Go To Index
CONSTITUTIONAL DEVELOPMENT IN ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF PAKISTAN
Descriptive Question Answers
CONTENT
-
The Need of a Constitution for a Country
-
Salient Features of the Objectives Resolution
-
Salient Features of 1956 Constitution
-
Main Causes of the Separation of East Pakistan
-
The Role of Pakistanis for the Prosperity of the Country
-
Salient Features of 1973 Constitution
-
Salient Features of 1962 Constitution
Q.1: Why is constitution necessary for a country?
Ans:
CONSTITUTION:
Constitution means the supreme law of any country. The basic document of rules and regulations of a state is called a constitution. In other words, constitution means a set of basic laws, rules and regulations which are necessary for running the administration of a state.
(1) HISTORY OF CONSTITUTION:
As far as the history of constitution is concerned, it is very old. The primitive man used to live in small families and tribes. Each family unit had its own rules and a way of living. Later, their family units became the big tribes to meet their economic, social and defense needs. With the passage of time, their tribes increased and they organized themselves into much bigger units with a certain territory. These big tribes and units needed some rules and regulations of their own called the "constitution".
(2) MODERN CONCEPT OF A CONSTITUTION:
In the modern states, specially in the democratic states, constitution is must because, without a constitution, no country can run the state properly. The main objectives of every state are the prosperity and welfare of the people.
In the modern world today, constitutions are generally of two types.
- Parliamentary form of Constitution:
In the Parliamentary form of constitution, Parliamentary system of government has been given. In this system, the president is called the head of the state and the Prime Minister is called the head of federal government.
- Presidential form of Constitution:
Under the Presidential form of constitution, Presidential system of government is followed. In this system, the President is the head of the state and he is also the head of the government.
(3) THE NEED FOR A CONSTITUTION:
Due to the following reasons, there is a need of a constitution for every country.
-
Provision of a System:
Constitution provides a system of government to run the states in smooth manner.
-
Rules and Regulations of the Different Institutions:
Constitution provides the basic rules and regulations for different institutions, like the Parliament, Judiciary and Administration.
-
Creates Equality:
Constitution creates, equality because it confirms that all are equal in the eyes of law.
-
Protects the Basic Rights of the People of a State:
A constitution protects the basic rights of its citizens.
-
Independence of Judiciary:
Constitution of any state provides the independence of Judiciary. Without provision Of justice, no society can be changed into a developed society.
-
Provision of a Permanent and Stable System:
It provides a permanent system to a state. Permanent system of government is necessary for a stable and strong government.
CONCLUSION:
The supreme law of any country is called a constitution. Constitution is must for any state. It provides complete and permanent system to a state. Without constitution, a state cannot protect the basic rights of the people as well as the independence of judiciary. Pakistan has a constitution which protects the basic rights of the people.
Q.2: Describe the salient features of the Objectives Resolution.
Ans:
INTRODUCTION:
Pakistan came into being in 1947. When Pakistan came into being, it had no constitution. The work of constitution-making was given to the first Constituent Assembly of Pakistan. Till 1949, no constitution was made. On 12
th March 1949, a resolution was passed by the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan called the Objectives Resolution, It was a reminder to the constitution-makers that the main objectives of the creation of Pakistan would he kept in the new constitution of the state. The new constitution would be Islamic.
OBJECTIVES RESOLUTION:
When constitution making was in process, in 1949, Allama Shabbir Ahmed Usmani and Mr. Liaquat Ali Khan decided to present a resolution in favour of an Islamic Constitution. Both worked very hard and Allama Shabbir Ahmed Usmani prepared the draft of the Objectives Resolution.
In this resolution, the main aims and objectives of the creation of Pakistan were reminded to the constitution-makers of Pakistan. This resolution was presented by the "Leader of the House", Mr. Liaquat Ali Khan and passed by all members of the assembly.
Islam was declared the foundation of the state in this resolution. It was a landmark in the history of constitution making in Pakistan.
MAIN FEATURES OF OBJECTIVE RESOLUTION:
The Objectives resolution was passed on l2
th March, 1949. Following are the main features of the resolution.
(1) Sovereignty of Allah Accepted:
It was accepted in the resolution that sovereignty of the entire universe belongs to Almighty Allah alone. The political power is a sacred trust which shall he exercised by the representatives of Pakistan.
(2) The Principle of Democracy Accepted:
The principles of democracy, equality and social justice were accepted. Pakistan came into being, under a democratic process. That is why, democracy must be there in the country. It is the fundamental right of every citizen to elect his representatives to rule over the country.
(3) Holy Quran and Sunnah, the Supreme Laws of the Country:
The Holy Quran and Sunnah will be the main sources of the laws of the country. People will lead their lives according to the principles set in the Holy Quran and Sunnah.
(4) The Rights of the Minorities shall be Protected:
The rights and interests of the minorities shall be protected. Their religions and cultures shall be protected and safeguarded.
(5) Federal System with Provincial Autonomy:
A Federal form of government with full provincial autonomy will be set up. Pakistan is a federation of four provinces. That is why, full provincial autonomy must be given to all four provinces to run the business of the provinces.
(6) Free and Fair Judiciary Granted:
Free and fair judiciary will be granted for the provision of justice to common man. Justice is the main principle of Islamic teachings. Without provision of justice, there is no concept of a welfare society.
(7) Steps for the Development of Poor Classes:
Steps for the development of poor classes will be taken for a developed Pakistan. In Pakistan, there is great poverty and people have very poor living standard. That is why, steps for the development of poor classes were suggested.
IMPORTANCE OF OBJECTIVES RESOLUTION:
Passing of the Objectives Resolution was an important event in the constitutional history of Pakistan. The Objectives Resolution was a milestone in the constitutional history of Pakistan.
It provided complete guideline for the 1956 Constitution. Due to the Objectives Resolution, the people of Pakistan got democracy and their basic rights. Later, its important features were kept in the 1962 and 1973 constitutions. It is written in the preamble of the 1973 constitution.
CONCLUSION:
The Objectives Resolution was a landmark in the constitutional history of Pakistan. It was a complete guideline for the future constitution of Pakistan. All its main features were embedded in all the three constitutions of Pakistan. It was passed due to the great efforts of Allama Shabbir Ahmed Usmani and Liaquat Ali Khan.
The Objectives Resolution has a great importance in the constitutional history of Pakistan because all the constitutions of Pakistan were made under the guidance of the Objectives Resolution.
Q.3: Describe the salient features of 1956 constitution.
Ans:
INTRODUCTION:
Pakistan came into existence in 1947. At that time, there was no constitution in the country. After the struggle of nine years, the first constitution of Pakistan was made in 1956. Pakistan remained for more than eight years without a constitution. So, the people of Pakistan welcomed it. A Federal Parliamentary form of government was introduced in it. It came into force on 23
rd March, 1956.
Here we are discussing the main features of 1956 constitution.
MAIN FEATURES OF 1956 CONSTITUTION:
(1) Federal Parliamentary form of Government was introduced:
Federal Parliamentary form of Government was introduced which was the demand of the people of Pakistan. This system was introduced because in Pakistan, there'are four provinces and all wanted provincial autonomy.
(2) Country Was Declared Islamic Republic:
In the introduction of the constitution, it was stated that sovereignty belongs to Almighty Allah only and Pakistan was declared an Islamic Republic.
(3) Democracy was Introduced:
Democracy was introduced in the country and the Governor General was replaced by the President.
Pakistan came into being under a democratic process. That is why, democracy must prevail in the country. It is the fundamental right of every citizen to elect his representatives to rule over the country.
(4) Distribution of Powers between Federal and Provincial Government:
The powers were distributed between the center and the two provinces of Pakistan, namely then the East Pakistan and West Pakistan under the Federal System of Government.
(5) Opportunities for Islamic Teachings Ensured:
It was ensured in the constitution that all opportunities will be provided to the Muslims to lead their lives according to the teachings of Islam.
(6) Free and Fair Judiciary Granted:
For the provision of justice to the common man, free and fair judiciary was granted.
Justice is the main principle of Islamic teachings. Without provision of justice, there is no concept of a welfare society.
(7) Basic Rights of the People were Ensured:
Some basic rights of the people of Pakistan were given to them. The constitution of any country provides basic rights to its citizens to lead a better and protected life.
(8) Muslim Head of State:
The office of the Head of the state was restricted to Muslims only.
(9) Laws According to Islam:
Any law against the teachings of Islam was to be amended. Pakistan came into being in the name of Islam, so only Holy Quran and Sunnah should be the supreme law of the country.
(10) The Rights of Non-Muslim Minority were Protected:
All basic rights of the non-Muslim minority were protected by the State. In Pakistan, all the basic rights of non-Muslims, specially the rights of worship were given to them.
(11) Urdu and Bengali were declared National Language:
Urdu and Bengali languages were declared the national languages of Pakistan. People of East Pakistan were 52% of the total population of Pakistan. So, on their demand, Bangla, along with Urdu was declared the national language of Pakistan.
(12) Provincial Autonomy:
Provincial autonomy was given in this constitution.
CONCLUSION:
After the creation of Pakistan, Pakistan remained for more than eight years without a constitution because the first constituent Assembly of Pakistan did not make a constitution for Pakistan which was its main task. In 1956, after a long struggle, a constitution was given to the country. It was an Islamic, democratic constitution.
After two years only of its enforcement, General Iskandar Mirza abrogated that constitution and imposed Martial Law in the country in 1958. Again, Pakistan became a land without a constitution.
Q.4: Why did East Pakistan separate from West Pakistan?
Ans:
INTRODUCTION:
Pakistan came into being in 1947. The Muslims of United India got this homeland on Muslim majority basis. In Punjab, Sindh, N.W.F.P., Baluchistan and Eastern Bengal, Muslims were in majority. That is why, along with Punjab, N.W.F.P., Sindh and Baluchistan, East Bengal became part of Pakistan called East Pakistan.
In 1971, East Pakistan was separated from West Pakistan and became an independent country, Bangladesh.
Here, we are discussing the main causes of the separation of East Pakistan.
MAIN CAUSES OF THE FALL OF EAST PAKISTAN:
Following were the main causes of the separation of East Pakistan:
(1) Odd Geographical Location of East and West Pakistan:
In 1947, when Pakistan came into being, the distance between the two parts of Pakistan was more than 1000 k.m., separated by India. The people of both parts could not come closer to each other. This created great distance and misunderstanding among the people of East and West Pakistan. India which had never accepted Pakistan, took advantage of this situation and started false propaganda against the people of West Pakistan which resulted in the separation of East Pakistan.
(2) Non-friendly Behavior of West Pakistan's Officers:
There was a lack of understanding between the people of both parts of Pakistan. The officers belonging to East Pakistan were more friendly and closer to the people as compared to the officers of West Pakistan. They maintained a distance from the people. Their behaviour towards the people was not good. This created a sense of hatred against West Pakistan. The people of East Pakistan started feeling jealous of the high officials of Pakistan.
(3) Military Governments:
Before the separation of East Pakistan, Martial Law was twice imposed in the country. Due to Martial Law, people of East Pakistan did not get their due share in the government as they liked parliamentary form of government. Ayub Khan accused the political leaders of East and West Pakistan that they were responsible for the failure of parliamentary system. The people of East Pakistan did not like military governments.
(4) Language Issue:
The people of East Pakistan wanted Bangla as the national language of Pakistan because 52% people were living in the Eastern part of the country. The Government of West Pakistan wanted Urdu as the national language of the country. They started strong protests and demonstrations against the government. It was a big cause of the separation of East Pakistan.
(5) Demand of Provincial Autonomy:
Some of the political leaders of East Pakistan demanded complete provincial autonomy. This demand was not accepted and India took the benefit of this situation by separating East Pakistan from West Pakistan.
(6) Sheikh Mujeeb's Six Points:
Sheikh Mujeeb was a very popular leader of Awami League Party. He demanded separate economic system for East Pakistan by presenting his famous six points. All the political parties of West Pakistan turned down the proposals of Sheikh Mujeeb. In disappointment, he started developing secret relations with India and India propagated against West Pakistan.
(7) Misguidance of Hindu Teachers:
A great number of Hindu teachers were teaching in East Pakistan in schools and colleges. They produced such literature which was against West Pakistan. They played a great role to create negative thinking against West Pakistan.
(8) Evil Plan of the Western Powers:
Some Western powers like Britain and the U.S.A. made some evil plans to separate East Pakistan because Pakistan was the biggest Islamic state of the world. Russia was also annoyed with Pakistan as some military bases were given to the
U.S.A. It openly supported India's aggression against Pakistan.
(9) Results of 1970 Elections:
Elections were held in 1970 in Pakistan in which Sheikh Mujeeb got majority seats in the National Assembly, but he did not get a single seat in West Pakistan. On the other hand, Z.A. Bhutto got majority seats in West Pakistan but did not get a single seat in East Pakistan. In this way, a. deadlock was created and when government was not handed over to Sheikh Mujeeb, The people of East Pakistan launched a great protest against West Pakistan causing separation of East Pakistan.
(10) Military Action in East Pakistan:
After the elections of 1970, when Government was not handed over to Sheikh Mujeeb, the people of East Pakistan started a great movement against West Pakistan supported by India. The Law and order situation had gone worst. Then military action was taken against the separatist movement of Awami League which fanned the flame. The people of East Pakistan started armed struggle against West Pakistan.
(11) India's Attack on East and West Pakistan:
India took the benefit of East Pakistan situation and attacked Pakistan Dec, 3
rd 1971. A war was fought between the two countries in which Pakistan Army and arms for the Army could not reach in time in East Pakistan to save it.
(12) Separation of East Pakistan:
On 16
th December 1971, the Indian Army entered into Dhaka and captured it. In this way, East Pakistan emerged as Bangladesh on the map of the World.
In 1974, on the event of the Second Islamic Summit Conference, Pakistan recognized Bangladesh as an independent country and now both the countries have very good brotherly relations.
CONCLUSION:
When Pakistan came into being in 1947, East Pakistan was part of Pakistan and 52% people of Pakistan were living in that part of Pakistan. Later, due to many problems and evil plans of the Western powers, East Pakistan did not remain with Pakistan and separated from West Pakistan.
Pakistan later accepted Bangladesh in 1974 and now both countries are enjoying good trade and cultural relations.
Q.5: What role should Pakistanis play for the prosperity of the country?
Ans:
INTRODUCTION:
Pakistan is our motherland. We got this homeland after great sacrifices. As Pakistanis, it is our duty to protect our land and we must work for the stability and unity of the country. It is also our responsibility to do work only for the prosperity and well being of the country .
ROLE OF A PAKISTANI FOR THE PROSPERITY OF THE COUNTRY:
In order to keep Pakistan strong and prosperous, following steps are needed.
(1)Hard Work:
We must work hard in all fields for the national development and to make our country economically independent. Pakistan is a developing country and we want to become a developed country. This target can be achieved only by hard work.
(2) National Unity:
Regionalism is very harmful for the unity and development of the state. We must promote national unity.
In Pakistan, four different nations are living in four different provinces with four different cultures and languages. Islam is a binding force among all these nations. National unity is necessary to unite the people.
(3) Patriotism:
Every Pakistani should be ready to sacrifice his life for the love of the country through words and deeds.
Patriotism is a great quality which must be there among the citizen of the state for the glory of the state. Prosperity of a country cannot be achieved without patriotism.
(4) Steps for the Promotion of Education:
It is our duty to educate our youth. We must spread and promote education in all regions. Without education, there is no concept of progress.
In Pakistan literacy rate is only 45%, which is among the lowest literacy rates of the world. So, to increase it, education must be promoted.
(5) Self-Reliance:
It is the duty of every Pakistani to work hard to make Pakistan a self-reliant state. Self sufficiency in food and other fields is necessary. We must avoid loans and aids from the Western countries for the dignity of the state.
(6) Social Justice:
Justice is the base of every developed and prosperous society. We must establish a system of government based on social justice. In Pakistan, there are different classes of the people. Mostly, people are poor. Without the provision of social justice, development of the country cannot be achieved.
(7) Steps to Vanish Corruption:
It is the duty of every Pakistani to cooperate with the government to eradicate corruption from the society. For a prosperous Pakistan, a corruption-free society is needed. Jihad against the evil of corruption must be done by the people of Pakistan to uproot corruption from Pakistan.
(8) Feel Proud as Pakistanis:
Pakistan is our beloved, homeland and we got this homeland after a long struggle. So, we must feel proud as Pakistanis.
CONCLUSION:
The Muslims of South Asia struggled very hard and rendered great sacrifices, only then Pakistan appeared on the map of the world. Now it is our duty and responsibility as Pakistanis to make it a strong, self reliant and corruption-free state. Every Pakistani must get proper education, work hard and cooperate with the government to make Pakistan a prosperous state.
Q.6: Write the salient features of 1973 constitution.
Ans:
INTRODUCTION:
The first Constitution of Pakistan was made in 1956 after 9 years of struggle which was dismissed by Iskandar Mirza. Then, Ayub Khan gave a new constitution in 1962 which was discarded by the people of Pakistan as being undemocratic. Then, in 1973, Mr. Z.A. Bhutto gave the third and present constitution of Pakistan, which is an Islamic democratic constitution. All the political parties of Pakistan unanimously passed it and it fulfills all the requirements of a democratic Islamic state.
HISTORY OF 1973 CONSTITUTION:
After the general elections of 1970, Sheikh Mujeeb-ur-Rehman of Awami League got a majority but the government was not handed over to him. Due to the, after a rebellious movement of the people of East Pakistan, it separated from West Pakistan. In the remaining Pakistan, government was handed over to Mr. Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto. He framed a complete constitution within one year and on l4
th August 1973, it was enforced in our country.
SALIENT FEATURES OF 1973 CONSTITUTION:
Following are the salient features of the 1973 constitution.
(1) An Islamic Constitution:
It is an Islamic constitution in which the sovereignty of Allah has been accepted and Islam has been declared the state religion.
(2) Objectives Resolution as Preamble:
The Objectives Resolution, which is an Islamic resolution, has been written in the preamble of the constitution, means the foundation of the constitution was laid on the objectives Resolution.
(3) Islamic Name of the Country:
An Islamic name "Islamic Republic of Pakistan" has been given to the country. Islam is our identity. So, the Islamic name of Pakistan is our recognition.
(4) Definition of a Muslim Given:
For the first time, the definition of a Muslim has been given in the constitution that a person, who has a firm belief in the oneness of Allah and in the Prophet hood of the Holy Prophet Hazrat Muhammad (P.B.U.H.) as the last prophet of Allah, will be considered a Muslim. The constitution of 1973 provides full security to the finality of the Prophet hood of Muhammad (P.B.U.H.).
(5) Muslim Head of State and Government:
It is given in the constitution that only a Muslim will be the head of the state (President) and the head of the government (Prime Minister). No non-Muslim can become Prime Minister or President of Pakistan as Pakistan is an Islamic Ideological state.
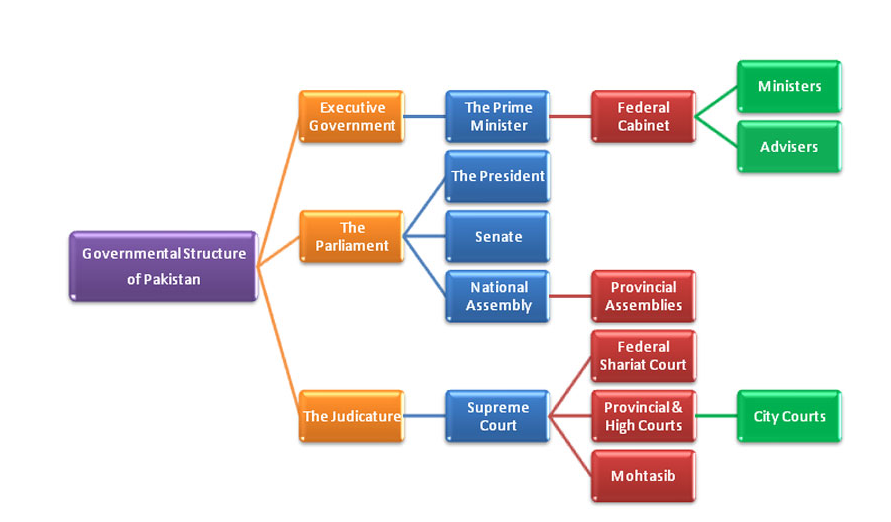
(6) Federal Parliamentary Form of Government Introduced:
Federal Parliamentary form of government has been introduced. Power has been divided between the federal and provincial governments.
(7) Bi-Cameral Legislature:
A Parliament consisting of two houses was established. The Upper House is called the-Senate and the Lower House is called the National Assembly.
(8) provincial Autonomy:
Complete provincial autonomy has been given to all provinces of Pakistan for complete unity.
Pakistan is a federation of four provinces. So, for the stability of federation provincial autonomy has been given to the people.
(9) Provision of the Basic Rights of the People:
Almost all types of basic rights of the people have been given to them. As compared to the constitutions of 1956 and 1962, more basic rights of the people have been given to them in these constitutions.
(10) Formation of Islamic Ideological Council:
Forth the first time in Pakistan, an Islamic Ideological Council has been set up consisting of leading ulema and scholars of Islamic teaching to guide the government about Islamic teachings and formation of an Islamic Society.
(11) Urdu as National Language:
Urdu which is the language of the common man has been declared the national language of Pakistan.
In Pakistan, different races are living in the four provinces of Pakistan who speak different languages, but or national unity, Urdu has been declared as the national language of Pakistan. Due to this language, people have come closer.
(12) Direct Mode of Elections has been Introduced:
Direct mode of elections based on "One Man One Vote" has been introduced. It is the fundamental right of every person to elect his representatives and executives.
(13) Free and Fair Judiciary:
Free and fair judiciary has been ensured by the state. Judiciary must be free and fair, because without free and fair judiciary, people's rights can not be protected and it is also necessary for check and balance of the government.
(14) Rights of Minorities have been Protected:
All rights and interests of the minorities have been fully safeguarded and protected.
Minorities are equal citizens of Pakistan. All types of their right and interests must be protected, specially their right of worship must be safeguarded by the state.
CONCLUSION:
The 1973 constitution is the present constitution of Pakistan. It was given by Mr. Z.A. Bhutto in 1973. It is an Islamic democratic constitution and protects all the basic rights of the people, of Pakistan. As, it is the present constitution of Pakistan and source of unity among the people it is the duty of every Pakistani to protect it.
This constitution was also dismissed by General Zia-ul-Haq and General Pervaiz Musharraf. As this constitution is a sign of unity among all the people, it is the duty of every Pakistani to protect it.
Q.7: Write the salient features of 1962 constitution.
Ans:
INTRODUCTION:
General Ayub Khan came in to power on 27
th Oct 1958. He gave the second constitution of Pakistan on June 8
th 1962. In this constitution, the system of government had been changed and for the first time, a presidential form of government was introduced to secure the rule of Ayub Khan. In this constitution, some Islamic provisions were given but indirect way of election was introduced. The people of Pakistan did not like this constitution because many rights of the people were not given in this constitution.
MAIN FEATURES OF 1962 CONSTITUTIONS:
The second Constitution of Pakistan, which was given by General Ayub Khan, had the following features.
(1) Objectives Resolution was Accepted:
The Objectives resolution which was an Islamic resolution was accepted in this constitution to set the pattern of government according to Islam.
(2) Islamic Name of the Country:
An Islamic name "Islamic Republic of Pakistan" was given to the country. Islam is our identity. So, Islamic name of Pakistan is our recognition.
(3) Laws According to Islam:
Any law against the teachings of Islam was to be amended. Pakistan came into being in the name of Islam. So, only Holy Quran and Sunnah should be the supreme law of the country.
(4) Federal Presidential System of Government Introduced:
For the first time in Pakistan, federal presidential form of government was introduced, in which the President was all in all and all types of powers had been given to him.
(5) Power were Concentrated in the Office of the President:
In this constitution all the power was concentrated in the office of the president intentionally because Ayub Khan himself was the president and he wanted all the powers of the government.
(6) Indirect Mode of Elections:
In the 1962 constitution, indirect mode of elections was introduced called The BD System (Basic Democracies System). In this system, people could not elect their representatives directly.
(7) Basic Rights of the People were given:
Some basic rights of the people were given to them but the right of speech and the right to criticize the government had not been given to the people.
(8) Free and Fair Judiciary:
Free and fair judiciary was ensured by the state.
Judiciary must be free and fair because without free and fair judiciary, people's rights can not he protected and it is also necessary for the check and balance of the government.
(9) Islamic Advisory Council was Established:
An Islamic Advisory council was established to guide the government about Islamic laws. Some Islamic provisions were also given in this constitution.
(10) Uni-Cameral Legislature was Introduced:
In 1962 constitution, Uni-Cameral Legislature was introduced.
CONCLUSION:
General Muhammad Avub Khan came into power in 1958. The country remained without a constitution upto 1962. In 1962, Ayub Khan gave the second constitution to the country. It was an Islamic constitution but the presidential form of government was introduced in it and indirect mode of elections was introduced.
This constitution remained in vogue upto 25
th March 1969 when Ayub Khan resigned and General Yahya Khan imposed Martial Law in the country by abrogating the 1962 constitution.