Search This Blog
Thursday 16 September 2021
English (C) Normal Paper I - Past Paper 2019 (MCQs Only) - HSC Part 1 - Science, Home Economics And Medical Technology Group
GO TO INDEX (Science)
English (C) Normal Paper I
English (C) Advance Paper 1 - Past Paper 2021 (MCQs Only) - For HSC Part 1 (Science, Home Economics Group) - For Failure, Improvements, Additional Subjects...
GO TO INDEX (Science)
GO TO INDEX (Home Economics)
English Advance Paper 1
Past Paper 2021 (MCQs Only)
For HSC Part 1
(Science, Home Economics Group)
For Failure, Improvements, Additional Subjects...
UNIT 01: PROBLEM SOLVING AND ALGORTHM DESIGNING - MCQs - Computer Science For Class X
GO TO INDEX
Computer Science For Class X
Unit 01: Problem Solving And Algorithm Designing
Multiple Choice Questions And Fill In The Blanks
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
A. ENCIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER:1. To "bake a cake" is an example of:
a. problem ✓
b. strategy
c. algorithm
d. solution
(Note: " Baking a cake" is problem and "Recipe of baking a cake" is Algorithm)
2. To find a feasible solution to a problem, the first step is to:
a. establish starting point
b. find available solutions
c. create a strategy
d. identify and analyze the problem ✓
3. Step by step solution of a problem in simple language is called:
a. Problem Solving
b. Algorithm ✓
c. flowchart
d. Data Structure
4. Shows the logic of program graphically.
a. Data Structure
b. Graph
c. Algorithm
d. Flowchart ✓
5. Symbol is used for input/output in flowchart.
a. Triangle
b. Square
c. Parallelogram ✓
d. Rectangle
6. Elements of data structure are not connected sequentially.
a. Array
b. Graph ✓
c. Queue
d. Stack
7. Stores data in hierarchal manner.
a. Stack
b. Queue
c. Array
d. Tree ✓
8. When that data is Pushed in stack, it means that data is:
a. inserted ✓
b. deleted
c. sorted
d. edited
9. In binary tree, each child can have maximum:
a. one node
b. two nodes ✓
c. three nodes
d. four nodes
10. Traversing an array means accessing:
a. first element
b. last element
c. any specific element
d. each and every element of the array ✓
11. The step by step solution of any program is called:
a. A flowchart
b. A pseudo code
c. An algorithm ✓
d. None of these
12. Which of the following is not one of the steps in a programming project:
a. Planning the solution
b. Coding the program
c. Testing the program
d. Selecting the hardware ✓
13. In preparing a program, one should first:
a. Plan the solution ✓
b. Documentation
c. Coding
d. define the problem
14. Problem solving steps of a program is called:
a. Top-down design
b. Flowchart
c. Algorithm ✓
d. Run time error
15. A pictorial representation of program is called:
a. A flowchart ✓
b. An algorithm
c. A Pseudocode
d. None of these
16. Step by step instruction to solve the C++ Program is called:
a. Algorithm ✓
b. Flowchart
c. Procedure
d. AlI of these
17. What does the symbol in a flowchart represent:
a. Decision ✓
b. Process
c. Start / Stop
d. Predefine process
18. What does an arrow represent in a flowchart?
a. Decision making
b. Data flow ✓
c. Start
d. Stop
19. In a flowchart a calculation (process) is represented by:
a. A rectangle ✓
b. A rhombus
c. a parallelogram
d. A circle
20. _____ symbol is used to represent input and output operation in a flowchart.
a. Circle
b. Rectangle
c. Diamond
d. Parallelogram ✓
21. When an algorithm is written in the form of a programming language, it becomes a:
a. Flowchart
b. Program ✓
c. Pseudo code
d. Syntax
22. A system wherein items are added from one and removed from the other end.
a. Stack
b. Linked list
c. Queue ✓
d. Array
23. Another name for 1-D arrays:
a. Linear array ✓
b. List
c. Horizontal array
d. Vertical array
24. A data structure that follows the FIFO principle.
a. Queue ✓
b. LL
c. Stack
d. Union
25. The process of drawing a flowchart for an algorithm is called ____.
a. Performance
b. Evaluation
c. Algorithmic representation
d. Flowcharting ✓
26. Which of the following Is not an advantage of a flowchart?
a. Better communication
b. Efficient coding
c. Systematic testing
d. Improper documentation ✓
27. Which one of the following is the process of inserting an element in the stack?
a. Insert
b. Add
c. Push ✓
d. None of them
28. Linear data structure arrange data in _____ method.
a. Non-linear
b. Linear ✓
c. Structure
d. None of the above
29. A data structure arrange data in _____ method.
a. Queue
b. LL
c. Stack ✓
d. Union
30. Which one of the following is the process of deleting an element in the stack?
a. Delete
b. Pop ✓
c. Push
d. Non of the above
31. Which one of the following is the process of inserting an element in the queue?
a. Insert
b. Enqueue ✓
c. Add
d. None of the above
32. Which one of the following the process of deleting an element in the queue?
a. Dequeue ✓
b. Add
c. Enqueue
d. None of above
33. Rearrange the given array or list of elements is known as:
a. Inserting
b. Arranging
c. Update
d. Sorting ✓
34. Which data structure has a hierarchical structure?
a. Tree ✓
b. Stack
c. Queue
d. None of the above
35. A data structure in which data items are not arranged in linear method:
a. Non-linear ✓
b. Linear
c. Structure
d. None of the above
Fill In The Blanks:
- Problem solving is the process of finding solutions of difficult or complex issues.
- A problem is a situation preventing something from being achieved.
- There are four basic steps involved in finding a solution; define the problem, generate alternative solutions, evaluate and select an alternative and implement and follow up on the solution.
- Problem and set are a starting point of solution.
- There are various strategies that can be used to formulate an algorithm for solving the problem.
- Using the strategy, various solutions to a given problem are planned and the most feasible solution is identified.
- Algorithm is a technical term for a set of instructions for solving a problem or sub-problem.
- Algorithms enable breaking down of problems and conceptualize solutions step-by-step.
- Algorithms are defined as generic steps of instructions so they can be written in any programming language.
- A flowchart writes the sequence of steps and logic of solving a problem, using graphical symbols.
- Flowcharts help in communicating the logic of a program to all others and make it easy for understanding.
- A data structure is a particular way of organizing data in a computer to use it effectively.
- In Linear data structure data elements are arranged in sequential order and each of the elements is connected to its previous and next element.
- Stack is a linear data structure in which items may be added or removed only at one end i.e. at the top of stack.
- Queue is a linear data structure in which that element inserted first will be removed first.
- Array is a linear data structure, which holds a list of finite data elements of same data type.
- Each element of array is referenced by a set of index of consecutive numbers.
- The elements of a non-linear data structure are not connected in a sequence.
- Each element of a non linear data structure can have multiple paths to connect to other elements.
- Tree is a non-linear data structure and is used to represent data containing a hierarchical relationship between elements.
- A graph is a non-linear data structure consisting (finite set) of data elements called nodes/vertices and edges that are lines that connect any two nodes in that graph.
Biology For Class X - Chapter No. 2 - Homeostasis - Multiple Choice Questions And Fill In The Blanks By Sir Saeed Sarang
GO TO INDEX
CHAPTER 2 - Homeostasis
Multiple Choice Questions And Fill In The Blanks
Special Thanks To Sir Saeed Sarang (Sindh Text Book Board)
Contact # 03023006727
Youtube Channel # Shafquat Ali YouTube
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer:
i) The internal condition of an organism is referred as:
(a) Homeostasis
(b) Internal environment ✓
(c) Internal metabolism
(d) Feedback mechanism
ii) A set of metabolism reaction which maintain internal environment is:
(a) Positive feedback
(b) Negative feedback
(c) Osmoregulation
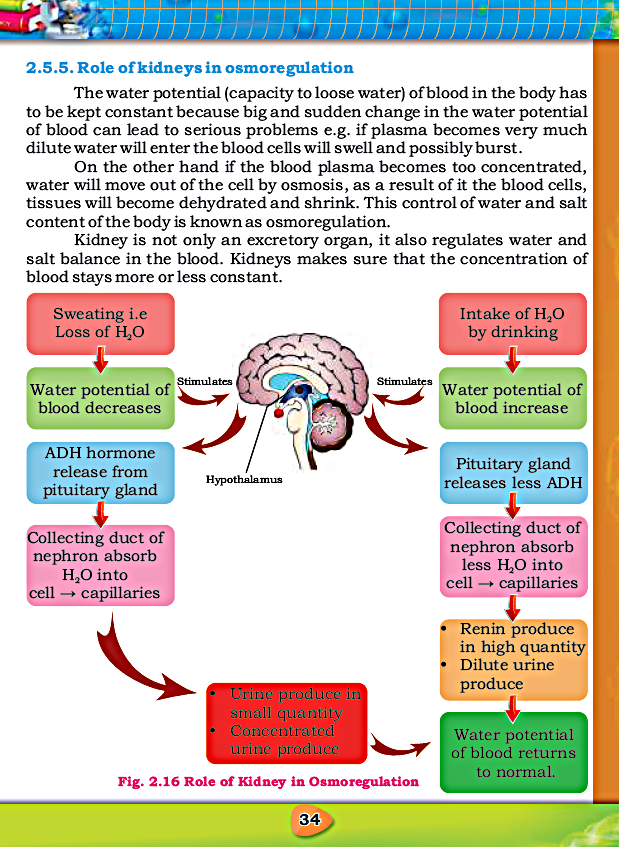
(d) Homeostasis ✓
iii) Removal of extra liquid water is:
(a) Exudation
(b) Guttation ✓
(c) Respiration
(d) Transpiration
iv) Plant grow near coastal area called:
(a) Xerophyte
(b) Halophyte ✓
(c) Epiphyte
(d) Hygrophyte
v) Organ of human body which is considered on the largest organ is:
(a) Skin ✓
(b) Digestive tract
(c) Liver
(d) Brain
vi) The maintenance of body temperature with in suitable limit is called
(a) Homeotherm
(b) Thermoregulation ✓
(c) Osmoregulation
(d) Heterotherm
vii) The kidney is enclosed in a membrane called
(a) Pericardium
(b) Peritoneum ✓
(c) Pleural membrane
(d) Plumule
viii) The network of blood capillaries present in the layer of skin:
(a) Epidermis
(b) Dermis ✓
(c) Hypodermis
(d) Endodermis
ix) Selective reabsorption in nephron takes place at
(a) Glomerulus
(b) Malpighian body
(c) Convulated tubules
(d) Loop of Henle's ✓
x) The hormone ADH release from
(a) Pituitary gland ✓
(b) Kidneys
(c) Liver
(d) Lungs
xi) Set point of human body temperature is:
a) 27°C
b) 37°C ✓
c) 47°C
d) 57°C
MORE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
12. Organisms maintain internal condition by:a) feedback mechanism ✓
b) thermoregulation
c) osmoregulation
d) guttation
13. When the rate of photosynthesis will be higher than respiration the plant gets:
a) extra O2 from the air and release extra CO2 in air through stomata
b) extra CO2 from the air and release extra O2 in air through stomata ✓
c) extra CO2 from th air and release extra H2O in air through stomata
d) extra O2 from the air and release extra H2O in air through stomata
14. It is the maintenance of internal water and salt conditions by osmosis:
a) homeotherm
b) thermoregulation
c) osmoregulation ✓
d) heterotherm
15. The removal of water in the form of vapour from the aerial part of a plant is called:
a) exudation
b) guttation
c) respiration
d) transpiration ✓
16. Transpiration occurs at/in:
a) day time only ✓
b) night time only
c) both day & night
d) windy conditions
17. Guttation occurs from the margin of leaves through special pores called:
a) glomerulus
b) epidermis
c) plumule
d) Hydathodes ✓
18. The plants which grow in fresh water are called:
a) Hydrophytes ✓
b) Halophytes
c) Mesophytes
d) Xerophytes
19. Hydrilla is a:
a) Hydrophytes ✓
b) Halophytes
c) Mesophytes
d) Xerophytes
20. Plants grow in the soil of low water quantity are called:
a) Hydrophytes
b) Halophytes
c) Mesophytes
d) Xerophytes ✓
21. They grow in desert or steep slopes or at high altitude:
a) Hydrophytes
b) Halophytes
c) Mesophytes
d) Xerophytes ✓
22. Cacti is an example of:
a) Hydrophytes
b) Halophytes
c) Mesophytes
d) Xerophytes ✓
23. Amoeba and paramecium pump out excess of water by:
a) Skin
b) Gills
c) Contractile vacuole ✓
d) Kidneys
24. Bodies or cells of fresh water animals have:
a) Hypertonic conditions ✓
b) hypotonic conditions
c) isotonic conditions
d) None of these
25. The removal of nitrogenous metabolic waste is called:
a) Metabolism
b) Excretion ✓
c) Respiration
d) Exudation
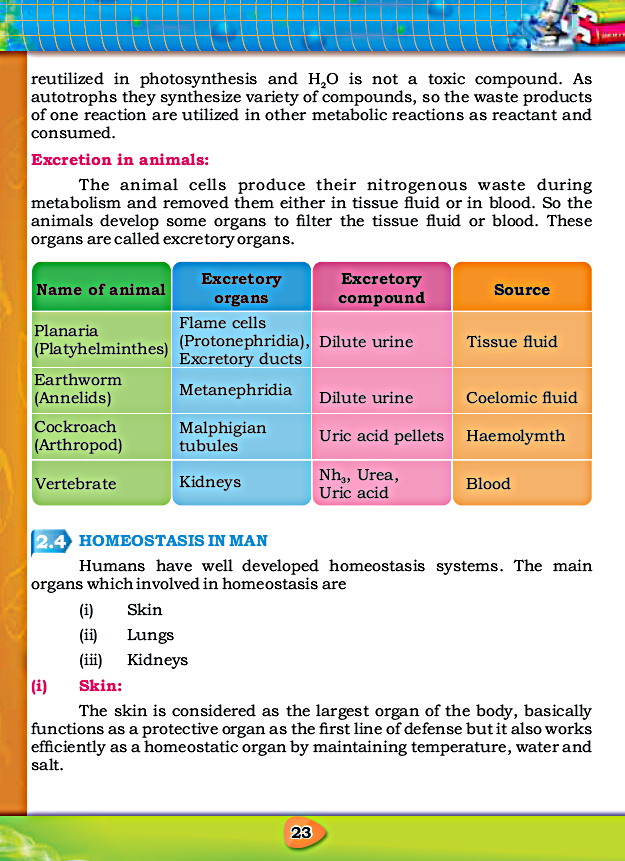
26. Metanephridia is an excretory organ of:
a) Planaria
b) Earthworm ✓
c) Cockroach
d) Arthropods
27. The excretory organ of a cockroach is:
a) Flame cell
b) Metanrphridia
c) Malphigian tubules ✓
d) Kidney
28. They are / It is called filter(s) of the body fluid:
a) Skin
b) Lungs
c) Liver
d) Kidneys ✓
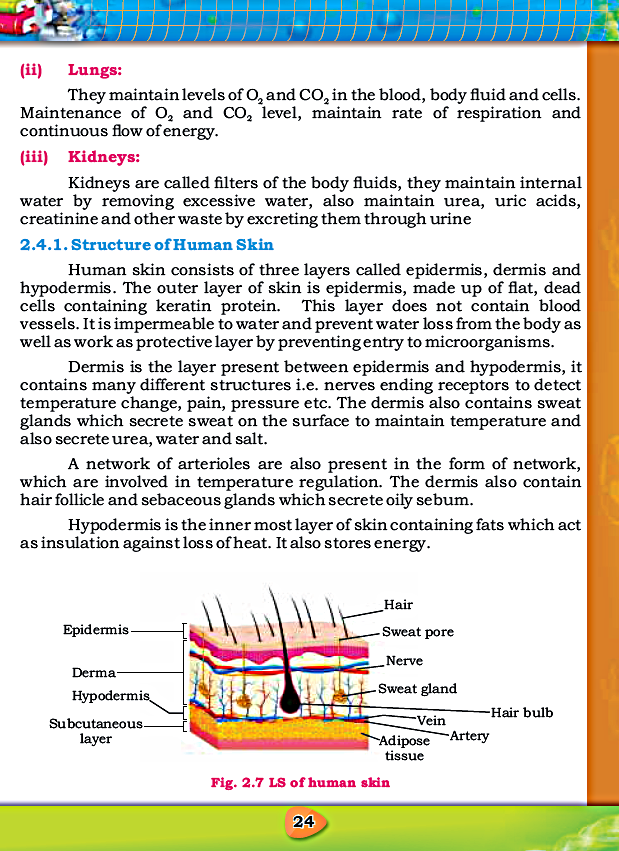
29. Human skin consists of:
a) Two layers
b) Three layers ✓
c) Four layers
d) Five layers
30. The outer layer of skin is called:
a) Epidermis ✓
b) Dermis
c) Hypodermis
d) Keratin
31. It is made up of flat, dead cells containing keratin protein:
a) Hypodermis
b) Dermis
c) Epidermis ✓
d) Creatinine
32. This layer of the skin contains receptors and sweat glands:
a) Creatinine
b) Epidermis
c) hypodermis
d) derm ✓
33. Which statement is correct?
a) Eidermis is the layer present between dermis and hypodermis.
b) Dermis is the layer present between the epidermis and hypodermis. ✓
c) Hypodermis is the layer present between the dermis and epidermis.
d) Double layers of hypodermis are present between dermis and epidermis.
34. Hair follicles, sebaceous glands and a network of arterioles are present in:
a) dermis ✓
b) hypodermis
c) keratin
d) epidermis
35. The innermost layer of the skin is:
a) epidermis
b) dermis
c) hypodermis ✓
d) keratin
36. Which statement is correct?
a) Hypodermis contains hair follicles and a network of arterioles.
b) Hypodermis contains fats and stores energy. ✓
c) Hypodermis contains sebaceous glands which secrete oily sebum.
d) Hypodermis contains sweat glands that secrete sweat on ho surface to maintain temperature.
37. The level of H+ in the blood is continuously monitored by special detectors (receptors):
a) Carotid bodies
b) Aortic bodies
c) Both of them ✓
d) None of these
38. Each kidney has as area in the center of concave surface which faces the vertebral column; this area is called:
a) Peritoneum
b) Cortex
c) Pelvis
d) Hilus ✓
39. A fluid is filled in between peritoneum and kidney are called:
a) Peritoneal fluid ✓
b) Peritoneum fluid
c) Hilus fluid
d) Peritoneum liquid
40. It is covered and protected by a fibrous capsule:
a) Cortex ✓
b) Medulla
c) Pelvis
d) Hilus
41. It is the inner lighter portion of the kidney:
a) Cortex
b) Medulla ✓
c) Pelvis
d) Hilus
42. It contains the conical projection called renal pyramids:
a) Pelvis
b) Cortex
c) Hilus
d) Medulla ✓
43. Each afferent arteriole divides into numerous blood capillaries in Bowman's capsule are collectively called:
a) Malpighian body
b) Renal corpuscle
c) Glomerulus ✓
d) loop of Henle's
44. Bowman's capsule with glomerulus is collectively called:
a) Malpighian body
b) Renal corpuscle
c) Both 'a' & 'b' ✓
d) None of these
45. Ultra-filtration occurs at:
a) Malpighian body ✓
b) glomerulus
c) proximal convoluted tubules
d) distal convoluted tubules
46. In the kidney, selective reabsorption occurs at:
a) Mapighian body
b) renal corpuscle
c) glomerulus
d) loop of Henle's ✓
47. They are the functional unit of the kidney:
a) renal corpuscles
b) Nephrons ✓
c) Malpighian bodies
d) Glomerulus
48. Urea is formed in:
a) Kidney
b) Pancreas
c) Liver ✓
d) Gall bladder
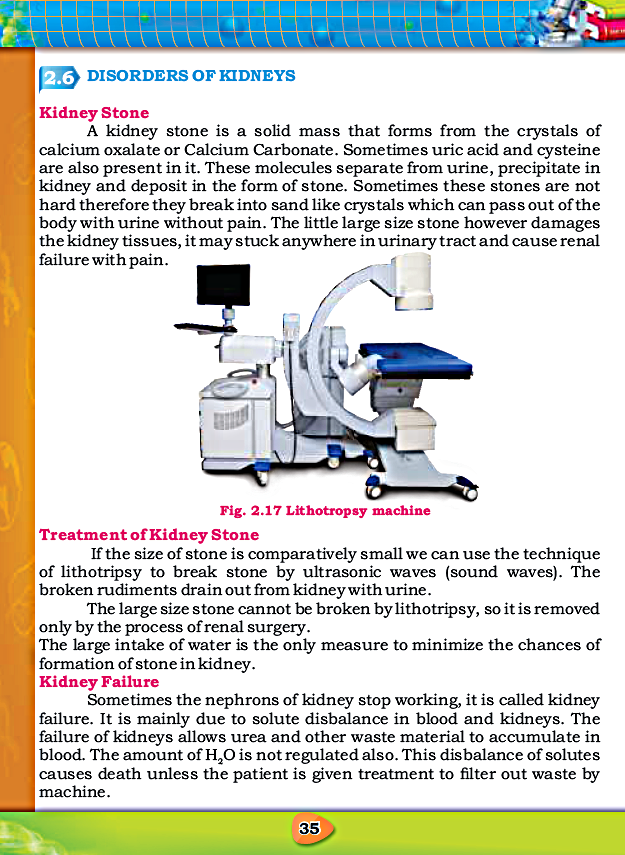
49. Kidney stone is a solid mass made of:
a) Calcium oxalate
b) Calcium carbonate
c) Both 'a' & 'b' ✓
d) None of these
Fill In The Blanks:
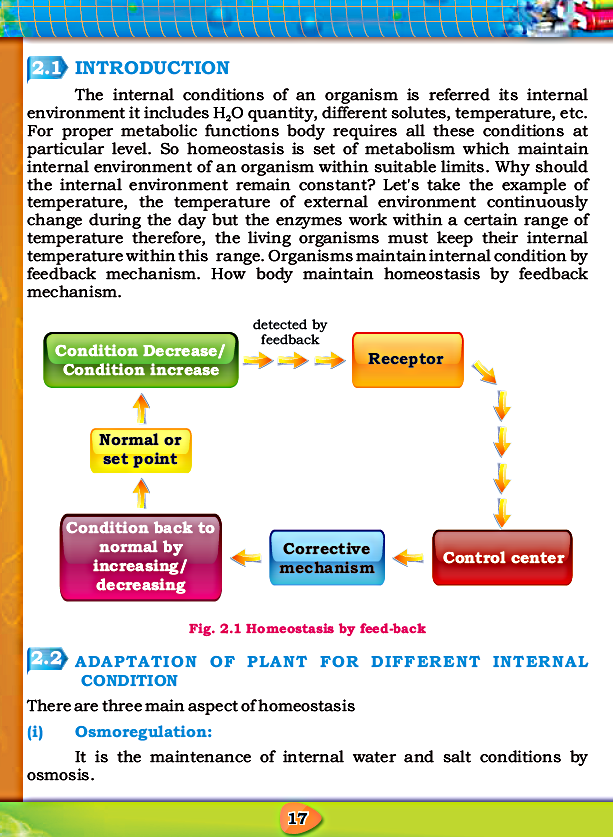
- Homeostasis is set of metabolism which maintain internal environment of an organism within suitable limits.
- Organisms maintain internal condition by feedback mechanism.
- There are three main aspects of homeostasis i.e. osmoregulation, thermoregulation and excretion.
- Osmoregulation is the maintenance of internal water and salt condition by osmosis.
- Thermoregulation is the maintenance of temperature within suitable limits where enzymes can work optimumly.
- Excretion is the process where metabolic toxic wastes, excess substances remove from body.
- Hydrophytes are the plants which grow in fresh water.
- Halophytes grow in sea marshes or in saltish water.
- Mesophytes are the plants grow in moderate water containing soil.
- Xerophytes are the plants grow in soil of low water quantity.
- The main organs involved in human homeostasis are skin, lungs and kidneys.
- Human skin is consist of three layers called epidermis, dermis and hypodermis.
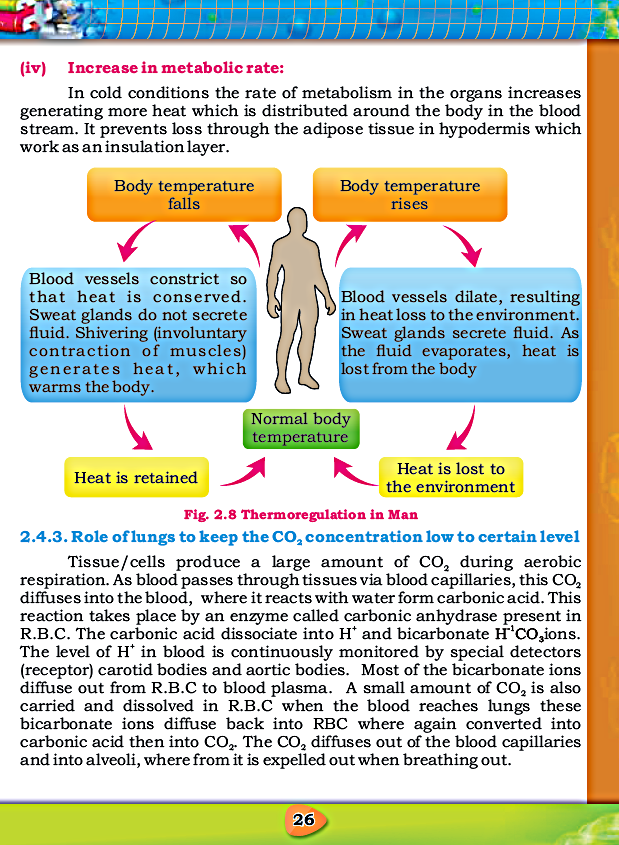
- Body temperature when rise body produce sweat, hair lies flat, vasodilation.
- When body temperature decrease the erection of hairs, vasocontraction, decrease in sweat production and increase in metabolic rate occurs.
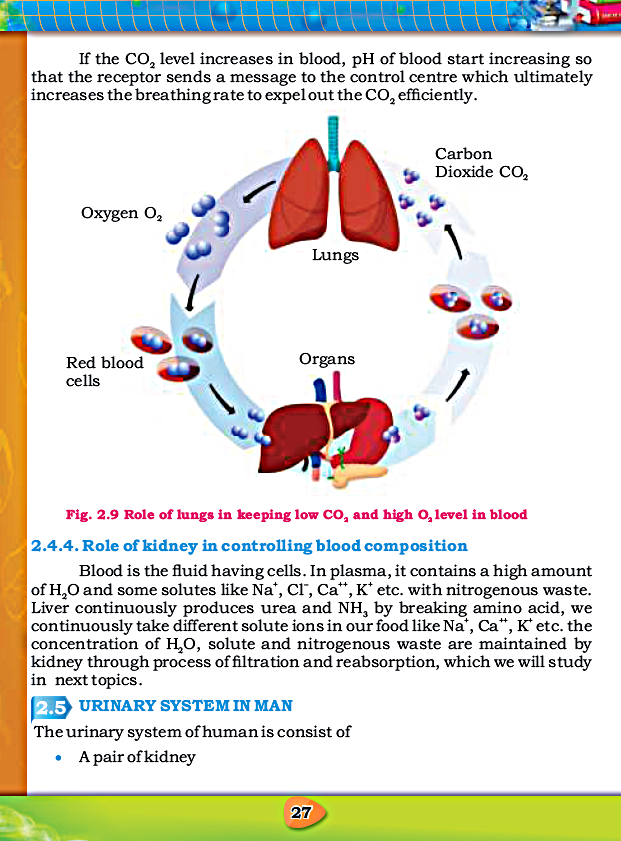
- Lungs keep the CO2 concentration at low level.
- Kidneys maintain blood composition by maintain level of H2O, solutes and nitrogenous waste by the process of filtration and reabsorption.
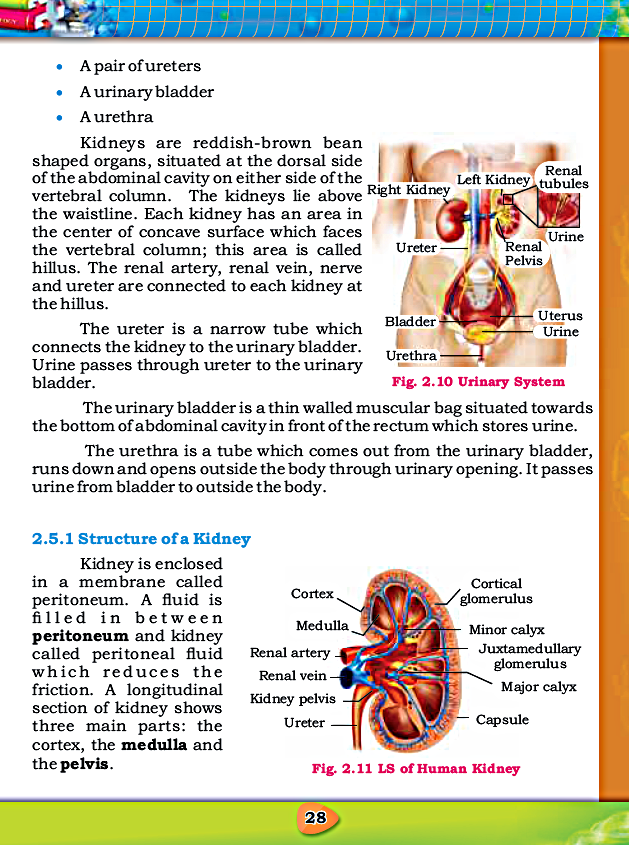
- Kidneys are situated at the dorsal side of the abdominal cavity on either side of the vertebral column.
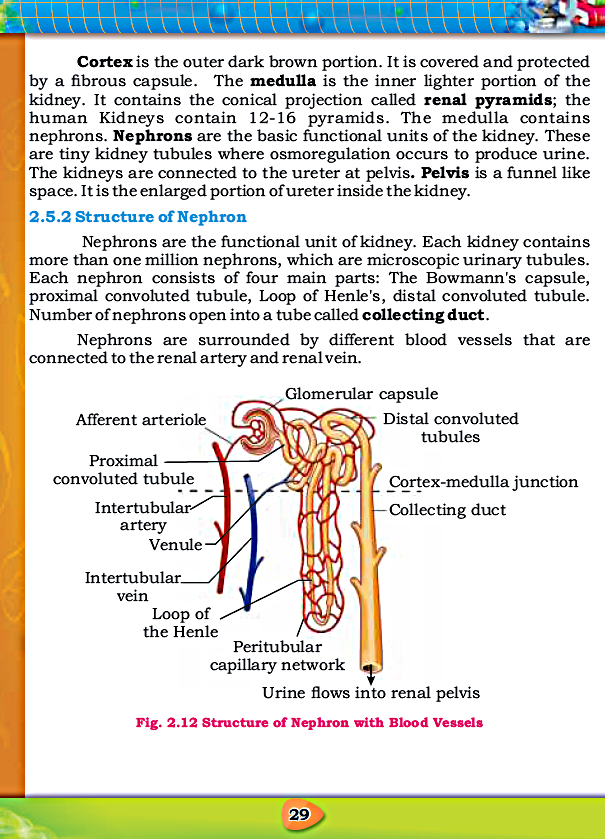
- Nephrons are functional unit of kidney.
- Urea is formed in liver and excreted from kidneys.
- Mixture of urea, creatinine, uric acid and water called urine.
- Kidney stone is a solid mass made of calcium oxalate or carbonate crystals.
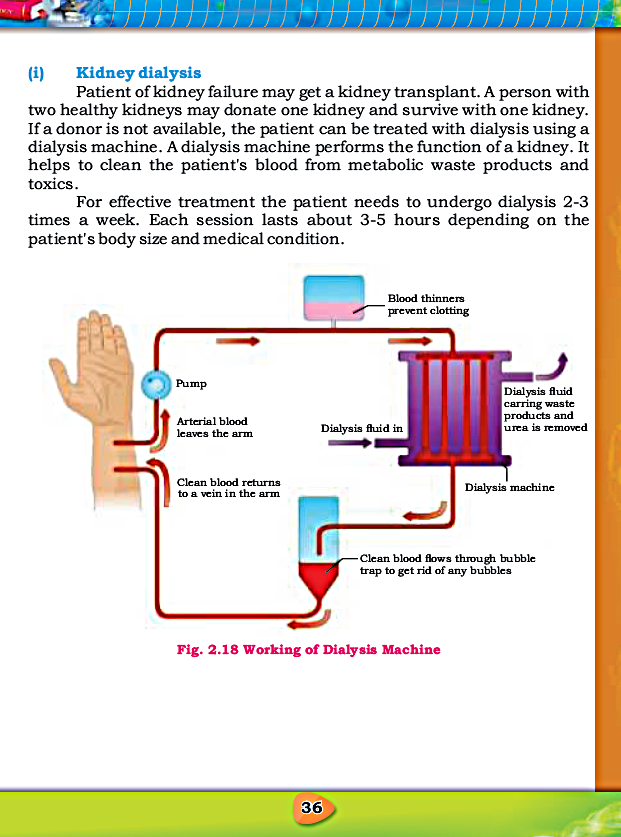
- Kidney failure patient can be treated with dialysis machine, dialysis machine performs the function of a kidney.
Biology For Class X - Chapter No. 1 - Gaseous Exchange - Multiple Choice Questions And Fill In The Blanks By Sir Saeed Sarang
GO TO INDEX
CHAPTER 1: GASEOUS EXCHANGE
Multiple Choice Questions And Fill In The Blanks
Special Thanks To Sir Saeed Sarang (Sindh Text Book Board)
Contact # 03023006727
Youtube Channel # Shafquat Ali YouTube
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Choose the correct answer:
i) The biological functions which perform gaseous exchange:
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Respiration
(c) Both a and b ✓
(d) Growth
ii) Plants do exchange of gases through:
(a) Roots
(b) Stomata
(c) Stem
(d) All of these ✓
iii) Each stoma is formed by:
(a) one guard cell
(b) two guards cells ✓
(c) three guard cells
(d) four guard cells
iv) Respiratory surface possesses following property:
(a) thin and wet
(b) permeable
(c) very large
(d) all of these ✓
v) Inspiration involves:
(a) Contraction of intercostals muscles
(b) contraction of diaphragm
(c) Inward movement of ribs
(d) Both a and b ✓
vi) Larynx is located on:
(a) Lungs
(b) Trachea ✓
(c) Bronchus
(d) Bronchiole
vii) The respiratory surface of human is:
(a) Nostril
(b) Bronchiole
(c) Alveoli ✓
(d) Trachea
viii) Increase in rate of breathing is due to the following:
(a) increase CO2 in blood ✓
(b) Increase O2 in blood
(c) decrease CO2 in blood
(d) decrease O2 in blood
ix) Which of the following disorder is associated with degeneration of alveoli?
(a) Bronchitis
(b) Lung cancer
(c) Asthma
(d) Emphysema ✓
x) Which of the following disorder is associated with inflammation of air passage ways?
(a) Bronchitis ✓
(b) Lung cancer
(c) Asthma
(d) Emphysema
11. Plants exchange gases for the processes of:
(a) photosynthesis
(b) respiration
(c) Both 'a' & 'b' ✓
(d) None of them
12. Carbon dioxide is taken in in the process of:
(a) respiration
(b) photosynthesis ✓
(c) inhalation
(d) All of them
13. Stomata are present in:
(a) leaves ✓
(b) stem
(c) roots
(d) lungs
14. These are microscopic opening present in the epidermis of leaves.
(a) Trachea
(a) Alveoli
(c) Guard cells
(d) Stomata ✓
15. The amount of molecular oxygen present in the air is about:
(a) 5%
(b) 12%
(c) 21% ✓
(d) 27%
16. The amount of molecular oxygen present n water is about:
(a) 5% ✓
(b) 12%
(c) 21%
(d) 27%
17. The total surface area of the respiratory surface in human is about:
(a) 10 times to the size of the body
(b) 20 times to the size of the body ✓
(c) 30 times to the size of the body
(d) 40 times to the size of the body
18. In humans, the process of respiration involves:
(a) breathing
(b) gaseous exchange
(c) cellular respiration
(d) All of these ✓
19. Each lung is soft spongy and:
(a) brownish in appearance
(b) reddish in appearance
(c) pinkish in appearance ✓
(d) black in appearance
20. It is wrapped in two Pleural membranes:
(a) Each lung ✓
(b) Each kidney
(c) Brain
(d) All of these
21. Ribs are attached with:
(a) diaphragm
(b) thorax
(c) trachea
(d) intercostal muscles ✓
22. In the lower part of the thorax, lies a sheet of muscles called:
(a) diaphragm ✓
(b) thorax
(c) trachea
(d) intercostal muscles
23. Each lung is made up of millions of:
(a) stoma
(b) bronchiole
(c) alveoli ✓
(d) trachea
24. The internal opening of nasal sacs opens into a long tube called:
(a) trachea ✓
(b) larynx
(c) bronchiole
(d) epiglottis
25. It contains vocal cords to produce sound:
(a) trachea
(b) larynx ✓
(c) bronchiole
(d) epiglottis
26. The opening of larynx is known as:
(a) trachea
(b) bronchiole
(c) epiglottis
(d) glottis ✓
27. The opening of larynx has a lid like cover called:
(a) larynx
(b) bronchiole
(c) epiglottis ✓
(d) glottis
28. Trachea in the center of the thorax bifurcates into wo smaller ducts, called:
(a) bronchi ✓
(b) epiglottis
(c) glottis
(d) bronchiole
29. Each bronchus have:
(a) T-shaped cartilaginous rings
(b) U-shaped cartilaginous rings
(c) O-shaped cartilaginous rings
(d) C-shaped cartilaginous rings ✓
30. Each bronchiole is a very thin tube that opens into:
(a) stoma
(b) epiglottis
(c) alveoli ✓
(d) bronchi
31. The process of breathing consists of:
(a) two phases ✓
(b) three phases
(c) four phases
(d) five phases
32. Lungs can be filled with a maximum amount of:
(a) 3 litres of air
(b) 5 litres of air ✓
(c) 6 litres of air
(d) 7 litres of air
33. we use normally about _____ of the air coming into the lungs.
(a) 1/2 litre ✓
(b) 1 litre
(c) 11/2 litre
(d) 2 litres
34. Expiration involves:
(a) relaxation of intercostal muscles
(b) relaxation of diaphragm
(c) inward movement of ribs
(d) All of these ✓
35. The gaseous exchange takes place at the level of alveoli. This gaseous exchange involves:
(a) osmosis
(b) diffusion ✓
(c) Both 'a' & 'b'
(d) None of these
36. It is regulated by the hypothalamus of our brain:
(a) Memory
(b) Thinking
(c) Breathing ✓
(d) Walking
37. In the following, the alveoli are infected so they may be filled with fluid or pus:
(a) Pneumonia ✓
(b) Bronchitis
(c) Emphysema
(d) Lung cancer
38. It is an allergic response to pollens, dust, smoke, fur, feathers and several other substances:
(a) pneumonia
(b) Bronchitis
(c) Emphysema
(d) Asthma ✓
Fill In The Blanks:
- Respiration and photosynthesis require exchange of gases.
- Respiration takes place in all living organisms.
- Photosynthesis occurs in green parts of plants.
- During respiration, oxygen is used and carbon dioxide is given out.
- In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is used and oxygen is given out.
- In terrestrial plants, most of the exchange of gases occurs through minute openings, stomata.
- The animals use either their body surface, or some internal surface for the exchange of gases.
- Respiratory surface must be thin, wet, permeable and large in relation to the volume of organism.
- The respiratory surface of man is alveoli present in lungs.
- Both lungs have millions of alveoli.
- Air passage ways lead the atmospheric air to alveoli.
- Air pollution causes number of respiratory problems.
- Clean air is essential for better respiratory health.
Tuesday 14 September 2021
Clothing And Textile (Ur) - Past Paper 2021 (MCQs Only) - For HSC Part 1 (Home Economics Group) - For Failure, Improvements, Additional Subjects...
GO TO INDEX
Clothing And Textile (Eng)
Past Paper 2021 (MCQs Only)
For HSC Part 1
(Home Economics Group)
For Failure, Improvements, Additional Subjects...
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)