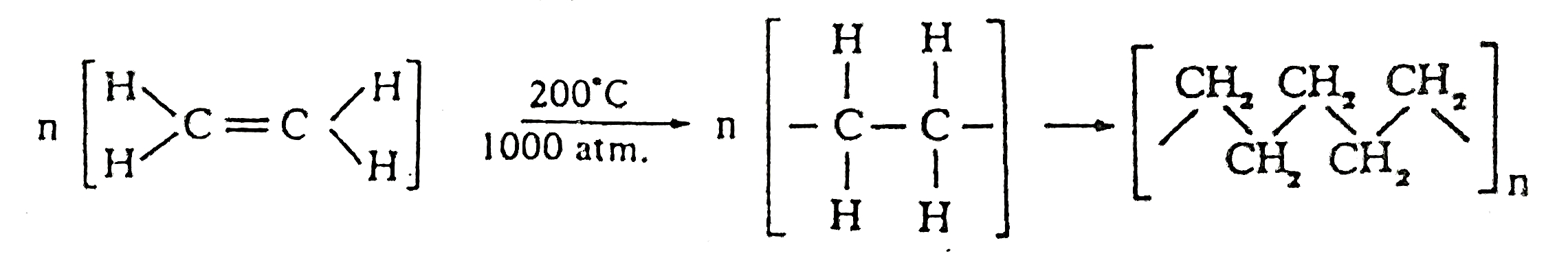Go To Index
Chapter No.11
Chemical Industries In Pakistan
Questions And Answers
Content
- Fertilizers
- Detergents
- Glass
- Rayon (Fibre)
- Plastic
- Paints
Q.1: What is a fertilizer? Give names and uses of some of the fertilizers.
FERTILIZER:
"Fertilizers are the substances which contain elements essential for the plant growth and which are introduced into the soil to obtain increased amount of crop regularity."Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium containing salts are specially important for the plants.
OR
"Fertilizers are commonly inorganic salts and containing elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium etc, which are very essential for the growth and development of plants. The yield of agricultural crops can be increased by introducing fertilizers to the soil."NEED OR USES OF FERTILIZERS:
Fertilizers stimulate the process of metabolism is the plant cells. The need of fertilizers are due to three reasons.
- To make up the deficiency of elements (like N, P, K) and become fertile again.
- To give an additional supply of food.
- To maintain pH of the soil near neutrality or slightly alkalinity i.e from pH 7 to 8. The soil having pH above 10 or below 3 is sterile.
CLASSIFICATION OF FERTILIZERS:
There are two types of fertilizers, depending upon the source and chemical nature:
- Natural or Organic Fertilizers
- Synthetic or Mineral Fertilizers
NATURAL OR ORGANIC FERTILIZERS:
These are derived from Plant and animals and may be organic or inorganic. They includes manures and peats for e.g
- Plant matter like oil cakes of cotton seed meal.
- Animal manure and peats like cow dung, sheep dung, and human excretion.
- Animal matter like ground fish and other animal products.
- Example of inorganic natural fertilizers are rock phosphate and Chillie salt peter etc.
Uses: Natural fertilizers provide more nutrient than synthetic fertilizers.
SYNTHETIC OR MINERAL FERTILIZERS:
Mineral fertilizers are obtained from mineral raw materials. These are preferred on natural fertilizers because they contain exact percentage of elements (e.g. Nitrogen and Phosphorus) as required for an specific crop. They are also called artificial fertilizers.
The important mineral fertilizers are:
a) Nitrogen Fertilizers:
Fertilizers containing nitrogen as essential elements are called "Nitrogenous Fertilizers". These fertilizers are Water soluble. Important nitrogen fertilizers are given below:
- Urea (NH2 - CO - NH2): It contains 46% nitrogen.
- Ammonia NH3: It has 82 % nitrogen.
- Ammonium Nitrates (NH4NO3): It has 33 % nitrogen and is an ideal nitrogen fertilizer.
- Ammonium Sulphate {(NH4)2SO4}: It is a favored fertilizer because it is less hydroscopic and can be handled safely. It contain only 21% nitrogen.
Importance or Uses of Nitrogen:
- It is necessary in the early stage for the rapid growth of plants.
- It is main constituent of proteins.
- It imparts green color to the leaves.
- It increase the yield and quality of plants.
- These help in the developments of root leaves and stem.
b) Potassic Fertilizers:
Fertilizers containing potassium as essential element are called "Potassic Fertilizers", such as:
- Chile saltpeter or Potassium Nitrate, KNO3.
- Potassium Sulphate K2SO4.
Importance or Uses of Potassium:
- It provides potassium to the plant or soil.
- It is required in the formation of starch, sugar and fibrous material.
- It resist plant diseases.
- It makes plant strong by making root healthy.
- It helps in ripening of seeds, fruits and cereals.
c) Phosphatic Fertilizers:
Fertilizers containing phosphorous as essential element are called "Phosphatic Fertilizers." The raw material for these fertilizers is phosphate rock or phosphorite, [Ca3(PO4)2]3CaF3, which being water insoluble can not be assimilated directly by the plants. Therefore it should he converted into soluble form before it can be taken in through the roots. The important phosphorus fertilizers are given below:
- Super Phosphates:
The mixture of calcium hydrogen phosphate Ca(H2.PO4)2 and gypsum or calcium sulphate (CaSO4) is called super phosphate. It contain 18-20% phosphorous in the form of assimilable P2O5, and also called phosphate of lime.
It is obtained by mixing phosphorite with sulphuric acid in special chambers. Following reaction takes place:
- Triple phosphate:
It is also a good phosphorus fertilizer and prepared by the reaction of phosphorite rock with phosphoric acid.Ca3(PO4)2 + 4H3PO4 ⟶ 3Ca(H2PO4)2
Importance or Uses of Phosphorus:
- It provides phosphorous to the plant soil.
- It stimulates the early growth and development of plants.
- It accelerates the seed and fruit formation processes.
- It also resist plant against diseases and frost.
SCOPE OF FERTILIZERS IN PAKISTAN:
Pakistan is an agricultural country It does not only prepare fertilizers of its own demand but also exports in a bulk.
INDUSTRIES IN PAKISTAN:
The important fertilizer factories of Pakistan are enlisted below:-
- TSF Plant and urea fertilizer plant, Hazara.
- Faisalabad Fertilizer Ltd.
- Pak American Fertilizer Ltd. at Daud Khel.
- Single Super Phosphate Plant at Jaran Wala.
- Natural Gas Fertilizer Factory, Multan.
- Dawood Urea Plant, Lahore.
- Dhariala Potash Fertilizer Project, Dhariala.
- Fauji Urea Complex, Sadiqabad.
- Exxon Fertilizer Co. Dahrki.
- Urea Plant, Mirpur Mathelo.
Q.2: What is a detergent? Describe the cleaning action of detergent.
DETERGENTS:
"Detergents are complex organic salts with a long carbon chain and defined as Sodium or potassium salt of alkyl or aryl sulphonated acid."Detergents are soapless cleansing agents. They react with the ions of the salts that cause hard water, thereby producing soluble compounds in which dirt and grease are readily carried away.
Structure:
All the detergents have the same basic structure. They are made up of two parts:- Hydrophobic (Water repelling group):
Hydrophobic part is the long hydro carbon chain which is covalently bonded. Being nonpolar in nature, it attracts oil and grease which are also nonpolar. - Hydrophilic (Water loving or attracting group):
Hydrophilic part is small ionic group like sulphonate (SO3-1 ), sulphate (-O-SO3-2 ), quaternary ammonium groups (NR4+1 ) or hydroxyl groups (-OH-1 ).
Difference between Soap and Detergent
| S.NO. | SOAPS | DETERGENTS |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Calcium and magnesium salts are insoluble in water. | Calcium and magnesium salts are soluble in water. |
| 2. | Hydrophilic part contains long chain of carboxyl group (C00-). | Hydrophilic part contains sulphonate (SO3-1 ), sulphate (-O-SO3-2 ), quaternary ammonium groups (NR4+1 ) or hydroxyl groups (-OH-1 ) etc. |
| 3. | Hydrocarbon chain of hydrophobic part can be broken down by bacteria. | Hydrocarbon chain of hydrophobic part cannot be broken down by bacteria. |
| 4. | It can be obtained by the natural resources | They are the synthetic materials. |
| 5. | They produces scum in hard water | Hard water do not effect its cleansing. |
| 6. | Examples are Lux, Palmolive, Capri etc. | Examples are Surf, Arial, Lquid handwash etc. |
Cleansing Action Of Detergents:
Remove Oil Or Grease stains:A detergent removes dirt very easily. The presence of two groups (hydrophobic and hydrophilic) allows the mixing of water with non-polar substances such as oil and grease. Grease is an organic covalent compound. The hydrophobic part of the detergents readily dissolves in grease (both being non-polar). The hydrophilic part of the detergent dissolves in water (both being polar) so that slight agitation removes the grease and it is carried away with the water along with dirt.
Merits Of Detergents:
The calcium and magnesium salts of detergent are soluble in hard water whereas corresponding salts of soaps are insoluble and reduces the foaming and cleansing action. This means that a detergent can be used in hard water and resulting products are soluble. Therefore, there is no wastage in the shape of scum (Precipitate).Demerits Of Detergents:
One disadvantage of detergent over soap is that hydrocarbon chain, unlike those of soaps which are derived from food substances (fats and oils) cannot be broken down by bacteria and dispersed. Therefore, bacteria remains in water.Scope In Pakistan:
Pakistan has developed a large detergent industry. These detergent are used as washing powder and washing liquids and sold under various brand names.Examples: Brite, Surf etc.
Q.3: What do you know about glass ? Describe in detail.
GLASS
"Glass is one of the most important artificial silicates. Glass is a super cooled liquid i.e. a solid solution without crystallization. The molecules are arranged in random position that's why a glass does not show sharp melting point."Preparation:
Ordinary soft glass or soda glass is a mixture of sodium silicate (Na2SiO3) and calcium silicate (CaSiO3). It is produced by heating sand, soda (Na2CO3) or sodium sulphate and lime stone (CaCO3) in a furnace at 1400°C.Na2CO3 (s) + SiO2 (s) ⟶ Na2SiO3 (s) + CO2 (g)
CaCO3 (s) + Si02 (s) ⟶ CaSiO3 (s) + CO2 (g)
OR
Na2CO3 + CaCO3 + 6SiO2 ⟶ 2CO2 + Na2O.Ca0.6SiO2
Where Na2O.Ca0.6SiO2 is glass.Properties:
- Glass is not a true solid because molecules are not arranged in a definite pattern.
- It is a super cooled liquid i.e a solid solution without crystallization.
- The molecules of glass are arranged in random position as in case of liquids that's why a glass does not have sharp melting point.
- On heating it gradually becomes more and more plastic in nature.
- Glass is attacked by hydrofluoric acid. This acid is used to make designs on glass. This process is called etching.
Types of Glass:
There are several types of glass:- Ordinary window glass:
is a mixture of sodium and calcium silicates. It is manufactured from sand, soda and lime-stone. It is further classified as:
a. Common Glass: It is used in making bottles.
b. Soda Glass: It is fusible and also called soft glass. It is expensive type of glass. We can use these type of glasses in bottles, windows and glass sheets.
c. Water Glass: It is a thick liquid and used as adhesive in paper as fire proofing.
d. Quartz Glass: It is used in making dishes, tubes etc. It resist heat upto 1000 °C. - Refractory potassium glass:
is obtained by using potash K2CO3 instead of soda. This is used for making chemical glass ware. - Pyrex glass:
is a borosilicate mixture which is produced by using boron oxide place of some of silica; this glass can withstand sudden changes of temperature. Pyrex glass is used in manufacturing of apparatus in laboratory. In fact pyrex glass has a very low coefficient of expansion i.e it expands greatly when heated. Pyrex glass is not manufactured in Pakistan. - Crystal Glass:
It is prepared by silica, lead oxide (PbO), Potassium carbonate and CaCO3. It is very expensive and a heavy glass. It is used in decorative show pieces. - Coloured glass:
is manufactured by adding certain transition metal oxides in ordinary glass. For example CuO gives light blue, CoO dark blue and Cr203 green. Addition of selenium oxide and zinc oxide gives red coloured glass.
Position Of Glass Industries In Pakistan:
In Pakistan there are about 25 glass Industries which arc producing about 75.000 tons of glass per year. Now a days, there Is definite improvement in the quality of glass.The names of some of the glass producing factories are:
- Indus Glass Work. Hyderabad.
- Toyo Nasik Glass Factory, Lahore.
- Khawaja Glass Works, KPK.
Q.4: Write short note on synthetic fibers.
FIBRE:
There are two types of fibres:1. Natural Fibre:
Silk is a natural fibre obtained by silk worm.
Synthetic Or Artificial Fibre:
Synthetic fibres are the man made polymers which consist of macro-molecules (Poly = many; macros = parts).
Preparation:
The polymers are built by linking together of many smaller units called monomers. This process is called polymerization. Synthetic fibres are usually prepared by condensation polymerization in which linking of two different substances occurs with the elimination of water. The resulting polymers are known as copolymers.
Examples:
The examples of important synthetic or artificial or man-made fibres are Nylon, Rayon, Dacron,Terylene etc.
Advantages:
Among the advantages of synthetic fibers are:
- Lightness of weight
- Ease of ironing
- Softness and
- Heat retention or heat conductivity.
Position Of Synthetic Fibre Industries in Pakistan:
The manufacture of synthetic fibers is one of the branches of the chemical industry that has been developing at a very fast rate in our country.
Govt. of Pakistan is taking all the measures to increase the production of all kinds of artificial and synthetic fibers in the coming years. A number of industries have been established to manufacture synthetic fibers.
1. RAYON (FIBRE):
"Rayon is synthetic cellulose fibre and is considered as the man-made fibre. It has soft silky appearance and commonly use as silk apparels."A French scientist "Chardonnet". discovered it in 1884, while he was investigating the silk worm disease.
Preparation:
Rayon is a fibre obtained mechanically from silk worms. The starting material is cellulose. The silk worm on mulberry tree eats cellulose, digests it and changes it into silk which comes out in a viscous form and solidifies on contact with air and becomes silk thread. Man does the same with cellulose, when preparing silk mechanically.
Preparation Of Viscose Rayon:
is manufactured from cellulose when it is digested with sodium hydroxide solution. When carbon disulphide is passed through the solution, a mixture of sodium cellulose xanthate is formed which is soluble in NaOH.
Due to very high viscosity, the silk thus obtained is called viscose rayon. The solution is forced through a spinneret into H2SO4 bath where cellulose is precipitated as fine threads. This artificial silk is cheaper than cellulose acetate silk or nitrocellulose silk. It is produced in the largest quantity.
Q.5: How nylon is prepared and state its characteristics?
2. NYLON:
(The name come from New York and London)"It is a synthetic fibre and developed for the production of stackings and other wearing apparel. It was introduced to public at New York worlds fair 1939."
Nylon is the type of polymer in which amide linkages (-CONH-) hold the chain together. Chemical structure of nylon is not similar to that of material silk but resembles it to certain extent.
Preparation:
Nylon is made of diamines and dibasic acids which can be synthesized from the common raw materials i.e coal, water and air.
Adipic acid (hexan dioic acid) when heated with hexamethylene diamine under nitrogen at 200 °C. a polymerization process occurs to give hexamethylene di-ammonium adipore commonly known as Nylon-6,6. The name Nylon-6,6 is also derived from the fact that both the components consist of six carbon atoms each.
Elimination of water forms the amide linkage. This is the same type of linkage found in proteins.
Merits:
1. It is stronger than other natural fiber.
2. It has good flexible tenacity
Uses:
It is mostly used:
- for stacking and other wearing apparel.
- to make fibre for clothing and carpeting.
- to make filaments for fishing lines and ropes.
- to make bristles for brushes tires.
- to make parachute fabrics.
- to make moulded objects such as gear and bearings.
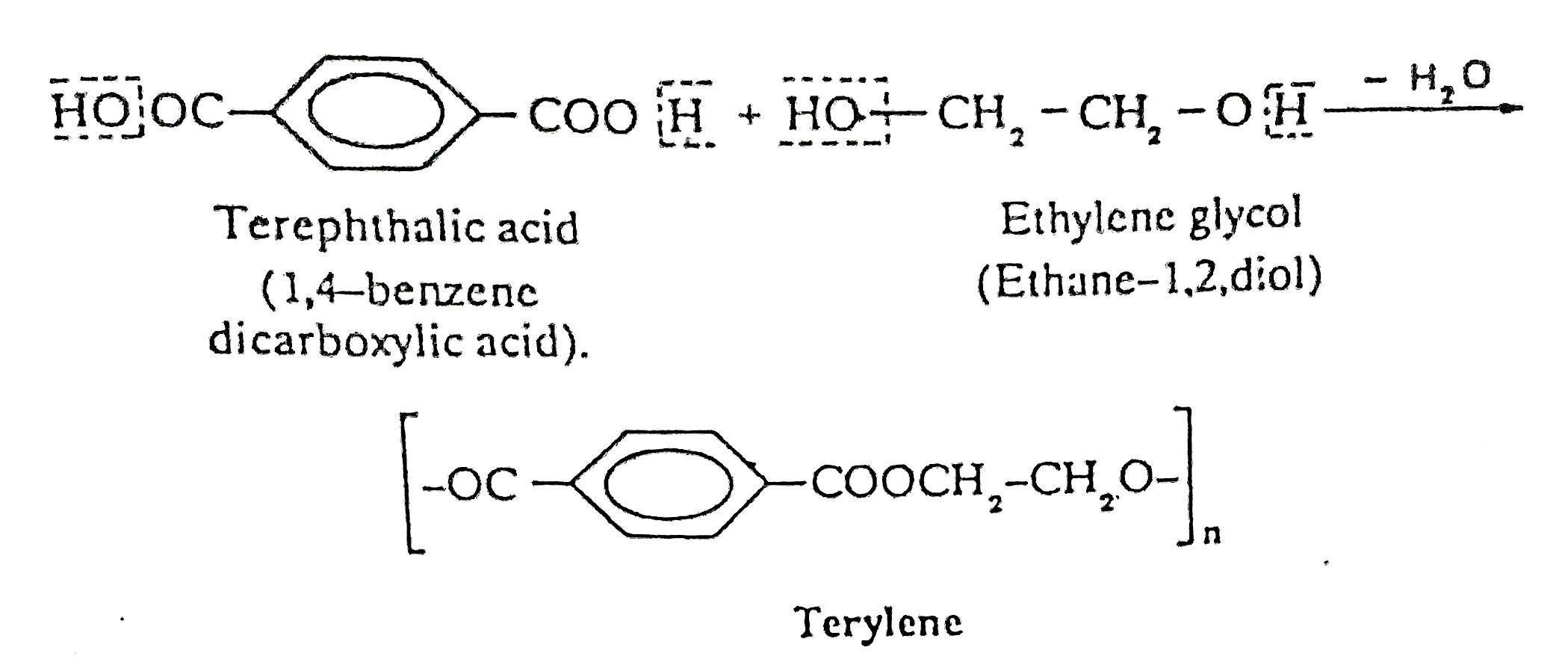
TERYLENE:
Terylene is the most important polyester fabric which is formed from many ester molecules. It is a synthetic fibre.Preparation:
It is obtained by heating ethylene glycol and tereph-thalic acid at 300 °C in the presence of metal oxide. During condensation polymerization, water molecule is eliminated giving rise to ester linkage.
It is commonly called Dacron or Polyester.
Uses:
Terylene is mainly used:
- in making bottles and sheets.
- in making clothing and fishing lines.
- in water tanks.
Q.6: What do you know about plastics?
PLASTICS:
These are synthetic polymers and physically solid material which contract on heat and then cast into moulds.Physical State: These are macromolecules, formed by addition or the condensation polymerization of simple, organic molecules. In other words, plastics are also polymers formed from monomers.
For example: polyethylene or polypropylene
Common Plastics:
1. Polyethylene Or Polyethene:
Ethylene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon polymerized in presence of suitable catalysts at 200 °C and 1000 atmospheric pressure. The extra bond opens, forming an unstable molecule which joins with many others of its own kind to form macro molecules called polyethylene or Polyethene.
n = degree of polymerization. (here n= 600 to 1000)
Uses:
Polyethylene is the most common plastic used:
- to form polythene bags and to package foods.
- in making bottles and pots.
2. Poly propylene:
It is superior to polyethylene in its resistance to breakage and to temperature. Polypropylene is prepared by addition polymerization of propene at 200 °C and 1000 atmospheric pressure.
Uses:
Polypropylene is the most common plastic used:
- to form polythene bags and to package foods.
- in making bottles and pots.
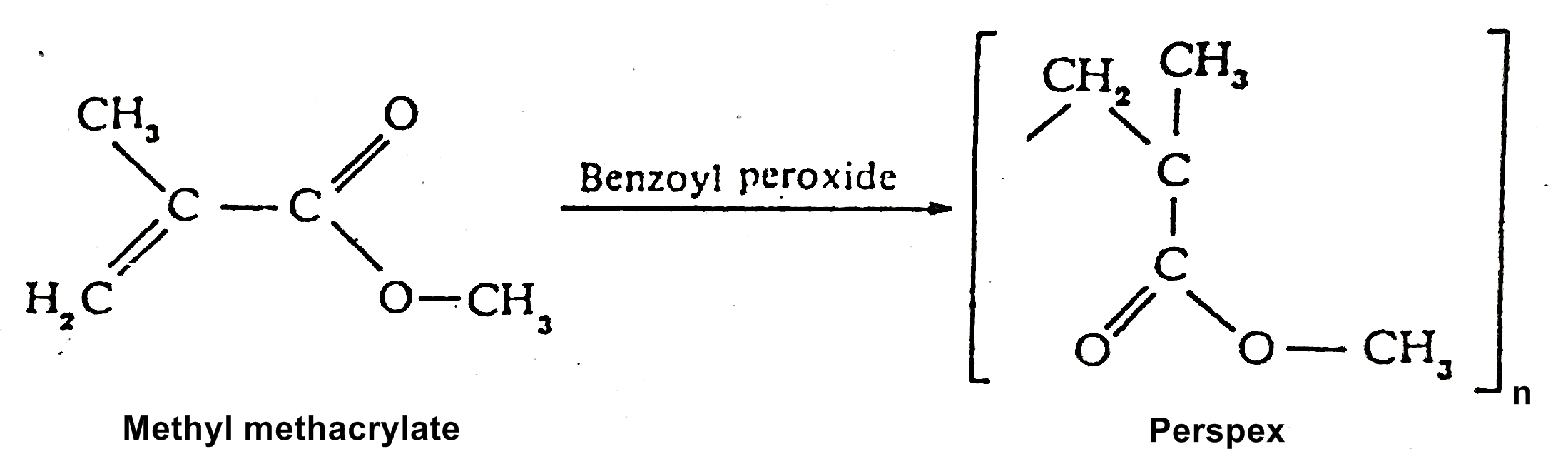
3. Perspex Or Transparent Plastic:
It is a polymer of (or prepared by addition polymerization) of methyl methacrylate, an ester of an unsaturated acid.
Glass like transparency and resistance to weathering make it useful as a glass substitute.
Uses:
The transparent plastic or perspex is used to make:
- combs and hair brushes
- in aircraft windows
- reflectors on auto vehicles
- T.V guard screens and
- Street light fittings.
4. PVC or Poly vinyl chloride:
It is the polymer of vinyl chloride (CH2 = CHCl).
Preparation:
In the presence of catalyst hydrogen peroxide at the temperature of 80°C, vinyl chloride polymerizes to poly vinyl chloride.
Uses:
PVC is used:
- for the insulating., covering for electrical cables
- for the manufacture of gramophone records, suit-case coverings etc.
- for making imitation leather.
- for making floor covering
- for making rubber like texture
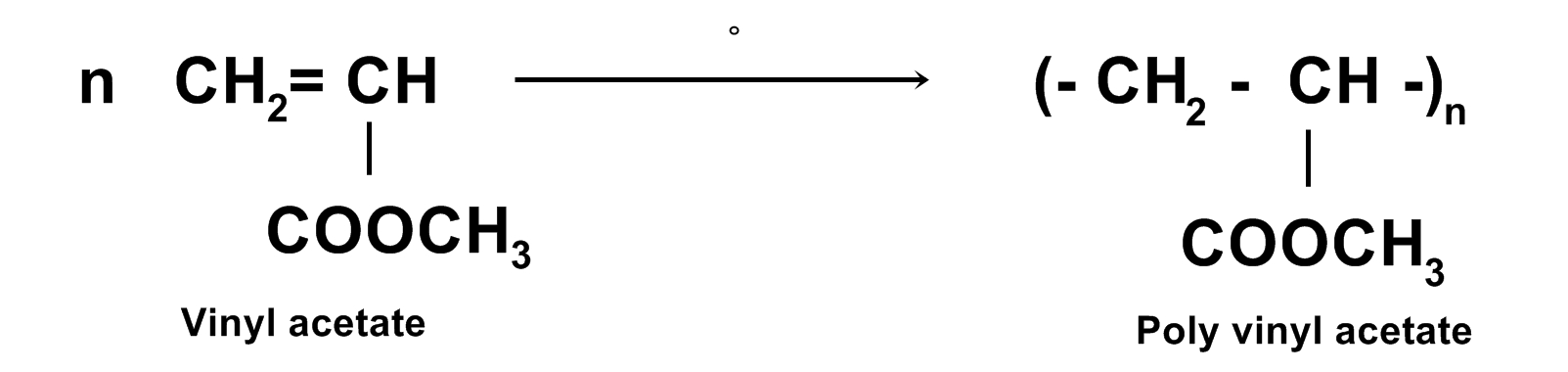
5. PVA or (Poly vinyl acetate):
It is the polymer of vinyl acetate (CH2 = CHO.CO.CH3).
Uses:
It is used:
- as an adhesive material
- as a binder for emulsion paints
- in the manufacture of chewing gum
- in the water proofing industries and in the textiles industries.
6. Bakelite:
It is a polymer of phenol and formaldehyde.
Uses:
Bakelite is used to make:
- buttons, switches, electrical boards
- cameras, radio and
- telephone components.
Components Of Plastics:
Plastics entirely consist of high molecular compounds (polymers).To produce specific properties, various compositions are used by mixing the polymer with the following substances.
1. Plasticizers:
Addition of plasticizer reduces the brittleness and improve the elasticity of plastics. They are organic substances in nature. One disadvantage of artificial plasticization is an increase in the rigidity and loss of elasticity when solvent evaporates.
2. Fillers: Usually increase the mechanical strength of plastics and resistance to fire. It also make the savings of the more costly polymer. Various fillers which are used are wood flour, saw dust.
3. Stabilizers:
It is antioxidant and prevent the chemical degradation of plastic.
4. Pigments:
These are used to color the plastic.
Properties Of Plastic:
- Plastics are generally tough, resistant to the action of acids and alkalis and not very much affected by the change of temperature.
- The plastics have a fair range of deformability and mouldability due to which articles of any desired shape and form can be manufactured.
Plastic Industry in Pakistan:
Plastic industry in Pakistan essentially consists of moulding of plastic powders into various articles of daily use. Modern plastics are assuming an ever increasing importance in our economy.
Types Of Plastic:
Plastics are of two types:
- Thermoplastic
- Thermosetting
is a material which softens on heating and hardens on cooling. This process of heating, softening, moulding and cooling can be repeated and it does not affect the properties of plastics. Such plastics are easily moulded into shapes but are not very heat resistant.
Examples:
The examples are:
- nitro cellulose
- cellulose acetate and
- vinyl polymers.
(ii) Thermosetting plastics:
are those materials which can be heated only once before they set i.e they can not be reworked. In other words, thermosetting plastics do not soften on reheating.
Examples:
The examples are:
- phenol formaldehyde or Bakelite
- urea formaldehyde
- silicones etc.
Q.7: Write short notes on:
(i) Paints
(ii) Varnishes
PAINTS:
Paints may be defined as liquid products which held in suspension solid colouring matter known as pigments, so blended that such mixture can be applied evenly to a surface for protective and decorative purposes.OR
The material used to coat over metals (iron articles) to prevent them from corrosion or rusting, and the walls, doors, windows, etc. for the decorative and protective purposes are called "paints".Components Of Paint:
Paints can be formulated with fantastic variety of colours, textures and resistances. A paint is usually composed of three components:-
- BINDER (Drying Oil):
i) A binder which hardens to form a continuous film on a surface.
ii) It suspends or adhere coloring particles (pigments) in paints.
iii) It is also known as vehicle.
iv) In an oil-based paint, linseed oil is often used as a binder. - PIGMENT:
i) A pigment which supplies the desired colour and opacity to the paint..
ii) These are finely powdered materials and insoluble in organic solvents.
iii) They protect against weather and provide impermeability to moisture.
iv) The pigment may be Titanium dioxide, TiO2 (White), Carbon black (C), Chrome yellow (PbCr02), oxides of iron (brown or red) or organic dyes of various colours. - VOLATILE SOLVENT (Thinner):
i) A volatile solvent which evaporates after application.
ii) It decreases the viscosity of paints.
iii) The solvent is usually turpentine, a mixture of hydrocarbons obtained from pine trees. - DRIERS:
They accelerate the drying of film and make it hard. - EXTENDER:
i) These are low refractive index inorganic material.
ii) They are used to reduce the cost of paint. - STABILIZER:
They stabilize the film and prevent its composition.
Classification Or Types Of Paints:
1. Oil - based Paints:
In an Oil - based paint, Linseed oil is often used as a binder. The solvent is volatile with some pigments as dispersed medium.
2. Water Based Paints:
In Water based paint (Emulsions) a synthetic polymer with rubber like properties is used as the binder. These "Latex" paints are emulsified in water to give a variety of spreading characteristics.
e.g: resin in water, distempers are water - based paints which are consists of pigments compounded with water and adhesive Zinc oxide casein.
3. Latex Paints:
Among the plastics used in latex paints are polyvinyl acetate, polymethyl methacrylate, polystyrene, styrene - butadiene copolymers and polytetrafluoro ethylene (Teflon).
4. Varnish:
Varnish is a mixture of resins, a volatile organic solvent such as ether, and a drying oil such as linseed oil. when it is applied on a surface, forms tough, solid, durable and a glossy film
Paint industry in Pakistan:-
A number of multinational companies are involved in the preparation of paints of various kinds.
Names of some of industries in Pakistan are given below:
- Berger Robbialac, Karachi.
- I.C.I. Dulux, Lahore.
- Buxly's paints, Karachi.
- Nelson paints, Karachi
VARNISH:
Varnish is a mixture of resins, a volatile organic solvent such as ether, and a drying oil such as linseed oil. when it is applied on a surface, forms tough, solid, durable and a glossy film.Preparation:
Resin is dissolved in a volatile organic solvent and then a drying oil is added when varnish is obtained.
Method OF Varnish Making And Applying:
- A varnish contains a mixture of resins, a volatile organic solvent drying oils.
- The drying oils (linseed oil) consist of esters of highly unsaturated acids containing two or more double bonds.
- When it is applied on a surface, It exposed to air and absorbs oxygen.
- The volatile organic solvent evaporates quickly.
- It dried up forming tough solid water insoluble film on the surface.
- The glossy appearance is due to the presence of resin.
Q.8: Why white lead has been banned as pigment for paints. Give reason?
White lead having approximate composition [Pb(OH)2 . 2PbCO3] was once extensively used, but it has now been banned for interior use due to high toxicity of lead. Infant illnesses have been attributed to the ingestion of chips of old lead paint.
Q.9: What is the difference between a manure and a fertilizer?
Ans: Difference between a Manure and fertilizers:
| S.NO. | Manure | Fertilizers |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manure is a natural substances. They are also known as organic fertilizers. | Fertilizer is a human-made or natural substances. They are known as minerals fertilizers. |
| 2. | It is obtained by decaying plant and animal waste | They are obtained from mineral raw materials |
| 3. | Manures are not very rich in essential plant nutrients | Fertilizers are rich in plant nutrient like nitrogen, phosphorous or potassium. |
| 4. | Manure provide a lot of humus to the soil. | Fertilizers does not provide any humus to the soil. |
| 5. | They can be prepared in the fields | They are prepared in factories. |
| 6. | Manure can applied to the soil to enhance its fertility | They can be applied to the soil to improve its fertility and increase the productivity. |