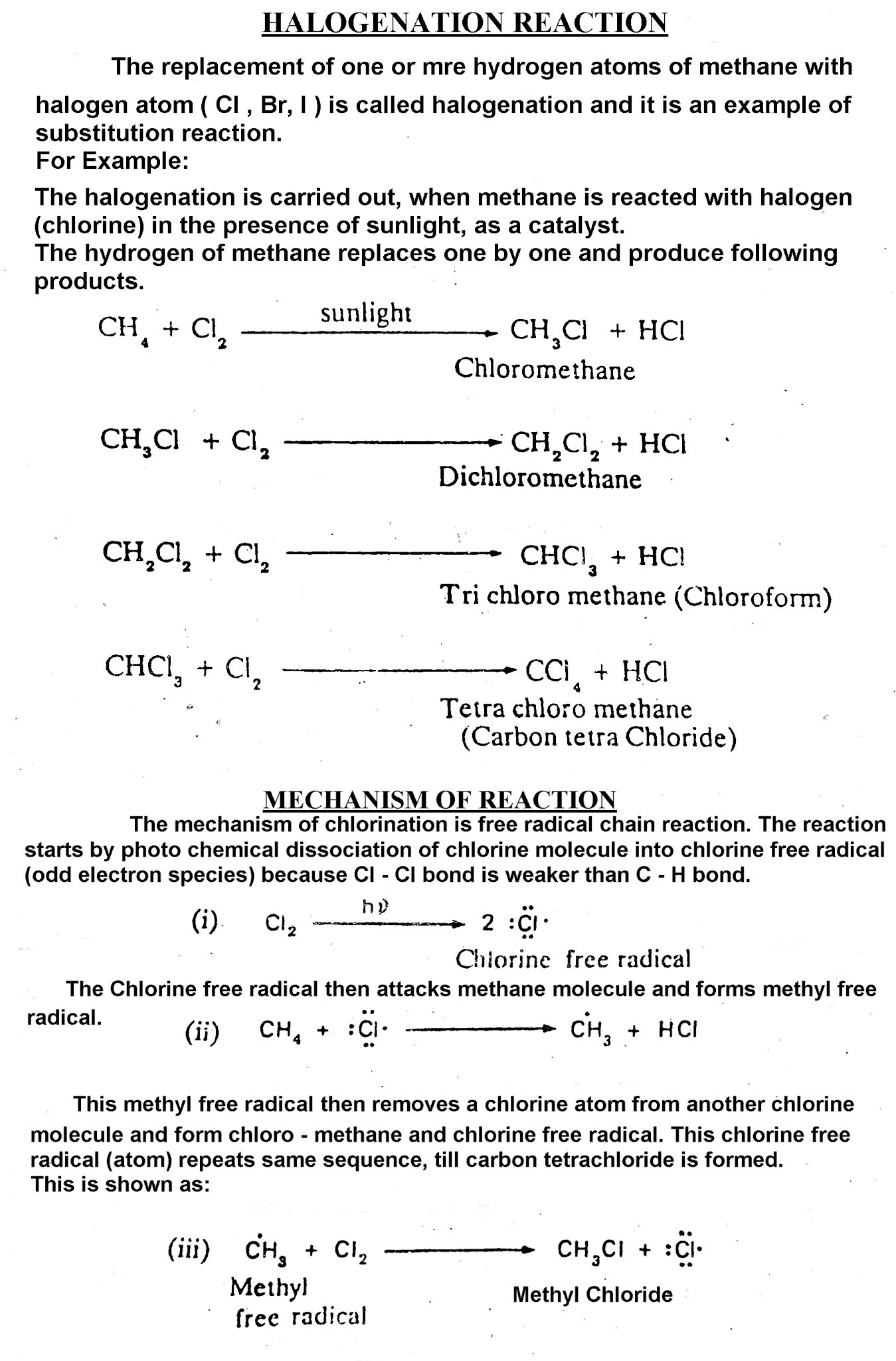
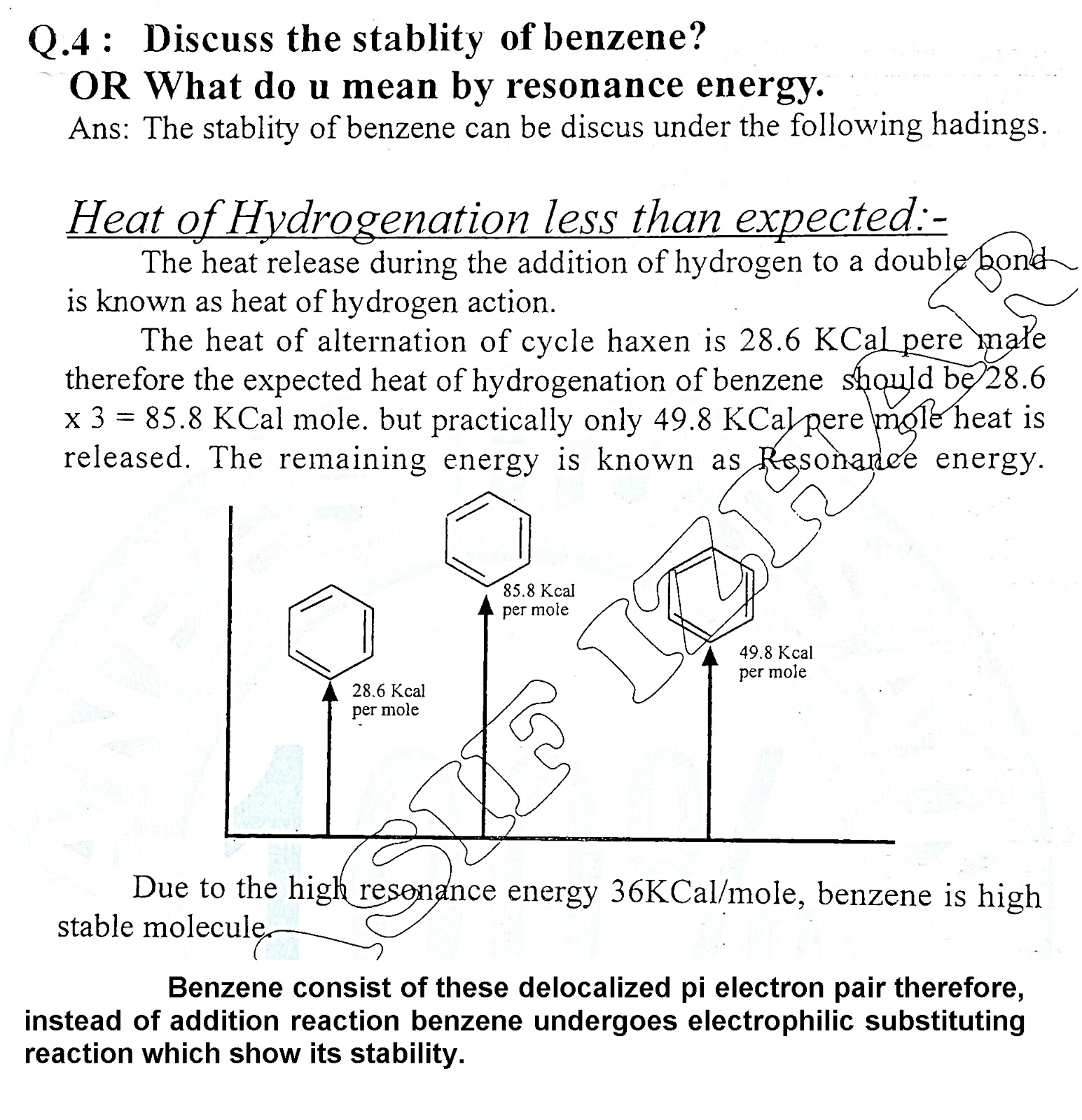
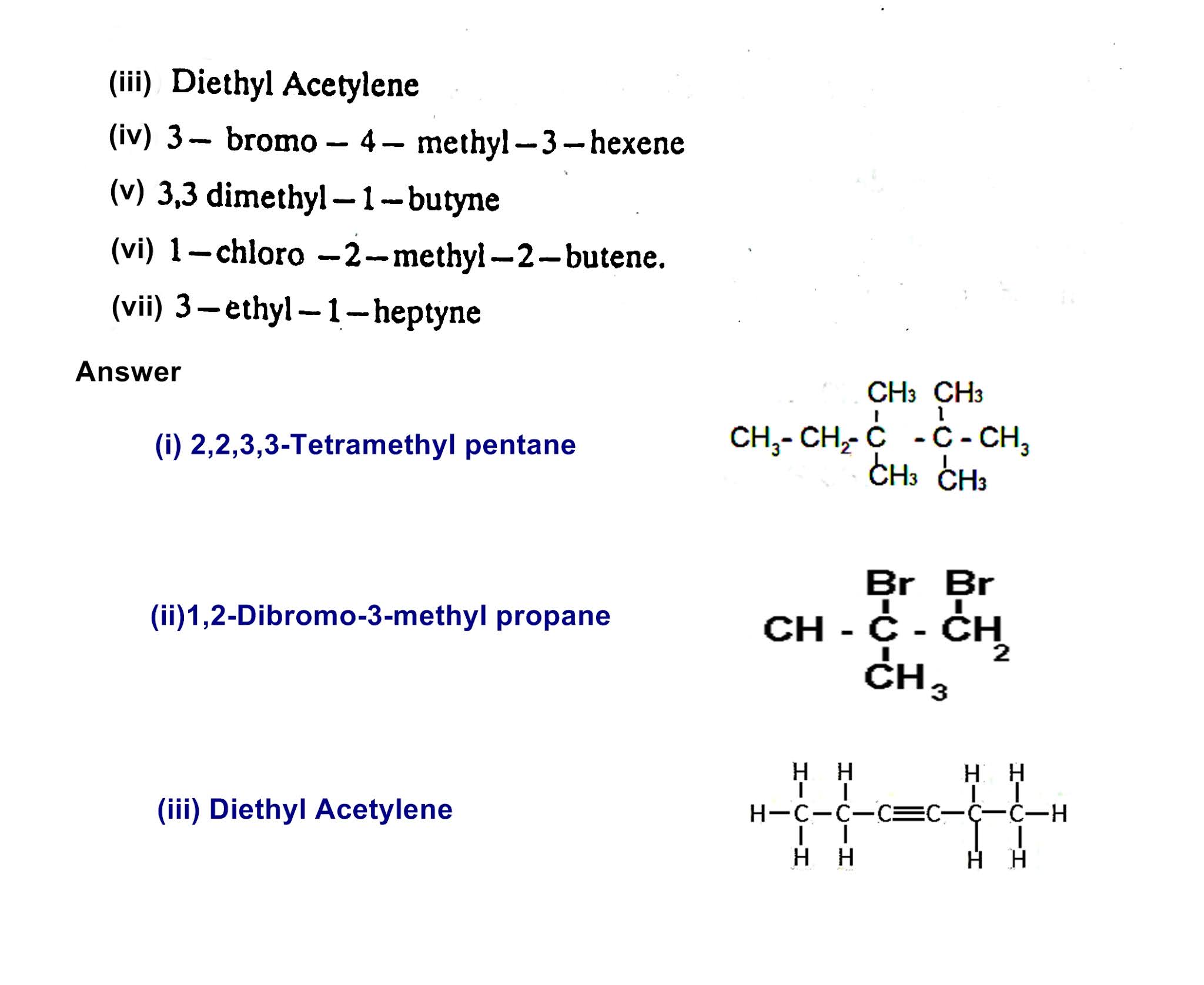
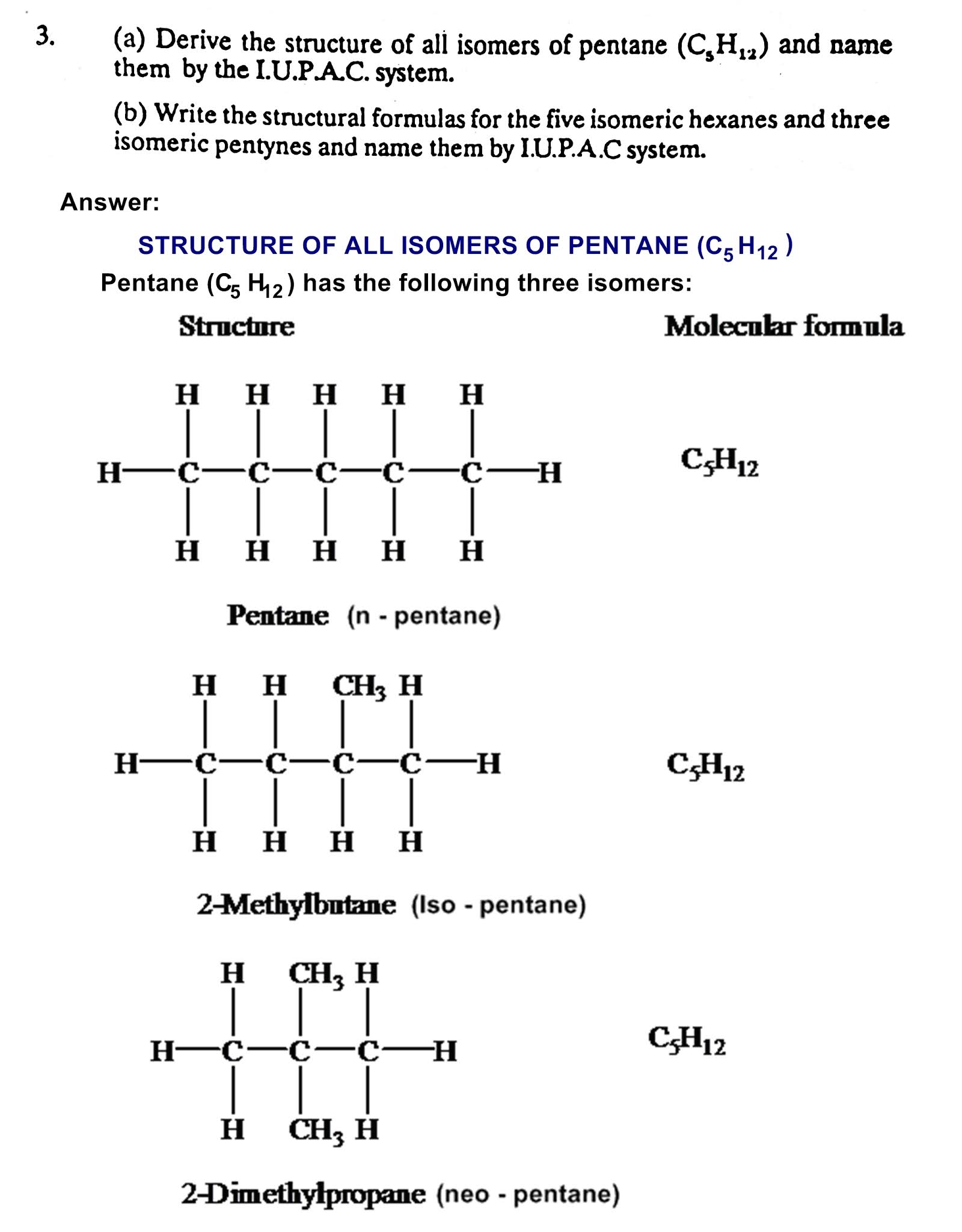
Active and Passive Voice
Definition Of Voice:
Voice is the form of the verb which indicates whether a person or a thing does something or something has been done to a person or a thing.OR
Voice is that form of a Verb which shows whether what is denoted by the Subject does something or has something done to it.Explanation:
Verb can be divided into two ways. that is
- (a) HELPING VERB: (is, am, are, was, were, been, being, shall be, will be)
(b) PRINCIPAL VERB: (eat, drink, see, play, go, run, ring, write. bark etc.) - (a) TRANSITIVE VERB: In transitive verb, action passes from the Subject (Doer) to the object. In other words, a transitive verb requires an object.
For example:- (i) You fly a kite. (ii) They play cricket. (iii) The cat killed a rat.
(b) INTRANSITIVE VERB: An intransitive verb does not require an object.
For example:- (i) I go to school. (ii) The dog barks. (iii)The sun shines.
But Intransitive Verb has no object: therefore, it has only one voice i.e. Active Voice.
Type Of Voice
1- Active Voice:
When a verb form shows that the subject (person or thing) has done something, or, in other words, is the doer of the action. it is known as Active Voice. The Active Voice is so called because the person denoted by the Subject acts.e.g.: I eat a mango
2- Passive Voice:
When a verb form shows that something has been done to the subject (person or thing) It is known as Passive Voice. The Passive Voice is so called because the person or thing denoted by the Subject is not active but passive, that is, suffers or receives some action.e.g: A mango is eaten by me.
Examples:
| S.No. | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Roma helps Harry. | Harry is helped by Roma. |
| 2. | Sam loves them. | They are loved by Sam. |
| 3. | The mason is building the wall. | The wall is being built by the mason. |
| 4. | The peon opened the gate. | The gate was opened by the peon. |
| 5. | Some boys were helping the wounded man. | The wounded man was being helped by some boys. |
| 6. | He will finish the work in a fortnight. | The work will be finished by him in a fortnight. |
| 7. | Who did this ? | By whom was this done? |
| 8. | Why did your brother write such a letter ? | Why was such a letter written by your brother ? |
RULES FOR CHANGING ACTIVE INTO PASSIVE VOICE
- A sentence can be separated into subject. verb and object.
e.g.: Nabeel(S) writes(V) a letter(O). - The object of the active voice must be turned into subject of the passive voice.
e.g.: A letter(S) is written(V) by Nabeel(O). - The 'be' form (is, am, are, was, were, be, being, been, etc.) must be used according to the tense of the verb and according to person and number of the noun in the subject position.
e.g.: A letter 'is' - Past participle of the verb must be used. (Principal verb will be change to its 3rd form)
e.g.: A letter is written. ( write changes to written) - Preposition 'by' must be added.
e.g.: A letter is written by - The subject of the active voice becomes the object of the passive voice.
e.g.: A letter is written by Nabeel.
Subject in Active Voive Object in Passive Voice Name of person or thing e.g Nabeel Name of person or thing e.g Nabeel I by me We by us You by you He by him She by her They by them
- A transitive verb is sometimes followed by numbers of objects In such cases, the sentence may have two positive forms. e.g.:
Active Voice: The principal granted him the permission.
Passive Voice: The permission was granted to him by the principal.
Passive Voice: He was granted the permission by the principal.
- Certain verbs are always followed by prepositions. So a preposition after the verb must be retained in Passive Voice. e.g.:
Active Voice: He laughed at her.
Passive Voice: She was laughed at by him. - Some ideas like commands/orders/requests may be expressed in Passive voice. e.g:
1. Please post these letters. (Active)
You are requested to post these letters. (Passive)
2. Close the door. (Active)
You are ordered to close the door. (Passive)
- Imperative sentences: (Sentences which have no subject and are expressed in order form):
Imperative sentences are of two type:
(i) "Do it" (Affirmative) and
(ii)(Don't do it" (Negative)
They can be turned into Passive Voice by using 'let'. - Formula: Let +Object + Be + Verb (Past Participle)
e.g.:
1. Post this letter. (Active)
Let the letter be posted. (Passive)
2. Close the door. (Active)
Let the door be closed. (Passive)
3. Help the poor. (Active)
Let the poor be helped. (Passive)
4. Don't do it again (Active)
Let it not be done again. (Passive) - Passive with Modal Auxiliaries: Modal auxiliaries or simple modals are 'will, would, shall, should, can, could, may, might, must, have to, has to, had to, ought to, had better etc.
Pattern: Modals + be + Verb (past participle)
Example:
Active Voice: She can type the letters.
Passive Voice: The letters can be typed by her.
Active Voice: They should not do it.
Passive Voice: It should not be done by them. - We can omit the agent (the subject of the active voice) in the passive voice if it is a pronoun or it is unimportant)
- A few verbs in Passive Voice we followed by a number of prepositions. In such cases, 'by' is not used.
A B C I. Astonished at 9. Disgusted with 17. Pleased with 2. Annoyed at 10. Disappointed at 18. Rejoiced at 3. Agitated at I I. Displeased at 19. Satisfied with 4. Amazed at 12. Ground in 20. Thronged with 5. Alarmed at 13.Interested at 21. Surprised at 6. Contained in 14. Killed with 22. Vexed at 7. Covered with 15. Lined with 8. Crowded with 16. Overgrown with
Active and Passive Voice Conversion Step By Step
| Active Voice Nabeel writes a letter. Subject + Verb + Object | Passive Voice A letter(1) is(4) written(3) by Nabeel(2) | Steps change according to.... | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple | Continuous | Perfect | 1: object become subject | ||
| PRESENT | Singular | is am -(I) | is being am being -(I) | has been | Nabeel - by Nabeel I - by me We - by us You - by you He - by him She - by she It - by it They - by them X - By X |
| Plural | are | are being | have been | ||
| PAST | Singular | was | was being | had been | |
| Plural | were | were being | |||
| FUTURE | 1st Person | shall be | There is no passive voice form for future continuous tense | shall have been | 3: Verb's past participle |
| 2nd & 3rd person | will be | will have been | 4: Find a) tense b) number c) person | ||
Some other patterns are given here:
(a) For WH-Questions
1. Active Voice: Who teaches you French?Passive Voice: By whom are you taught French?
OR
By whom French is taught to you?2. Active Voice: Who taught you English?
Passive Voice: By whom were you taught tnglish?
OR
By whom English was taught to you?3. Active Voice: Who has done it?
Passive Voice: By whom has it been done?
(b)Passive Sentences With Two Objectives
- Rewriting an active sentence with two objects in passive voice means that one of the two objects becomes the subject, the other one remains an object.
- When there are two objects after a verb, the first object is usually an indirect object or a pronoun and the second object is a direct object or a noun.
- The subject of passive voice is often the indirect object.
- Active Voice: He made her fool.
Passive Voice: She was made fool by him. - Active Voice: He gave me a present.
Passive Voice: I was given a present by him.
| Subject | Verb | Object 1 | Object 2 | |
| Active | Raja | wrote | a letter | to me |
| Passive | A letter | was written | to me | by Raja |
| Passive | I | was written | a letter | by Raja |
(c) Passive without subject
We use passive voice when:(i) We don't know the agent.
(ii) We don't want to mention the agent.
(If a passive sentence does not indicate the subject, someone or somebody may be added to it or whatever is best suited.)
Pattern: to be (form) + V (past participle)
1. A song is sung. (Passive)
Someone sings a song. (Active)
2. Letters were written (Passive)
Someone wrote letters (Active)
3. The thief is caught. (Passive)
The Policeman catches the thief. (Active)
4. This book has been studied. (Passive)
Students have studied this book. (Active)
5. By whom has it been done? (Passive)
Who has done it? (Active)
6. I have to write a letter. (Passive)
A letter has to be written by me. (Active)
7. The matter has to be solved. (Passive)
Somebody has to solve the matter. (Active)
(d) PERSONAL PASSIVE
- People know that he is a good swimmer.
- They say that Farhat is in hospital.
- They think that the children are in bed.
- People believe that the robber has worked in the bank.
- People believe that nuclear power stations are dangerous.
- His colleagues thought that he was on holiday.
- People know that cars pollute the environment.
- They suppose that the new product will came out soon.
- They found that the mission was impossible.
- They believe that she will win a gold medal.
Active / Passive Transformation
According to Tenses
According to Tenses
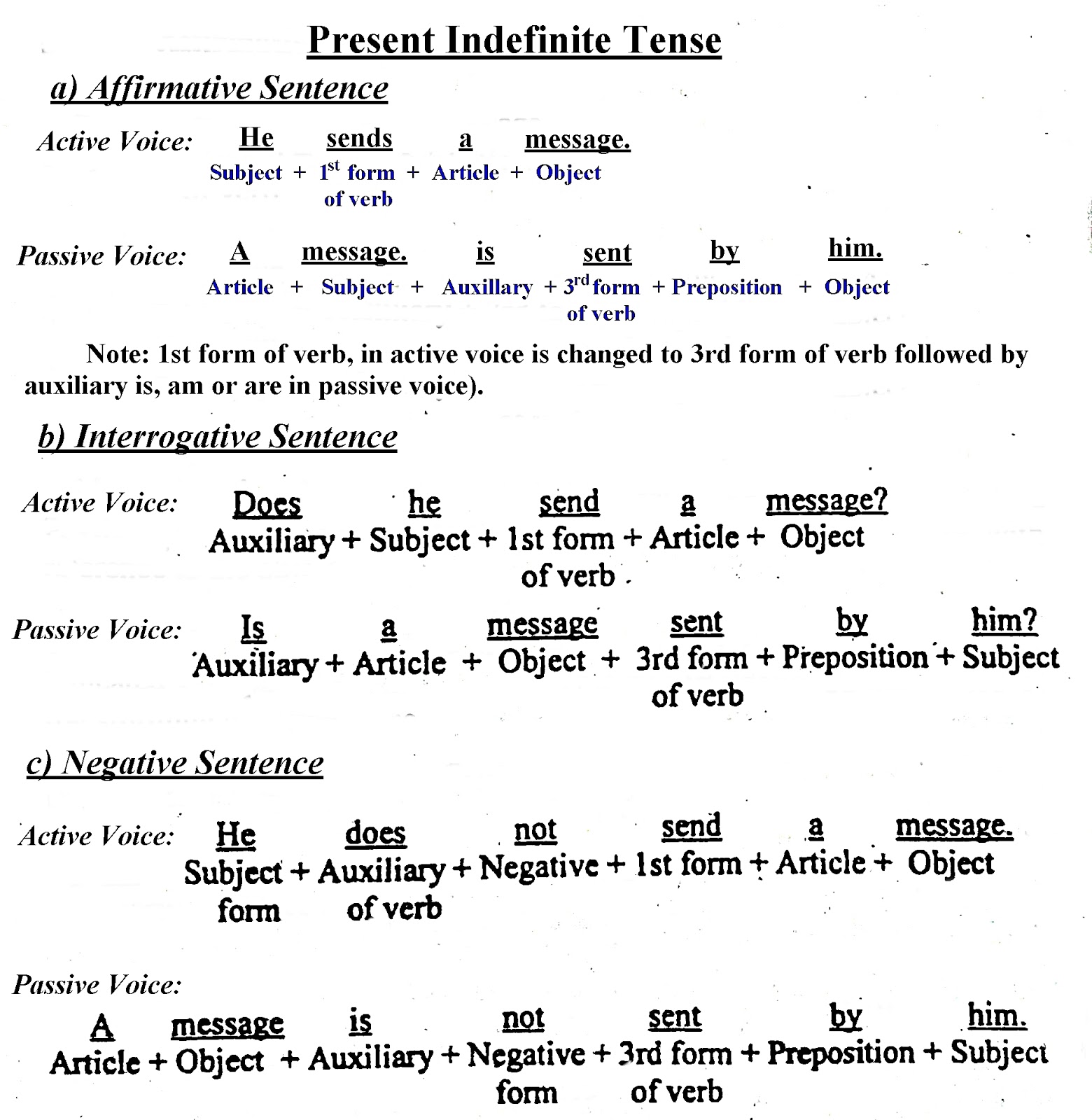
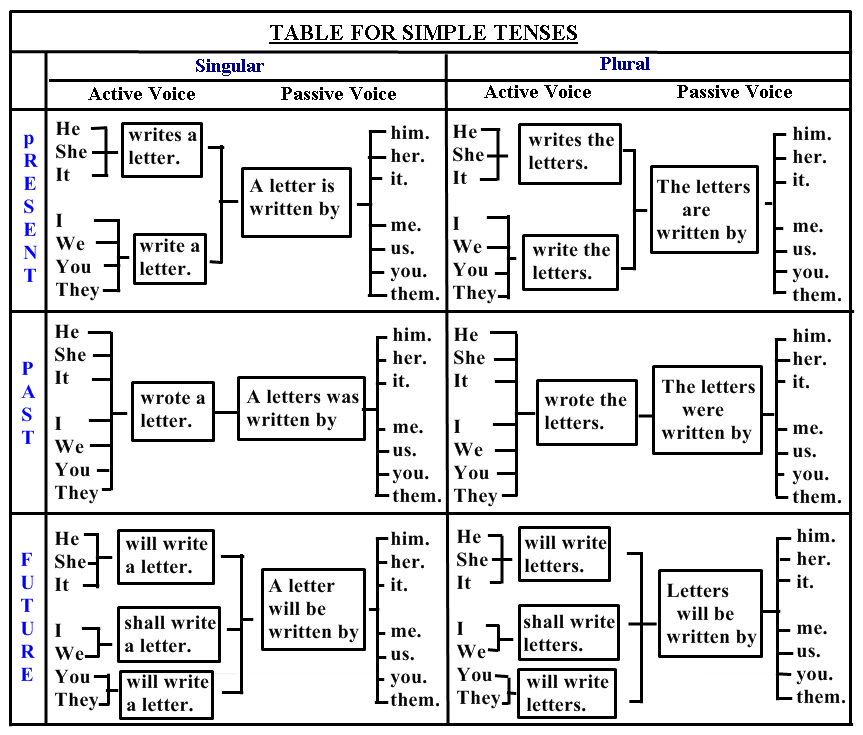
SIMPLE / INDEFINITE TENSE
Passive Voice Of Present Indefinite Tense
Active Voice: I write essays. {I(S) write(V) essays(O)}Passive Voice: Essays are written by me.
Note:
- There are 3 forms of "be" (is / are / am) in the present.
- We use them according to the subject of passive voice.
| Type Of Sentence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | He takes a catch. | A catch is taken by him. |
| Negative | She does not like tea. | Tea is not liked by her. |
| Interrogative | Do you love books? | Are books loved by you? |
| WH- Question | Who knows it? | By whom is it known? Or Who is it known by? |
Passive Voice Of Past Indefinite Tense
Note:There are two forms of 'be' (was / were) in the past. We use them according to the subject of passive voice.
| Type Of Sentence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | He dug a hole. | A hole was dug by him. |
| Negative | We did not do it. | It was not done by us. |
| Interrogative | Did you love books? | Were books loved by you? |
| WH- Question | What caused the explosion? | What was the explosion caused by? |
Passive Voice Of Future Indefinite Tense
Note: We use them 'be' in the future tense of the passive voice.
| Type Of Sentence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | The police will catch the thief. | The thief will be caught by the police. |
| Negative | We will not do it. | It will not be done by us. |
| Interrogative | Will you not help her? | Will she not be helped by you? |
| WH- Question | How will you do it? | What will it be done by you? |
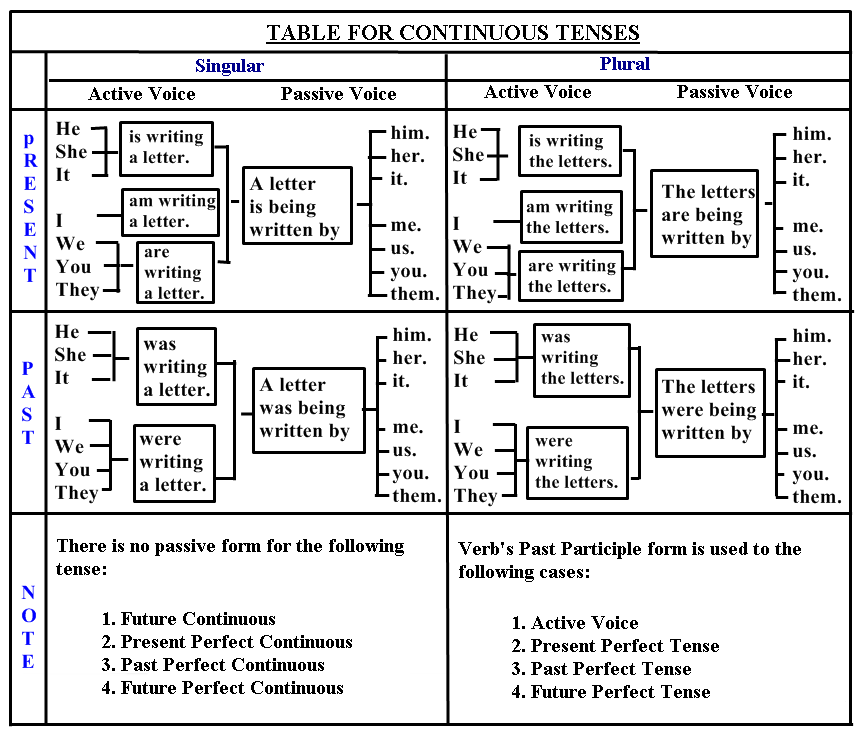
Passive Voice Of Present Continuous Tense
Note:- Here we add "being" after the form 'be' (is / am/ are) and before the verb.
- Remove 'ing' from the verb and change it into past participle.
- The form of 'be' (if am) than change it into (is / are ) according to the subject.
| Type Of Sentence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | I am writing letters. | Letters are being written by me. |
| Negative | He is not helping us. | We are not being helped by him. |
| Interrogative | are you not helping her? | Is she not be helped by you? |
| WH- Question | What is troubling you? | What are you being troubled by? |
Passive Voice Of Past Continuous Tense
Note:- Here we add "being" after the form 'be' (was / were) and before the verb.
- Remove 'ing' from the verb and change it into past participle.
| Type Of Sentence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | I was watching a play on TV. | A play was being watched on TV by me. |
| Negative | He was not helping us. | We were not being helped by him. |
| Interrogative | Were you doing homework? | Was homework being done by you? |
| WH- Question | Who was teasing you? | By whom were you being teased? Or Who were you being teased by? |
Note : In Past Continuous Tense "I was" is correct and "I were" is wrong.
Passive voice is made for only two continuous tenses (i) Present Continuous and (ii) Past Continuous.
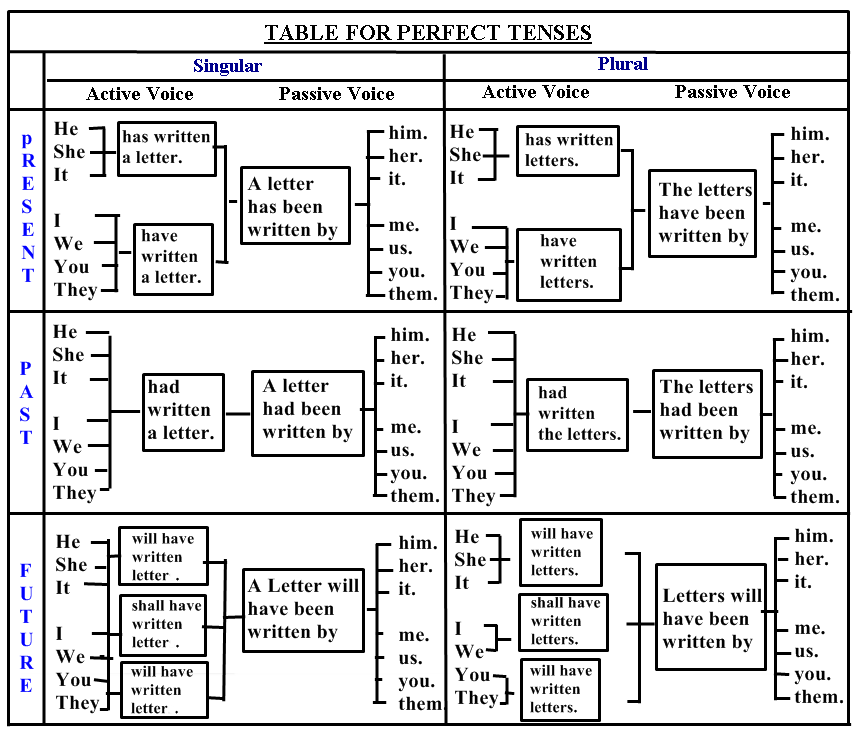
Passive Voice Of Present Perfect Tense
Note:Here we add "been" after has or have and before the verb (past participle).
| Type Of Sentence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | I Have seen this film. | This film has been seen by me. |
| Negative | He has not helped us. | We have not been helped by him. |
| Interrogative | Have you got the visa? | Has the visa been got by you? |
| WH- Question | Who has done it? | By whom has it been done? Or Who has it been done by? |
Passive Voice Of Past Perfect Tense
Note:Here we add "been" after had and before the verb (past participle).
| Type Of Sentence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | She had visited Paris. | Paris had been visited by her. |
| Negative | He had not helped us. | We had not been helped by him. |
| Interrogative | Had you got the visa? | Had the visa been got by you? |
| WH- Question | Who had eaten my food? | By whom had my food been
eaten? Or Who had my food been eaten by? |
Passive Voice Of Future Perfect Tense
Note:Here we add "been" after will have and before the verb (past participle).
| Type Of Sentence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | We will have completed the lesson by tomorrow. | The lesson will have been completed by tomorrow by us. |
| Negative | He will not have helped us. | We will not have been helped by him. |
| Interrogative | Will he have learnt this lesson in a week? | Will this lesson have been learnt in a week by him? |
| WH- Question | Who will have eaten my food? | By whom will have my food been eaten? Or Who will have my food been eaten by? |