth of bacteria can be considered as:
(a) Vaccine
(b) Bactericidal
(c) Bacteriostatic
(d) Antibiotics ✓
6. Haris is addicted to a drug , which left the following effect on Haris:
i. Blurred vision
ii. Making unseen faces in imagination
iii. Euphoria
Identify the drug, to which Haris is addicted?
(a) Narcotics
(b) Hallucinogen ✓
(c) Antibiotics
(d) Antiseptic
7. Which one is not the effect of misuse of antibiotics?
(a) Diarrhea
(b) Immunization ✓
(c) Stomach upset
(d) Antibiotic resistance
B. SHORT QUESTION:
Q.1: Why antibiotics are not effective against viral infection?Ans: Antibiotics are useless against viral infections mainly due to the following reasons:
- Antibiotics are used to treat infections caused by bacteria. Antibiotics cannot kill viruses because they are different from bacteria; they have different structure and different way of surviving.
- Viruses don't have cell walls that can be attacked by antibiotics, instead they are surrounded by protective coat.
- Unlike bacteria, viruses are simple that they use their host cells to perform their activities for them.
- Antibiotics work by targeting the growth machinery in bacteria. While virus cannot reproduce on their own, instead they attach themselves to healthy cell and reprogram those cells to make new not virus.
- The antiviral drugs work differently to antibiotics; by interfering with the viral enzymes instead.
Q.2: Why the sedative is used for?
Ans: Sedatives drugs are central nervous system (CNS) depressants, a category of drugs that slow normal brain function. Sedatives are used for the following purposes:
- To reduce heart rate and breathing
- To reduce anxiety and tension
- To treat seizures
- They are helpful in panic disorders
- To cure sleep disorders
Q.3: Why addiction is considered as harmful condition? Or What are the problems associated to drug addiction?
Ans: Drug Addiction:
Addiction is considered to be a very harmful condition because addictive drugs act on pleasure center of the brain and therefore affects the way a person processes information.
Drug abusers go through withdrawal of social contact or communication. Many studies by the experts of social sciences prove that there exists a close relationship between drug addiction and crime.
Problems Associated To Drug Addiction:
The problem associated with drug abuse extend beyond immediate personal impact.
- Weakened Immune System & Health Issues:
Due to weakened immune system, addictive people suffer with health issues which increases the risk of illnesses and infection. Such as heart and lung diseases, liver failure, blood vessels infections etc. - Damage Social Life:
Addiction can damage the one's social life. They face social stigma. i.e. the society dislikes them because of their unpredictable behaviours. The addictive people are short tempered and mostly their violent acts results in harm to others or society. - Involvement in Crimes:
Addictive people can easily involved in various crimes e.g. Robbery, stealing / snatching, law violator and a criminal. - Brain Damage & Psychic Patients:
Seizures, stroke, mental confusion and brain damage. Problems with memory, attention and decision making, which make daily living more difficult. Drug addicts may become psychic patients also. - Disturbed Family Life:
The family of an addict person is also affected, when the addict does not get its need he become, angry, aggressive, harsh, short temper and does not behave well, ultimately lose relations. - Death Occur:
The most severe effect of drug abuse is death, if overdosed.
Q.4: How drugs (medicine) can be taken from natural source?
Ans: Natural Sources of drugs:
Drugs can be taken from natural sources through plant, animal, micro organisms and minerals.
1. Drugs from Plants:
Many important medicines are obtained from plants. Plants produce special substances in their roots, leaves, flowers or seeds that help to form drugs in laboratory or can be used directly as herbs to treat certain diseases.
Example:
- Cinchona tree contains Quinine in its bark which is used in the prevention and treatment of malaria.
- Opium is used as pain-killer drug extracted from unripe seed pods of the opium poppy.
2. Drugs from microorganisms:
Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi not only produce primary metabolites but are also capable of making secondary metabolites, which constitute half of the pharmaceutical on the market as antibiotics and antifungal drugs.
Example:
- Tetracycline is produced by bacteria.
- Lovastatin are produced by fungi.
3. Drugs obtained from animals:
Certain animal parts and animal products are used as drugs in therapeutics. The major group of animal products used in medicine is hormones, enzymes, animal's extractive, organs and bile acids.
Example:
- Gonadotropin hormone is prepared commercially from either horse serum or from the urine of pregnant woman. They controlled the production of sex hormone in the body.
- Hyaluronidase enzyme is produced by some microorganisms found in the heads of leeches, in snake venom and in mammalian testes.
- Now a day, scientists are more excited about drugs derived from the sea anemone.
4. Drugs from minerals:
Some of the drugs are synthesized from minerals or can be given with minerals as supplement.
Example:
- Iron is used in treatment of iron deficiency (anemia).
- Zinc is used to make zinc oxide paste which is used in wounds and in eczema.
- Gold salts are used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis etc.
Q.5: Is it possible to get drugs from animals name some of them?
Ans: Yes it is possible to get drugs from animals. The healing of human ailment by using therapeutics based on medicines obtained from animals or ultimately derived from them is known as zootherapy. Certain animal parts and animal products are used as drugs in therapeutics. The major group of animal products used in medicine is hormones, enzymes, animal's extractive, organs and bile acids.
Example:
- Gonadotropin hormone is prepared commercially from either horse serum or from the urine of pregnant woman. They controlled the production of sex hormone in the body.
- Hyaluronidase enzyme is produced by some microorganisms found in the heads of leeches, in snake venom and in mammalian testes.
- Drugs produced by animals are usually their glandular products. Fish liver oil, musk, bees wax, certain hormones and antitoxins are also obtained from animal sources.
- Now a day, scientists are more excited about drugs derived from the sea anemone.
Q.6: Do we have any harm of antibiotics? If, so mention them.
Ans: Yes, antibiotics have some harm because they can cause side effects based on they work. Antibiotics are prescribed for a particular infection, but can harm normal flora beneficial to our body. Some of the harmful side effects are as follows:
- Antibiotic resistance
- Diarrhea
- Upset stomach
- Thrush, which is a fungal infection that can affect the mouth or digestive tract.
- Vaginal yeast infection caused by Candidia albican (discharge, burning, pain, itchiness).
- Can cause yellowing of teeth.
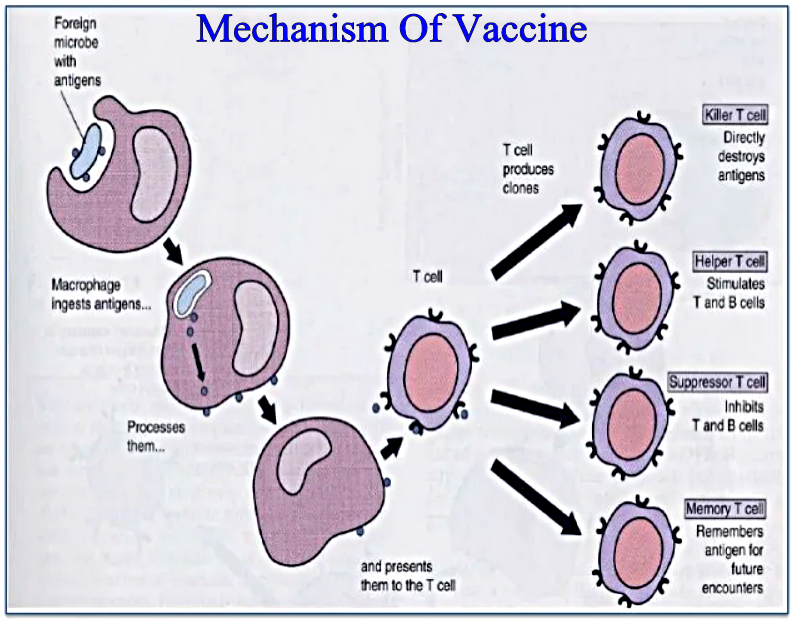
Q.7: How vaccines work against pathogen? Explain the process with the help of diagram.
Ans: VACCINE:
A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins on one of its surface proteins. A vaccine can confer active immunity against a specific harmful agent by stimulating the immune system to attack the agent.
Mechanism Or Working of Vaccine:
C. EXTENSIVE RESPONSE QUESTION:
(i) How bacteria produce antibiotics resistance?Ans: ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE:
Antibiotics are most important in medicine but overuse of antibiotics can cause antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria develop the ability to survive exposure to antibiotics that were designed to kill them or stop their growth. Antibiotic resistant bacteria are free to grow, multiply and cause infection within the host even when exposed to antibiotics. As such bacteria are not affected by commonly used antibiotics, so this condition is called antibiotic resistance.
There are two main ways for bacteria to withstand the effects of an antibiotic:
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE MECHANISMS:
1. Stop the antibiotic from reaching its target:
Pump the antibiotic out from the bacterial cell. Bacteria can produce pumps that sit in their membrane or cell wall. These so-called efflux pumps are very common in bacteria and can transport a variety of compounds such as signal molecules and nutrients. some of these pumps can also transport antibiotics out from the bacterium, in this way lowering the antibiotic concentration inside the bacterial cell.
In some cases mutations in the bacterial DNA can make the bacteria produce more of a certain pump, which in turn increases resistance. Decrease permeability of the membrane that surrounds the bacterial cell. Certain changes in the bacterial membrane make it more difficult to pass through. In this way, less of the antibiotic gets into the bacteria.
2. Modify or bypass the target of the antibiotic:
Camouflage the target. Changes in the composition or structure of the target in the bacterium (resulting from mutations in the bacterial DNA) can stop the antibiotic from interacting with the target. Alternatively, the bacteria can add different chemical groups to the target structure, in this way shielding it from the antibiotic.
Express alternative proteins. Some bacteria are able to produce alternative proteins that can be used instead of the ones that are inhibited by the antibiotic.
Some bacteria are naturally resistant to certain antibiotics. For example an antibiotic that destroys the cell wall of the bacteria. If a bacterium does not have a cell wall, the antibiotic will have no effect. This phenomenon is called intrinsic resistance. When a bacterium that was previously susceptible to an antibiotic evolves resistance, it is called acquired resistance.
Conclusion:
- Sometimes bacteria become habitual for that antibiotic or alter strategy to hinder the effect of antibiotic.
- The change either protects the bacterium from the action of the medication or neutralized the medication.
- They can acquire resistance by getting a resistance gene encoded to its chromosomes.
- Another cause of antibiotic resistance is their use in diseases in which they have no effect (e.g. antibiotics are not effective against infections caused by viruses).
(ii) Describe the mode of vaccination?
Ans: MODE OF VACCINATION:
There are many approaches to vaccine development, but vaccines can be broadly classified by the antigen(s), the active component(s) that generate a specific immune response against the disease-causing organism, are prepared.
CLASSIFICATION OF VACCINES:
Live attenuated vaccines:
The virus or bacteria is functional/alive but has been weakened so it can replicate in the body several times and generate an immune response without causing the disease, e.g. chickenpox, measles, mumps and rubella, rotavirus, and shingles vaccine viruses. The BCG vaccine contains live weakened tuberculosis bacteria.
Inactivated or dead vaccines:
Inactivated vaccines do not contain live viruses or bacteria. Viruses in these vaccines are inactivated or split, e.g., polio or influenza vaccines in New Zealand, and bacteria killed. New Zealand does not have a killed bacteria vaccine on the Immunization Schedule, but a travel-related vaccine is available for purchase. They cannot cause the disease but the inclusion of adjuvant (immune enhancers) in the vaccine help generate an immune response.
Subunit vaccines:
These vaccines present proteins or sugars derived from the disease-causing organism.
Protein vaccines:
Protein vaccines may include fragments extracted from a virus or bacteria such as inactivated bacterial toxoid proteins, e.g. tetanus and diphtheria vaccines, or be engineered without the disease-causing organism, e.g. virus-like particles in hepatitis B and human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines Pure polysaccharide vaccines.
Some vaccines only include sugar/carbohydrate (polysaccharide) molecules found on the outside of some bacteria, e.g. some vaccines to protect against pneumococcal or typhoid disease. This type of vaccine can generate a protective immune response in older children and adults and cannot cause the disease.
Nucleic acid-based vaccines:
At present, different types of nucleic-acid vaccines are in developmental, pre-clinical and clinical evaluation phases, e.g. for prevention of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), influenza and malaria diseases and treat some cancers. This vaccine platform is also being used to develop vaccines to prevent COVID-19 disease.
Source: Special Thanks To Sir Syed Arif Ali
No comments:
Post a Comment