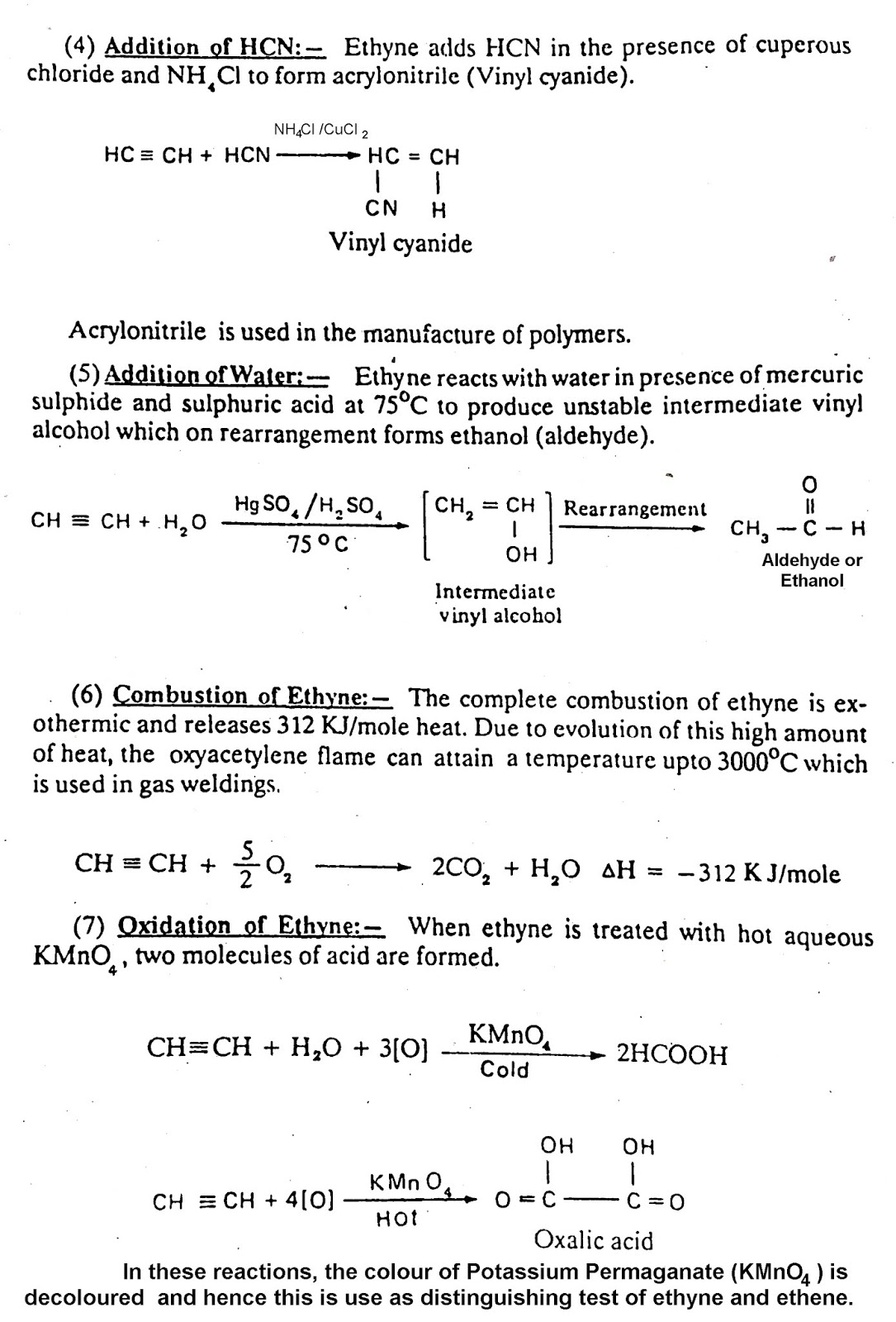
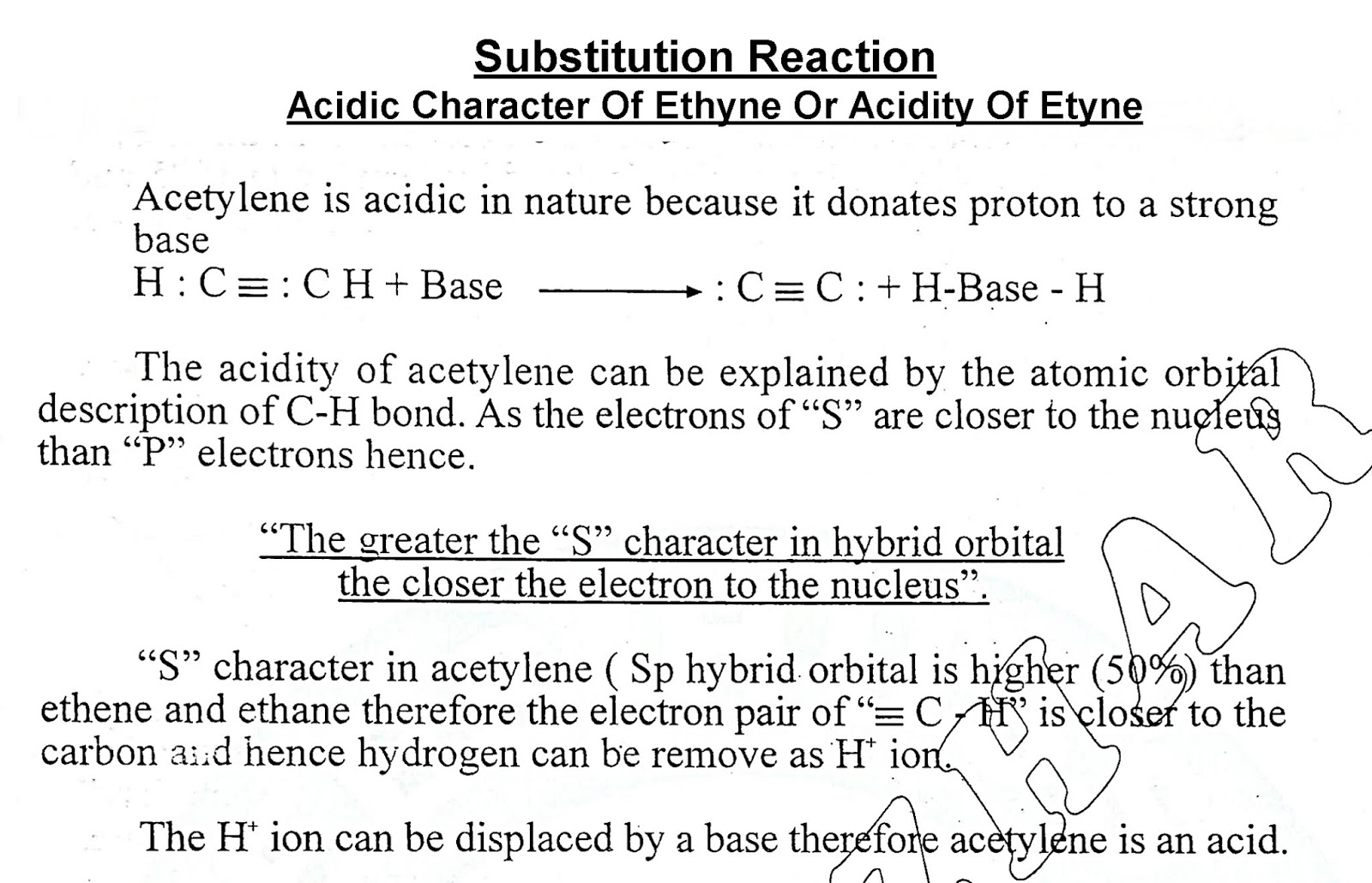
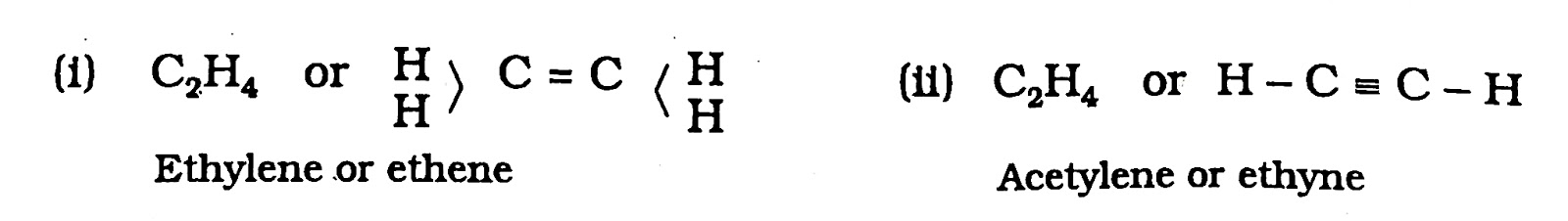Search This Blog
Monday 29 June 2020
Friday 26 June 2020
Tuesday 23 June 2020
Chemistry For HSC Part 2 - Chapter No.7 - Hydrocarbons (Questions And Answers)
Go To Index
Chapter No.7
Chemistry Of Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons (Questions And Answers)
Hydrocarbons
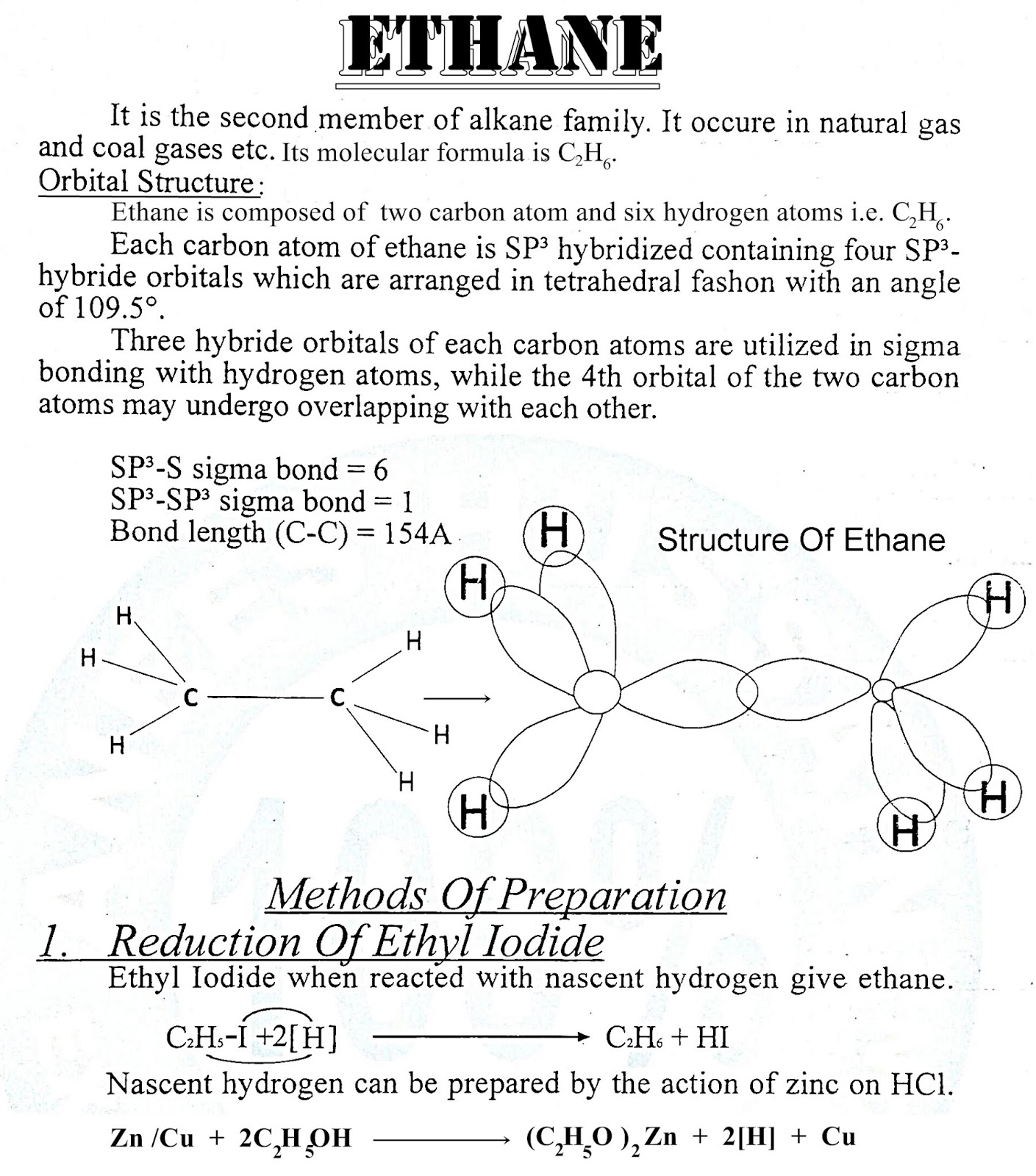
HYDROCARBONS:
"Organic compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only are called "Hydrocarbons".On the basis of structure and bonding, hydrocarbons are divided into two main classes:
- Aliphatic Hydrocarbon
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon
1. ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONS OR OPEN CHAIN AND CLOSED CHAIN HYDROCARBONS:
- These were so named because of the fact that first compounds of this class to be studies were fatty acid (Greek : aliphos = fat).
- It is a fundamental class of organic compounds and deals with alkanes, alkene and their cyclic analogs.
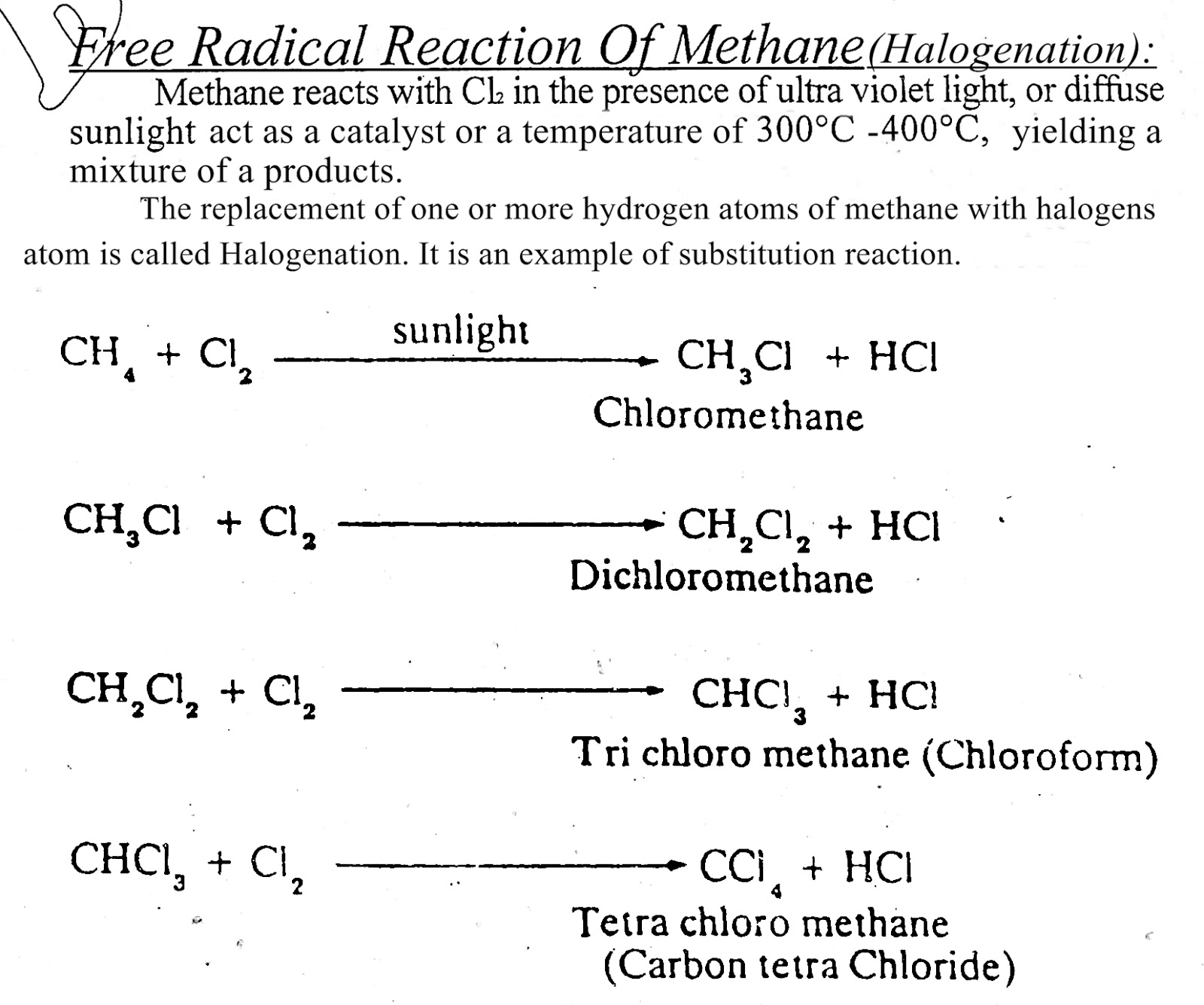
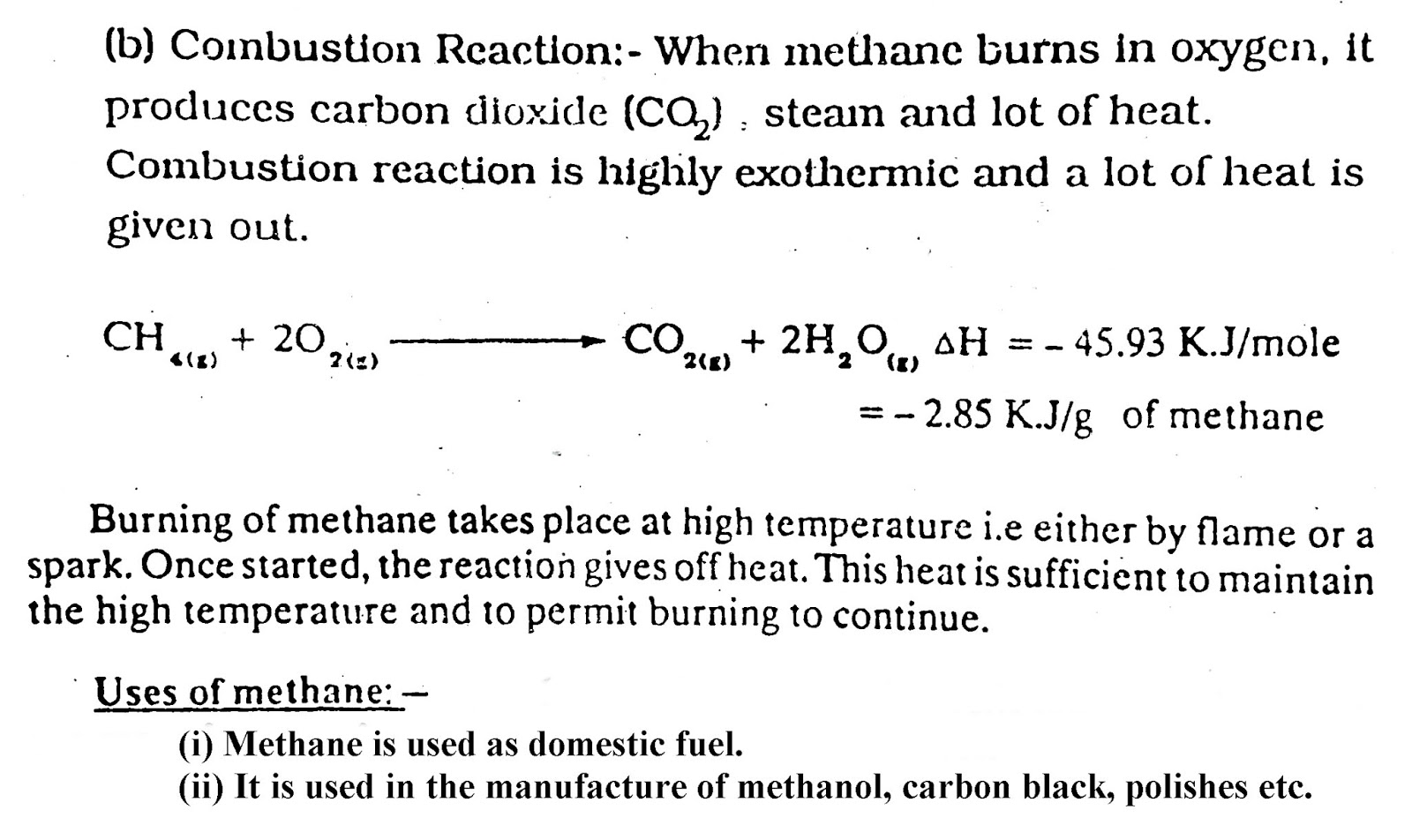
- These compounds under go chiefly addition and free radical substitutions.
- In aliphatic hydrocarbons, the carbon atoms are attached to another carbon to form chains.
- These chains may be either open or closed (rings) chains.
A. Open Chain Hydrocarbons:
The open chains hydrocarbons, on the basis of saturation of valence are classified as
- saturated and
- unsaturated hydrocarbons.
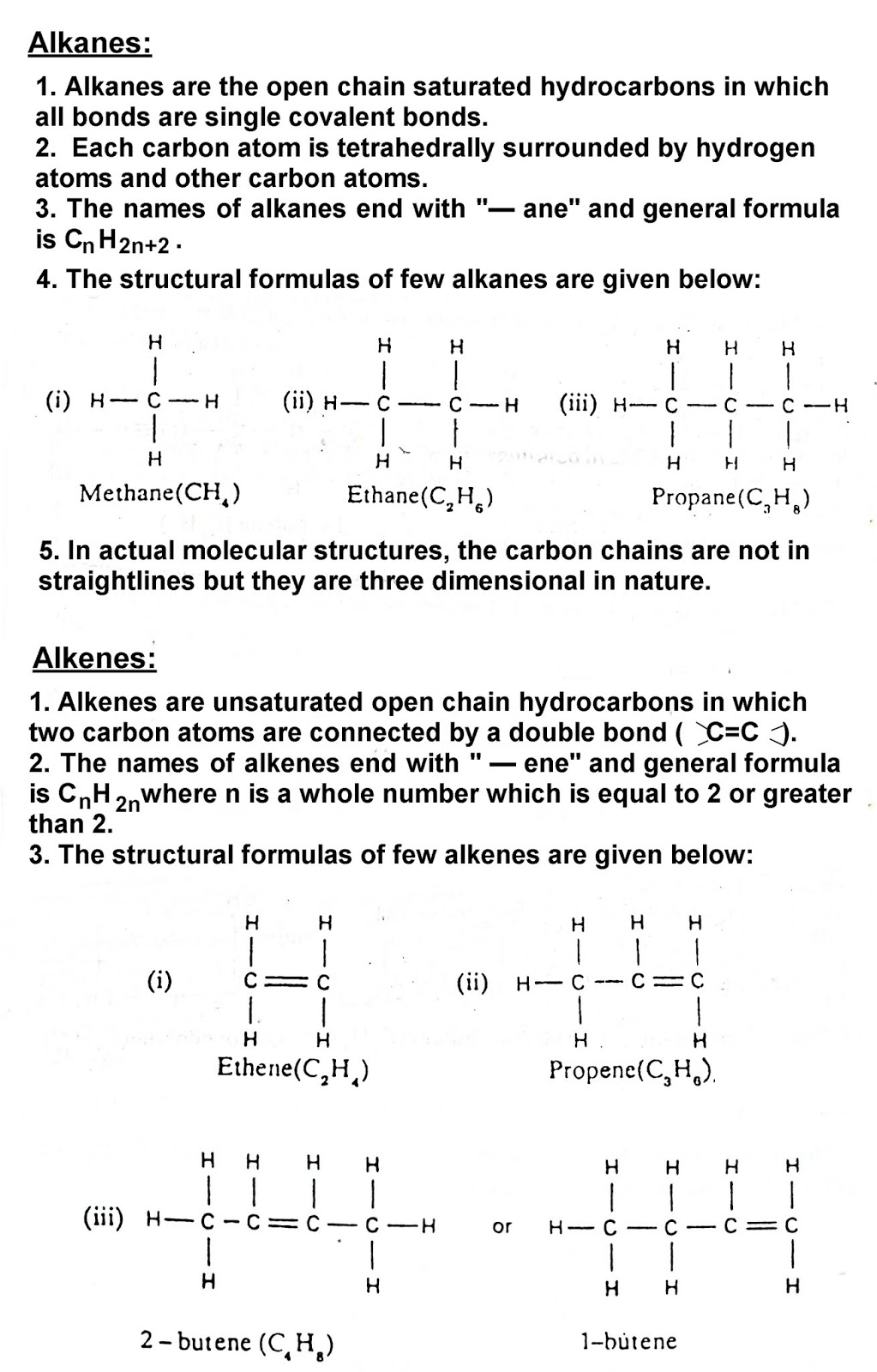
(i) Saturated Hydrocarbons:
- The compounds in which all the valencies of carbon atoms are fully satisfied by single bonds, are called saturated hydrocarbons.
- These are called alkane for an open chain and cyclo alkane for a close chain.
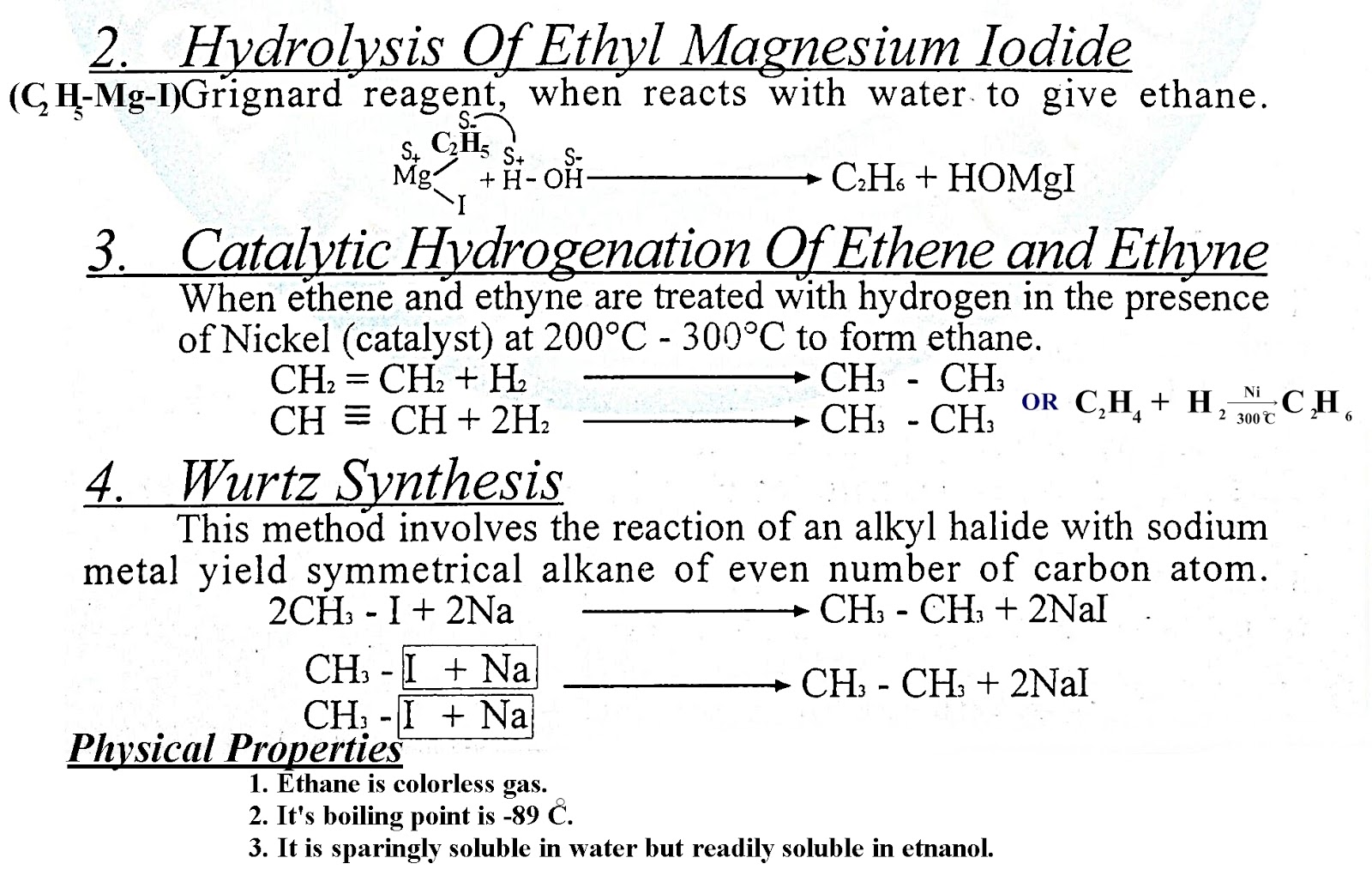
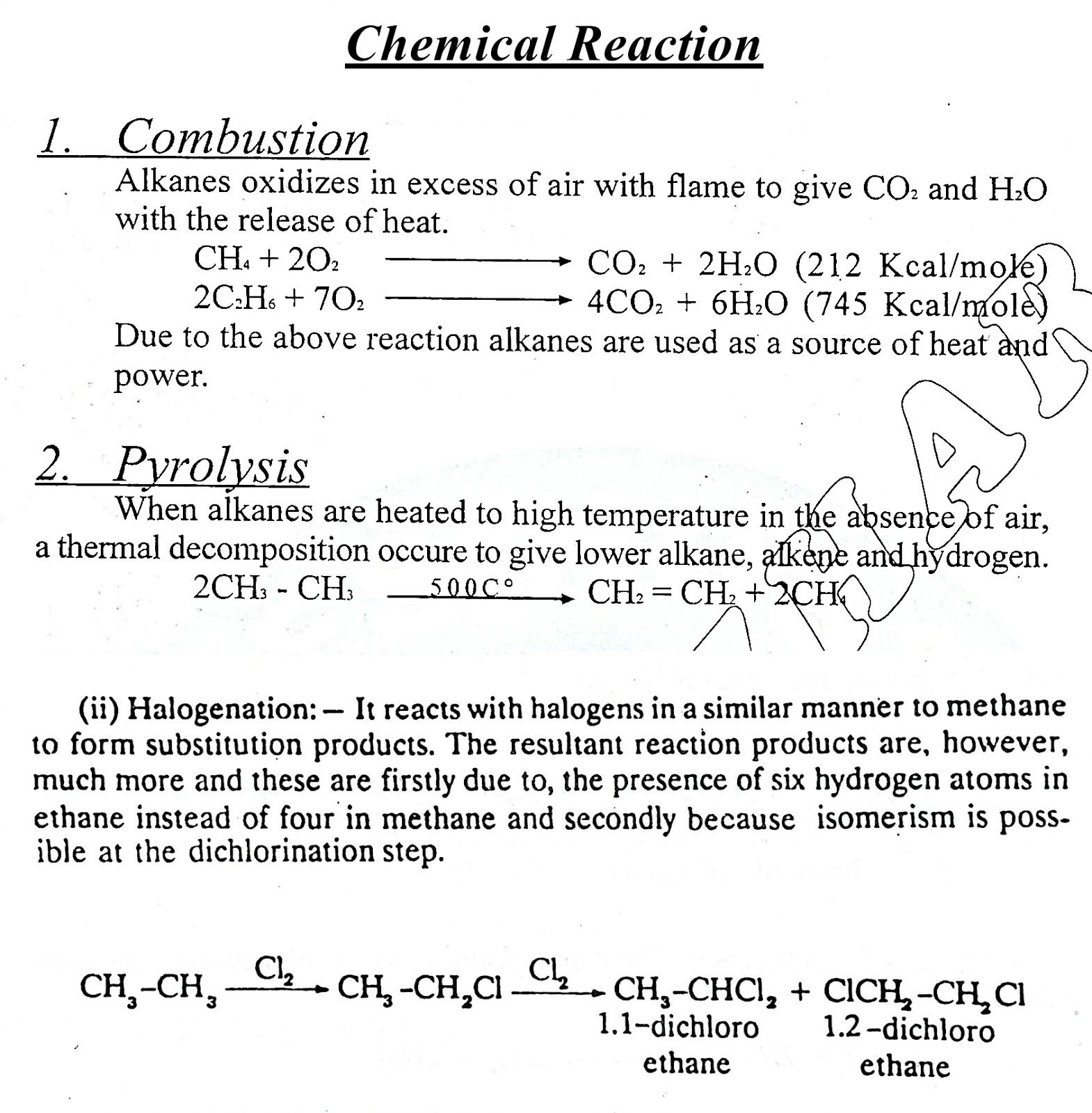
- The examples of saturated hydrocarbons are alkanes.
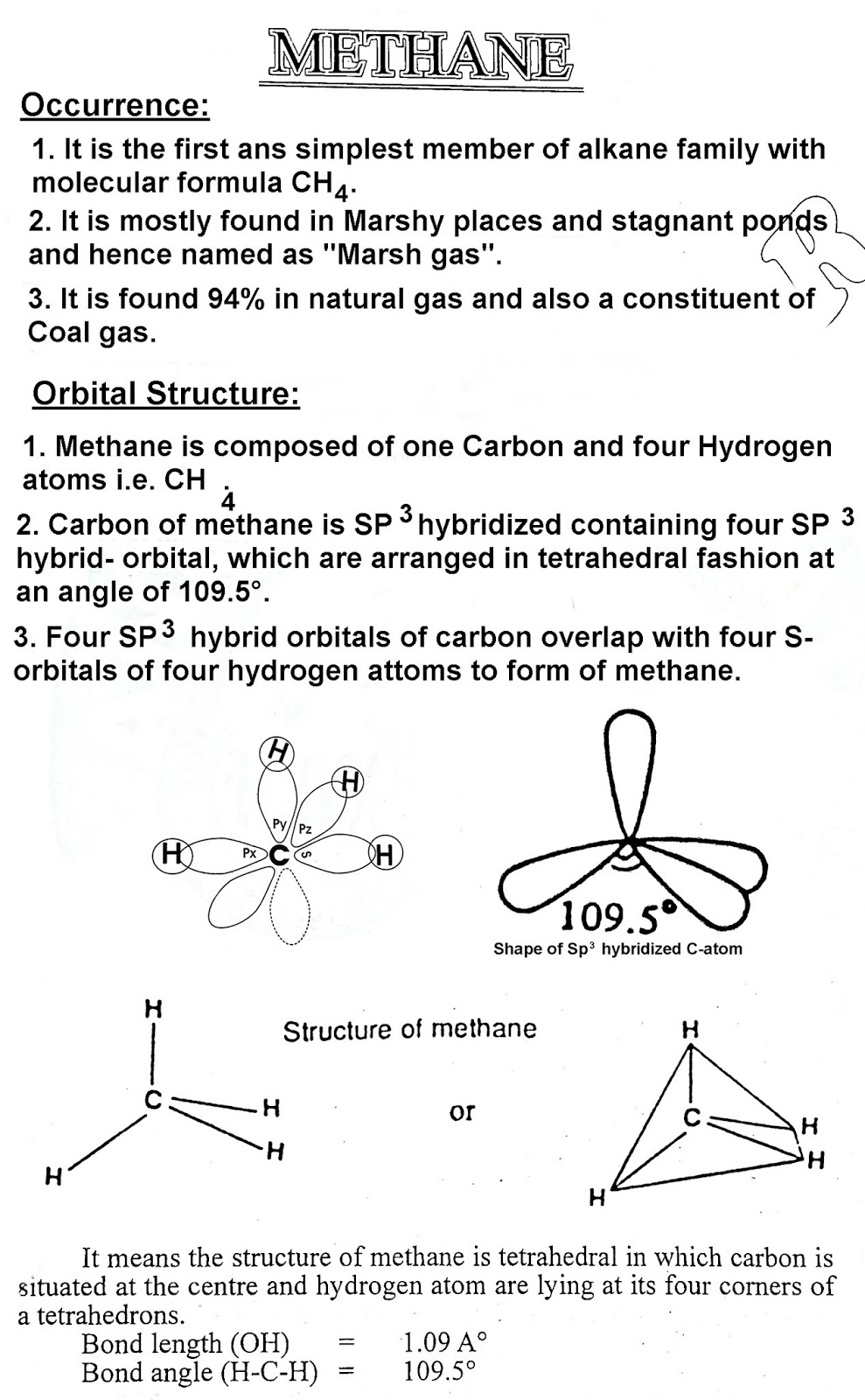
- (i) Methane CH4
- (ii) Ethane C2H6
- These are chemically stable and non polar molecules.
- These compounds do not decolorize KMnO4 and Br2.
- The physical state, B.P, M.P, density etc increase by increasing the carbon chain.
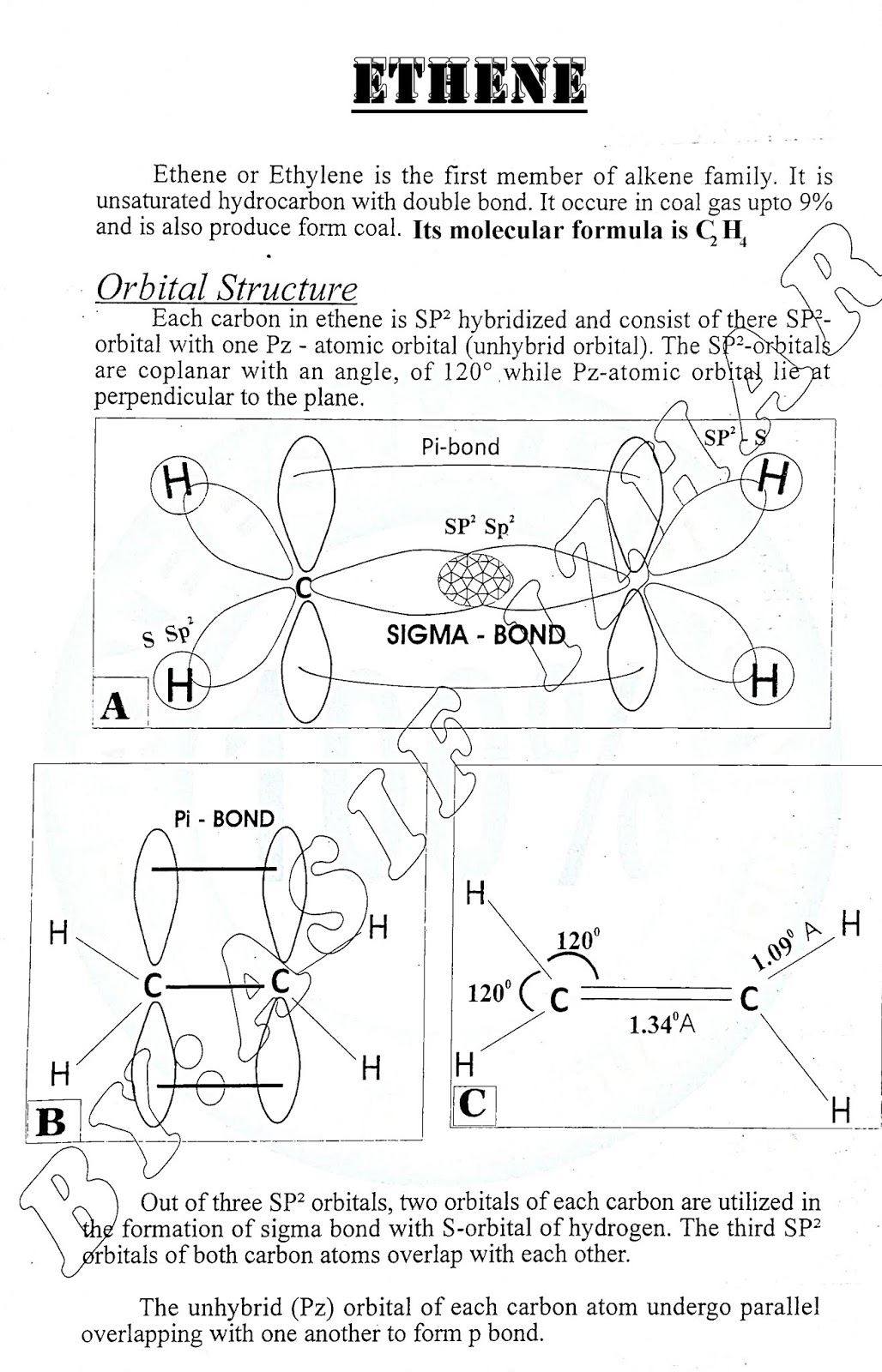
(ii) Unsaturated Hydrocarbon:
- The compounds in which all the valencies of carbon atoms are not fully utilized, are called unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- In these hydrocarbons one or more double or triple bond is present in the carbon chain.
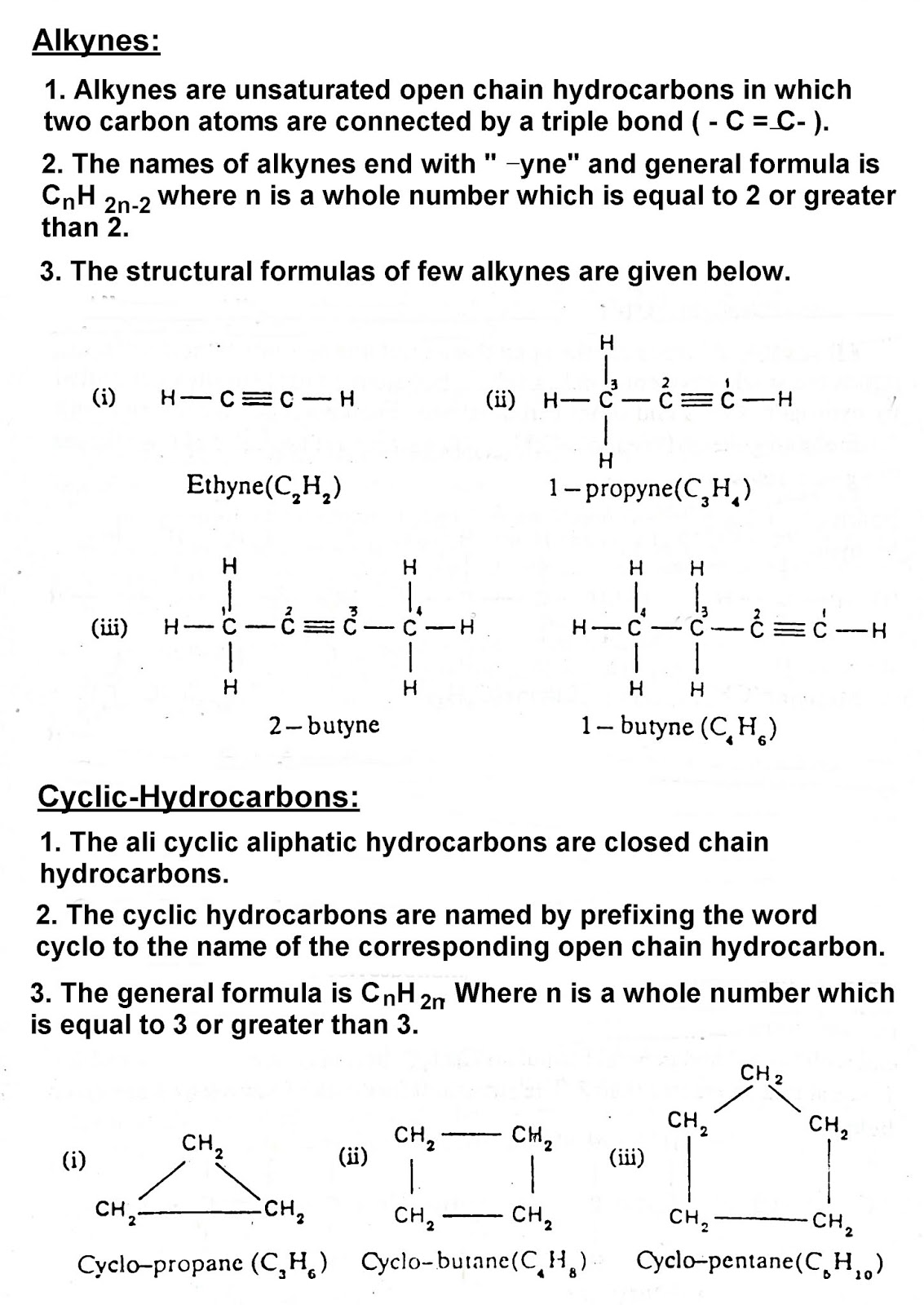
- Alkenes and alkynes are the examples of unsaturated open chain hydrocarbons.
-
The examples of unsaturated hydrocarbons are:
- These are chemically reactive and polar molecules.
- Their important reactions are addition reaction, oxidation reaction etc.
- These compounds have tendency to decolourize KMnO4 and Br2.
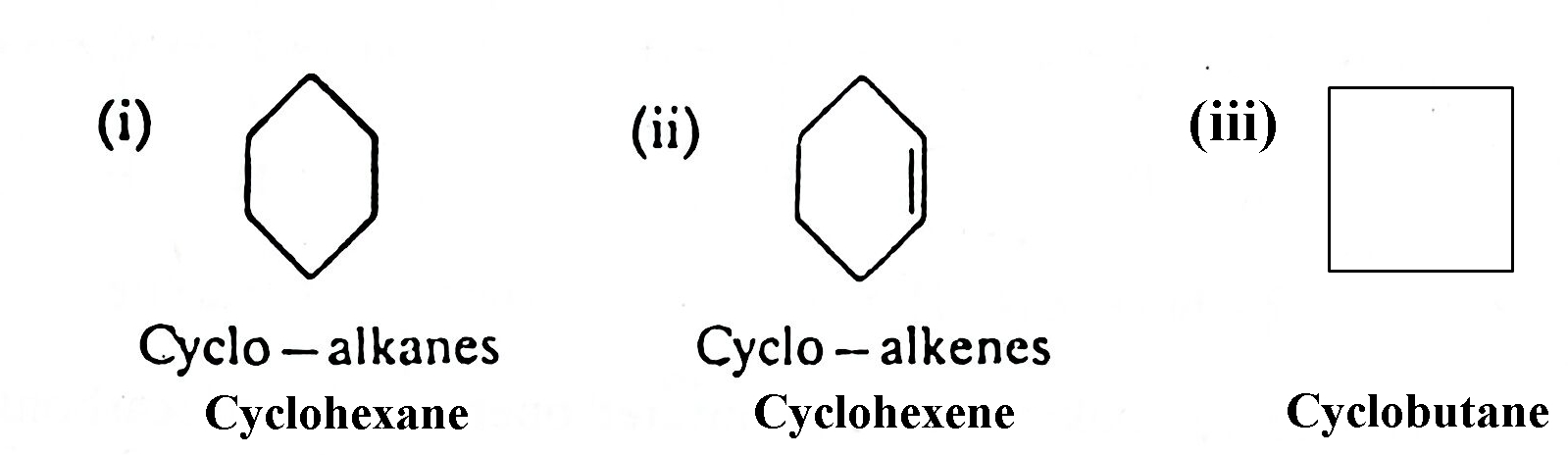
B. Cyclic Hydrocarbon OR Closed Chain Hydrocarbons:
The hydrocarbons which contain closed chain of carbon atoms are called cyclic hydrocarbons.
In these compound the terminal of the chain join together to give a cycle or ring.
The examples are cyclo alkanes and cyclo alkenes.
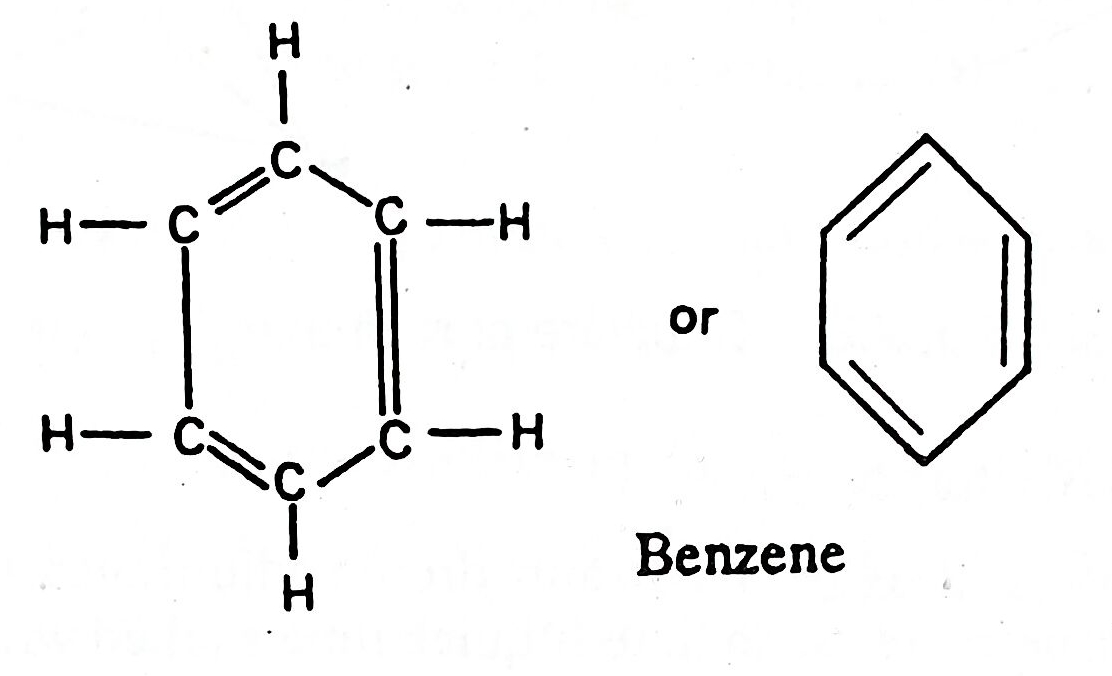
2. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS:
- Aromatic hydrocarbons are special class of cyclic compounds containing Benzene ring.
- Benzene ring is a six-member ring of carbon atoms with alternative double bonds.
- Other aromatic hydrocarbons are mostly related to benzene and its derivatives (homologs) and are called as "Arenes".
- These compounds are further divided into homo-nuclear and hetero-nuclear aromatic compounds.
Alkanes. Alkenes, Alkynes and Cyclic-Hydrocarbons
Continuation of Physical Properties of methane:
5. Liquefies at 161.4 °C and solidifies at -184 °C.
6. It is more soluble in organic solvents like acetone, ether and alcohol.
4. It solidifies at -172 °C.
Continuation of Physical Properties of ethene:
(v) Liquid ethene boils at - 150 °C and solid hydrocarbon melts at -169 °C.
(v) Liquid acetylene boils at -82 °C.
(vi) It is more soluble in alcohol and very soluble in acetone.
Monday 22 June 2020
Chapter No.4 - Land and Climate of Pakistan - Descriptive Question Answers - Pakistan Studies For Class X
Go To Index
LAND AND CLIMATE OF PAKISTAN
Descriptive Question Answers
Contents
- What do you mean by a climate?
- Different climatic regions of Pakistan
- Effects of climate on the Human life
- Environmental Pollution
- Relationship between Population growth and Environmental Pollution
- Importance of Location of Pakistan
- Physical features of Pakistan
- Benefits of Northern, Eastern, Mountains Regions
- Neighboring countries of Pakistan
Q.1: What do you understand by climate?
Ans. CLIMATE:
The average conditions of temperature, pressure of air, humidity, rainfall etc. are called the climate of a certain place.
In other words, the long lasting conditions of weather in a particular place such as air pressure, temperature, humidity and rainfall are termed as the climate of an area.
1. LOCATION OF PAKISTAN ON THE GLOBE:
Pakistan is situated in the north of Tropic of Cancer. It is a Sub- tropical country.
2. MONSOON REGION:
Pakistan situated in the western part of monsoon region.
3. DIFFERENT WEATHERS OF PAKISTAN:
Following are the different weathers of Pakistan.
- Summer:
Summer usually lats from April to September. In Pakistan, summers are very hot, almost in all areas of Pakistan except the northern areas, where summers are pleasant. The maximum temperature of Sibi and Jacobabad is about 50 ℃. Summer season is very hot in Punjab and Sindh also. - Winter:
In Pakistan, winter lasts from November to February. Winters are of severe type in parts of country. Specially in the northern areas, winters are very severe. Sometimes, temperature decreases upto 20 ℃. In winter, Punjan and Sindh are very cool except the coastal areas of Pakistan where climate is mild. In Pakistan the lowest temperature has been recorded at Quetta. - Rainy Season:
In Pakistan, during summer, there are rains from mid-July to September. This is called the rainy season. There is heavy rainfall in the mountainous region, specially in the northern areas of Pakistan. There is rainfall in .Punjab plain also. In Pakistan, the highest rainfall has been recorded at Murree, Punjab.
4. CLIMATIC REGIONS OF PAKISTAN:
With respect to temperature, Pakistan may he divided into four zones.
- a) The North and North Western Mountainous Region.
- b) The Upper Indus Plain.
- c) The Lower Indus Plain and the Coastal areas.
- d) The Baluchistan Plateau and Thar Desert.
CONCLUSION:
The generalized picture of atmosphere is called climate. In Pakistan, there is continental type of climate. Summers are hot and winters are very cold in most areas of Pakistan. The climate of Pakistan is different in different parts of the country. It is not a region of very high rainfall.
Q.2: What are the different climatic regions-of Pakistan?
Ans. CLIMATE:
The long-lasting conditions of weather in a particular place, such as air pressure, temperature, humidity and rainfall are termed as climate.
CLIMATIC REGIONS OF PAKISTAN:
As far as climate is concerned, Pakistan has been divided into four regions.
- SUB-TROPICAL HIGHLAND:
a) Location:
It includes Pakistan's northern mountain ranges (outer and central Himalayas) North western mountain ranges (Waziristan, Zhob and Loralai) and the mountain ranges of Balochistan (Quetta, Sarawan, central Makran and Jhalawan).
b) Summer season:
Here, summers are quite cool. In summer, temperature more than 58°C has been recorded at Sibi.
c) Winter Season:
Here, winters are long and extremely cold. There is fog in winter. season. In the valleys of Baluchistan, lowest temperature has been recorded at Quetta.
d) Rainfall:
In this region, rainfall continues throughout the year. Mostly it rains at the end of summer season. Here, average rainfall has been recorded below 25 mm. - SUB-TROPICAL CONTINENTAL PLATEAU:
a) Location:
Most of the parts of Baluchistan are included in it such as Sibi and Jacobabad.
b) Summer Season:
Summer remains in this region from May to mid September. In this season hot and dusty winds continuously blow.
c) Winter Season:
Winter season remains in this region for few months only. Winters are not very cold like those in the northern areas.
d) Rainfall:
In this region there, is a few mm rainfall during the months of January and February. Here, normally 50 mm rain has been recorded.
- SUB-TROPICAL CONTINENTAL LOWLAND:
a) Location:
The Upper Indus plain (Punjab plain) and lower Indus plain (Sindh plain) are included in this climatic region.
b) Summer Season:
In this region, summers are very long and hot. Here, average temperature is 40°C during summer.
c) Winter Season:
Here, winter season remains for more than four months and like summer, it is of severe type.
d) Rainfall:
In this region, the northern Punjab receives late summer monsoon rains while the rest of Punjab receives less rainfall. There is winter rainfall in this area also. - SUB-TROPICAL COAST LAND:
a) Location:
This climatic region includes coastal areas of Sindh and Baluchistan provinces.
b) Summer Season:
During summer, the temperature is moderate. The range of temperature is less in this region due to sea breeze. Climate remains mild during summer. Humidity is high in summer in this region.
c) Winter Season:
Winter season is not very long in this region. Winters are not very cold in this region.
d) Rainfall:
Here, annual average rainfall is 180 mm. The plain of Lasbela receives rainfall in summer and winter seasons.
CONCLUSION:
Pakistan has continental type of climate. Here,: summers are hot almost in all climatic regions except northern areas. Winters are also cold and very cold in the mountainous region. Pakistan is situated in monsoon region of climate but, being in the western part of this region, does not possess its characteristics. The climate of Pakistan is arid, hot and continental.
Q.3: How does climate affect the human life?
Ans. Introduction:
Climatic conditions of any region affect the human life .greatly. The climatic and . weather conditions of -a particular area influence the way . of living, dresses, food, occupations, sports, customs and economic set-up of the people of that area. In Pakistan, there is great variation in climate, that is why there is great difference in the customs, dresses, foods and occupations of the people in different parts of the country.
INFLUENCE OF CLIMATE ON LIFE:
Here, we are discussing influence of the climate on the life of the people of different parts of Pakistan.
- NORTHERN MOUNTAINOUS AREAS:
a) Climate:-
In Northern Mountainous areas of Pakistan, the winters are extremely cold. Here temperature falls below freezing point and snow spreads all around. Severe cold influences human, animal and plant life of the area. Life activities stop and people face great hardships in winter season.
b) Dresses and Food:-
People start storing food items. Due to snowfall, most of the people migrate to plain areas during winter in search of jobs and food and when summer season set, in they return to their homes and restart trade, cultivation and labour. Life activities become normal during summer season. The climate has an effect on their health. Their colour is fair and they have strong physique. The tough life style has made them bold and brave. They use warm clothes in winter season.
c) Crops:-
As this area is not a fertile one, people do not grow any crop in this region. So, no crops grow in that area. - UPPER AND LOWER INDUS PLAIN:
a) Climate:-
Both summer and winter greatly affect the lifestyle of the people of. Punjab (Upper Indus Plain) and people of Sindh (Lower Indus Plain). People work normally in the winter season but in summer working efficiency decreases.
b) Dresses and Food:-
Here, people use heavy clothes in winter and light clothes in summer. Here people's food is also very simple.
c) Crops:-
Punjab and Sindh plains are the most fertile lands of Pakistan. That is why these areas are thickly populated and people are attached to the profession of agriculture. People have many jobs to do.
d) Floods and Wind Storms:-
In this region, people are affected in the rainy season by floods and wind storms. Many people are killed and great loss of property occurs.
- SOUTHERN AREAS OF PAKISTAN:
a) Climate:-
Most-of the southern areas of Pakistan are deserts and hot. Windstorm and sandy cyclones are a frequent feature. The weather is very hot in this region.
b) Dresses and Food:-
As this region is very hot and sandy,- people use coarse clothes to protect them from heat and hot wind. Here, people use cold drinks made from milk and use very simple food. They use turban and cover their bodies with clothes.
c) Floods and Sandy Cyclones:-
Floods and sandy cyclones hit this area in summer due to which people face a lot of problems.
- THE BALUCHISTAN PLATEAU:
a) Climate:-
This region has extreme climate. Winter is cold and in some areas, there is snowfall. Mostly people remain in homes and prepare gifts for sale. People migrate-from their areas and come back to their houses in the summer season.
b) Shortage of Water and Food:-
During summer season, there is very hot climate and there is shortage of water in this region. Water is only collected through underground canals called "Karez". There is shortage of food also as nothing is grown due to shortage of water.
- COASTAL AREAS:
a) Climate:-
In the coastal region, climate is mild. Here, life activities are in full swing. People do different jobs.
b) Sea Storms:-
Sometimes, sea storms affect the life activities of the people living in the coastal areas.
In Pakistan, there is continental type of climate due to which climate is different in all parts of Pakistan. People living in severe cold region face hardships and problems. In the same way,.people of plain and desert areas face flood, windstorms, lack of water and shortage of food. Climate greatly affects the daily life of the people. It affects their dresses and food also.
Environmental Pollution:
Q.4: What is Environmental.Pollution?Ans. INTRODUCTION:
An undesirable change in the characteristics of the air, water or land that can - adversely affect the health is called pollution. Environmental pollution means destabilizing the balance of atmospheric composition.
Environmental pollution has emerged as a big problem throughout the world. Environmental pollution is due to unhealthy changes in our environment. The main cause of environmental pollution is increasing population.
TYPES OF ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION:
Environmental pollution is of three types.
1. AIR POLLUTION (Atmosphere):
Air pollution turns the clear and odourless air into poisonous gases that harm our health, kill plants and damage property. People pour hundreds of millions of tons of gases and particles into the atmosphere each year. Neat and clean atmosphere is essential for human health. Air is mostly composed of Oxygen, Nitrogen and Carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide and Carbon monoxide make the air polluted.
Following are the main causes of air pollution.
MAIN CAUSES OF AIR POLLUTION:
- Air pollution is mostly due to the burning process of gasoline to. power motor vehicles. Pollution ranges from small amount of colourless gases to clouds of thick black smoke.
- Factories and furnaces add tons of pollution in the air each day.
- Due to different nuclear tests, radiation is created which pollutes the atmosphere. Thermal power plants also pollute the air.
- Nowadays, there is a great use of pesticides in our agriculture to kill the harmful insects. Due to great use of pesticides, air has been polluted.
2. WATER POLLUTION:
Water pollution reduces the amount of pure and fresh water that is available for drinking and cleaning. It is also important for swimming and fishing. It is a great blessing of Almighty Allah for man. Water maintains 70% weight of the human body. The total area of planet earth is 71% water and 29% land. 97% water on the earth is salty and not suitable for drinking and for other use. As a good solvent, it dissolves solids, gases and liquids. Due to following reasons, it is polluted.
MAIN CAUSES OF WATER POLLUTION:
- Dumping of wastes of factories and homes into rivers, oceans and lakes is the most important cause of water pollution.
- Contamination. of water by water pipes is another reason of water pollution because lead, which is a harmful substance, is used to join the pipes.
- Pouring of oil into sea water is very harmful for marine life.
- If sewerage system opens in a lake or river, water is polluted.
- Nuclear waste dumping is another source of water pollution, specially sea water.
3. LAND POLLUTION:
Land pollution damages the thin layer of the fertile soil that covers much of time earth. When a number of harmful things are inducted into the earth, such type of pollution is created.
MAIN CAUSES OF LAND POLLUTION:
- Nuclear tests and explosions create soil pollution.
- Plastic bags are not made of food grade material. When used for packing food is they are not good for health. When burnt with garbage, they create pollution.
- Chemical products can cause poisoning specially the factories put different chemical substances outside the factories, and these are very harmful for human health.
STEPS TO CONTROL THE POLLUTION:
To control pollution, following steps are necessary.
- Environmental Awareness:
Environmental awareness must be created among the people to control it. Through T.V., newspapers and the conferences, awareness must be created. - Less Use of Fuel Emitting Gases:
There should be less use of fuel-emitting gasses. "CNC:" type of fuel should be adopted. - Separation of Poisonous Chemicals:
Poisonous chemical substances should-be separated and cleaned before water is drained into rivers and lakes. - Dirty Water should be Cleaned:
The dirty water (sewerage) of the cities should be cleaned through machines in big ponds. - Appropriate Way of Burning Garbage:
Garbage must be burnt in an appropriate manner. - Proper Use of Human and Animal Waste:
There should be proper use of human as well as animal waste. It should be used as fertilizer. - Use of Polythene bags should be stopped:
Polythene bags are very harmful for human health. The use of polythene bags should be stopped. - Tree Plantation:
More and more trees should be planted to reduce pollution. - General Cleanliness:
Arrangements should be made for general cleanliness. Public places, parks and streets must be cleaned. - Provision of Funds to the Environmental Institutions:
Proper funds and staff should be-provided to the institutions which control pollution.
CONCLUSION:-
Destabilizing the balance of atmospheric composition is called environmental pollution. It has many causes but-the main cause is lack of awareness of the people about pollution. It is the duty of every citizen to adopt such steps to control pollution. It can be controlled with the joint efforts of the government and the people. Government should take more steps to control pollution.
Q.5: What is the relationship between population growth and environmental pollution?
Ans. INTRODUCTION:-
Environmental pollution means destabilizing the balance of atmospheric composition. All types of environmental problems depend on population size. Environmental pollution has emerged as a big problem throughout the world. This is due to increasing population.
Here, we are discussing the main features of the relationship between population growth and environmental pollution.
MAIN FEATURES OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN POPULATION GROWTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION:
Environmental pollution is the main problem which the people of the world are facing today. It is due to the rapid growth of population as new industries are established, new cities and towns are set up and garbage is increasing with the passage of time.
- Rapid Industrialization:
Rapid growth of population is one of the main reasons of pollution. To fulfill the-needs and demands of different products, new industries are set up. All over the world, chemical industries, leather industries and heavy mechanical industries are responsible for air, water and noise pollution. Oxygen has reduced due to these industries. - Pesticides:
With the growth of population, agriculture has also increased. There is great use of pesticides in agriculture nowadays. Most of the pesticide are poisonous and they are used' to- kill insects to save the crops. Pesticides affect the natural cycles in soil and water. We can control this by reducing population. - De-Forestation:
Due to growth of population, new town and cities are established. As a result, forest area is being reduced and cutting down of rain-forests creates environmental problems. To solve the lodging problems of man, forest area should not be reduced. - Garbage Disposal:
Garbage is a product of consumer society. Different diseases are caused by garbage. Residential and industrial, both types of garbage, affect human life. Increasing population is the main reason of the production of garbage. We can overcome this problem by reducing high growth rate of population. - Chemical - Waste:
Many chemical substances are used in different industries. Industries manufacture the products for the people. The chemical substances and their wastes are very harmful for human beings and our environment. In future, more industries will be set up with increase in population. - Noise Pollution:
Noise is a very troublesome pollution in the urban areas. People living near cities are exposed to loud noise most of the time. The noise comes from aeroplanes, vehicles, construction of different projects, industries, speakers used -by street vendors, crackers, pressure horns and Hi-Fi music etc. Due to increase in population, noise pollution, has also increased. - Air Pollution:
Air travel has increased in the whole world with the passage of time and increase in population, due to which air pollution has enhanced. - Water Pollution:
World's population is rapidly growing and there is extensive use of water by people. Industrial waste is also let out into rivers and seas. Water is a basic necessity of all living things. Pure water is needed for the population in but water is polluted due to industries.
CONCLUSION:
Our increasing population is the mother of all problems. When there are more people, we arc in need of more food, more goods and more shelter. For this purpose, we have to develop new industries and for shelter, we have to clear forests. In this way, we are destroying our environment. Environmental pollution is due to increase in population. When population is reduced, environmental pollution will also be reduced. We are destroying natural environment at the cost of our health.
Q.6: Define the importance of the location of Pakistan in the South Asian region?
Ans. INTRODUCTION:
Pakistan is our motherland. We got this homeland after great sacrifices of the Muslims of South Asia. Pakistan is situated in the southern side of Asia. It is considered as part of South Asia. It has great importance in the Southern Asian region due to its ideal location in the region. Pakistan has geographical, political and economic importance in this region, due to its God-gifted location.
1. LOCATION OF PAKISTAN:
The Islamic Republic of Pakistan is located between latitude of 23.35° to 37.05° north and extends from longitude 60.50° east covering an area of 7, 96, 096 square kilometres.
Pakistan consists of four provinces, a Federal capital Area and Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) — Areawise, the province of Baluchistan is the biggest and Punjab province has the highest population.
To the south west of Pakistan is Iran. In the east, India is situated, in the north, China and in the north west lies Afghanistan.
In the south of Pakistan is the Arabian Sea which is a very important sea route. The border between Pakistan and Afghanistan is called Durand Line which is 2252 km long.
2. IMPORTANCE OF LOCATION OF PAKISTAN:
Pakistan has great importance in South Asia. It has great geographical, political and economic importance.
Here we are discussing geographical, political and economic importance of the location of Pakistan.
a) China:
In the north, China is situated, most of the rivers of Pakistan come from the northern side and there are high mountains in this region. China is a very important country of the world. Karakaram Highway joins Pakistan and China. Pakistan and China possess excellent relations from the beginning and frequently both the countries help each other. Both have trade relations also.
b) Afghanistan:
To the north west of Pakistan, lies an Islamic country, Afghanistan. The border between the two countries is called the Durand Line which is 2252 km long. Pakistan has good trade relations with Afghanistan and Pakistan provides transit route to Afghanistan for its trade through land and sea, Afghanistan is one of the member of the E.C.O. along with Pakistan.
c) Iran:
Iran is situated on the South-West border of Pakistan. Iran and Pakistan have ideal relations from the beginning and Iran was the first country of the world which recognized Pakistan when Pakistan, got independence in l947. It is one of the leading oil-producing countries and it is a founder member of E.C.O along with Pakistan. Both the countries have trade and-cultural co-operation.
d) India:
To the east of Pakistan lies India is situated India is called the biggest democracy of the world. It is also the Second Most populated country of the world. Pakistan is trying is level best to form better relations with India. The Kashmir dispute is the main issue between the two countries.
e) Arabian Sea:
To the south of Pakistan, Arabian Sea is situated which is an important trade route. Most trade of Pakistan via sea is carried out through this trade route.
f) The Gulf Countries:
Another importance of the location of Pakistan is that it is situated near the oil-producing states of Gulf. These states have great importance in the world due to their mineral oil. Pakistan has very good relations with all these countries from Morocco to Indonesia.
g) Muslim Countries of Middle East:
Muslim countries of the Middle East like Saudi Arabia and U.A.E. are situated near Pakistan and they are considered as second home for Pakistan.
h) Karachi an International Harbour and Airport:
Karachi is the biggest city of Pakistan and with its international larbour and airport, connects Europe with Asia through sea and air routes. Pakistan carries out its trade with different countries through Karachi port.
i) Indus Valley and Gandhara Civilizations:
In Pakistan, two great civilizations Of the world, Indus valley and Gandhara which are of international importance for tourists. These tourists also visit the valleys of Kaghan and Swat in the northern areas of Pakistan.
j) Protocol Among Pakistan, Afghanistan and Turkmenistan:
Pakistan has good relations with Afghanistan and Turkmenistan and these countries have signed a protocol on the supply of gas through pipeline passing through Afghanistan to Pakistan. This agreement would help in the betterment of relations among them.
k) Kashmir Issue:
The Kashmir issue is the main dispute between India and Pakistan. If this issue is resolved between the two countries, long -lasting peace will be established in South Asia. Pakistan has made many efforts to reduce tension.
l) Pakistan, The Seventh Atomic Nation:
Pakistan is the seventh atomic nation in the world. It is the only atomic power among the Muslim countries. Due to this, Pakistan enjoys high prestige in the Muslim world. Having this the nuclear capability, Pakistan has great importance in South Asia.
CONCLUSION:
Pakistan is our sweet homeland. Allah has blessed it with an ideal location. It has great geographical economic and political importance due to its location. All the neighbouring countries are important countries of the world and due to these countries, Pakistan has great importance in South Asia.
Q.7: Give brief account of the physical features of Pakistan.
Ans. INTRODUCTION:
Pakistan is situated in the North West of South Asia. The variety of landscape divides Pakistan into four main physical regions. We should be thankful to God for blessing us with sea, mountains, plains, plateaus, deserts and valleys in Pakistan.
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF PAKISTAN:
The land surface of Pakistan can be divided into the following physical features.
I.) Mountains.
2) Plateaus.
3) Plains.
4) Deserts including coastal areas.
1 ) MOUNTAINS:
Physically, the mountains of Pakistan are divided into two parts.
a) Northern and North-Eastern Mountains
b) North-Western and Western Mountains.
A) North and North-Eastern Mountains:
This includes the Himalayas and the Karakoram.
1. The Himalayas:
The Himalayas are spread like an arch in the North of South Asian sub-continent. The western parts of these mountain ranges pass through Jammu and Kashmir and some part of Pakistan. Four important Himalayan Ranges are:
a) The Sub-Himalayas or the Sivalik Range.
b) The lesser Himalayas or the Pir Panjal Range.
c) Central Himalayas (Great Himalayas).
d) The Ladakh Range.
2. The Karakoram:
The mountain of Karakoram is located, in the North-West Himalaya. Northern Kashmir and Gilgit are situated here. Its average height is 1000m. Its highest peak is Godwin Austin (K.2) which is 8611 metres high from the sea level. This mountain range is situated between Pakistan and China. Karakoram highway is built in this range.
B) North-Western and Western Mountains:
a) The Hindu Kush Mountains.
b) The Koh-i-Safed Range.
c) The Waziristan Hills.
d) The Sulaiman Range.
e) The Kirthar Range.
2. PLATEAUS:
Two plateaus located in Pakistan are:
a) The Potwar Plateau:
It lies between the river Indus and Jhelum. It begins near Jhelum, Mianwali, Rawalpindi and some parts of Islamabad are included in it. The average height of the Salt range is 75.0 to 900 metres. This area is barren but full of mineral wealth. In this area, there is no cultivation. Its famous rivers are "Soan" and Huro.
b) The Plateau of Balochistan:
The vast plateau of Balochistan lies in the Sulaiman and Kirther mountain. It is also dry area like Potowar. The average height over here is 600 to 900 metres. The Chaghai mountain separates it from Afghanistan, It is mostly a desert and barren region. Hub is the main river of this region. Many valuable minerals like coal, natural gas, iron, chromite and copper have been found in many parts of the region.
3) PLAINS:
The vast plain area of Pakistan has been divided into three main parts.
a) The Upper Indus Plain or the Punjab Plain:
The plain in which river Indus flows in Punjab is called the upper Indus plain. It is situated in the South of Sub-Himalaya and Salt range. It is irrigated by the Indus and its tributaries. It is the most fertile land of Pakistan.
b) The Lower Indus Plain or Sindh Plain:
The plain in which river Indus flows, when it enters Sindh province is called the Lower Indus plain. It is a flat plain like Punjab plain. It has been formed by the Alluvium deposited by the Indus. It is also very fertile land and almost all type of crops grow in this plain. It is playing important role in the national economy, To the eastern side of this plain, the famous Thar desert is situated. There is a network of canals in this plain.
c) The Indus delta:
When Indus river merges into Arabian Sea, it becomes slow and makes delta near Thatta called "Indus Delta". It is a marshy land and very fertile, hence Thatta is an agricultural area. In the soil of Indus Delta, all types of useful salts and minerals are deposited which are needed for good crops.
4) THE DESERTS INCLUDING COASTAL AREAS OF PAKISTAN:
Desert means, a place having sand everywhere but no water nor grass. There are deserts in Sindh and Punjab provinces and nearly the whole of Balochistan has desert-type climate.
a) Thar and Nara Desert:
It is situated in Sindh and is the biggest desert of Pakistan and among ten big deserts of the world. People lead very hard life in this desert. It is the extension of Rajasthan Desert of India. Nara desert is situated near Khairpur. Thar and Nara deserts are agriculturally poor areas.
b) Thal Desert:
Thal desert is located in the district of Mianwali, Muzaffargarh and Dera Ghazi Khan. There is agriculture in this area because the land is fertile and it is irrigated by the Indus canal water.
c) Cholistan Desert:
About sixty percent area of Bahawalpur region and its south-eastern area is called the Cholistan desert. Its major part is located in India.
d) The Chaghai and Kharan Desert:
The north western deserts of Chaghai and Kharan are very dry regions. Here, average rainfall is less than 25mm. Density of population is very low in this region.
e) Coastal Area:
The total length of the coast of Pakistan is nearly 700 km. The coast between the border of Iran and Hub river is called Makran coast. It is 500 m in length. All the coastal areas of Pakistan are located in the Arabian Sea. The most important harbour of Pakistan is Karachi. Other ports are Port Qasim. Sonmiani, Pasni, Jewani and Gwadar. Cultivation is done in this plain. It is playing a leading role in the economy of the country, as our country is an agricultural country. In the east of the Indus lies the desert of Thal. There is a big network of canals in this plain to water the lands. In the western plain, of the Indus, there are "Derajat".
CONCLUSION:
Allah Almighty has blessed Pakistan with mountains, plateaus, plains, sea and rivers. Most of the mountains of Pakistan are situated in the northern regions. The Upper and Lower plains of Indus arc the most important plains of Pakistan. Thar and Thal deserts are the main deserts of Pakistan. Sindh and Balochistan have the coastal areas of Pakistan.
Q.8: Mention the benefits of the Northern-eastern mountainous region.
Ans. INTRODUCTION:
The northern-eastern mountainous region is the main mountainous region of Pakistan. The world's highest mountain range, the Himalayas is situated in this region. This region has great importance for Pakistan because Pakistan gets many benefits from these mountains. It is the forest area of Pakistan as well as the main source of getting river water.
Here, we are discussing the main benefits and importance of Northern mountainous region.
MAIN BENEFITS OF NORTHERN-MOUNTAINOUS REGION:
Following are the main benefits of Northern Mountainous region:
1. Natural Defence to Pakistan:
The Northern Mountains of Pakistan are very high mountains so they provide natural defence to Pakistan.
They save Pakistan from its enemies as they are very high mountains.
2. Forest Area of Pakistan:
It is the main forest area of Pakistan. 80% forests of the country are over here. Very precious trees are grown here which fulfill the needs and requirements of the country.
Very precious type of wood is available in this region which is playing its role in the development of the country as it is used in different industries as raw material.
3. Sources of the Main Rivers:
Most of the rivers of Pakistan and the most important river Indus have their sources in the northern mountains. When snow melts and there is heavy rainfall in this area, water comes in the rivers to irrigate the lands.
Many barrages, Terbela dam, Manila Dam have been built on the rivers which are coming from the northern areas.
4. Protection from Cold Freezing Winds:
They protect Pakistan from cold and freezing winds of North Pole. Otherwise Punjab and K.P.K. would have been covered with snow during winter season.
5. Mineral Deposits:
Many valuable minerals are found in this region which are used as raw materials in different industries for a better economy of Pakistan.
Minerals play great role in the development of any country. So, minerals which are found in the northern areas are playing great role in the national progress.
6. Heavy Rain Fall Area:
In the rainy season, there is heavy rainfall in this region and their mountains cause rainfall in Punjab and Sindh.
Pakistan is an agricultural country and for our crops, we need plenty of water and that water is generally comes from the heavy rainfall in the northern areas.
7. Source of Energy:
In Pakistan, mostly hydro-electricity is produced and most of the dams are built on these rivers, which come from the northern region. It is one of the greatest benefits of Northern Mountains.
In Pakistan, there is lack of energy resources. Mostly energy is taken through hydro-electricity and water -resources which are coming from the northern areas are playing great role to fulfill our energy problems.
8. Add Beauty to the Country:
The northern areas of Pakistan are the most beautiful parts of Pakistan, which add beauty to the country.
In the northern areas of Pakistan, there are beautiful grassy fields. High mountains and beautiful waterfalls add beauty to the country.
9. Trade through Karakoram Highway:
Karakoram Highway is a great trade route situated in the Northern Mountains. This highway has strengthened the good relation between Pakistan and China.
Along with the trade, this trade route has great defence importance.
10. Animal Life:
Mostly, wild animals and precious birds are found in the northern areas of Pakistan.
In the northern areas, different wild animals of international importance are found, due to which many tourists visits Pakistan every year.
CONCLUSION:
Pakistan is a great gift of Allah. High mountains are situated in the Northern region of Pakistan. They have great importance for Pakistan, because these high mountains provide defence, river water, minerals, precious .wood and many other benefits to Pakistan. These mountains have great role in the economy of the country.
Q.9: Name the neighbouring counties of Pakistan.
Ans. INTRODUCTION:
Pakistan is situated on the Southern side of Asia. It is, therefore, considered as a part of South Asia. As far as the location of Pakistan is concerned, it has great importance in ,South Asia because the countries, which are in the surroundings of Pakistan, arc very important.
The neighbouring countries of Pakistan have geographically, economically and politically great importance in the world and due to these neighbouring countries, Pakistan has great importance in the world.
NEIGHBOURING COUNTRIES OF PAKISTAN:
Following are the neighbouring countries of Pakistan.
1) CHINA:
It is situated in the north of Pakistan. Pakistan shares a common boundary of about 585 km with China and is connected with it through Karakoram Highway. China is an important country. It is one of the five permanent members of the U.N. Security Council and one of the biggest exporters in the world.
Pakistan has very good relations with this country from the very beginning. It is time-tested friend of Pakistan and we have trade relations with it also.
2) IRAN:
In the South-west of Pakistan, Iran is situated. It is an Islamic country and Pakistan has rail and road links with-this country.
Iran and Pakistan have very good brotherly relations. Iran was the first country. which recognized Pakistan as an independent state.
It is one of the leading oil-producing'countries and both the countries have great cooperation in many fields. Pakistan and Iran have trade relations also.
3) AFGHANISTAN:
In the North-west of Pakistan, Afghanistan is situated. The boundary between Pakistan and Afghanistan is called "Durand Line", which is 2252 km long. Pakistan and Afghanistan have good relations nowadays as compared to the past.
Both the countries have trade relations with each other.
4) INDIA:
India is situated to the east of Pakistan. It is the second-most populous country of the world and the world's biggest democracy also. Pakistan did not have good relations with this country in the past. Four wars had been fought with his country. Kashmir is the bone of contention between the two countries.
Nowadays both countries have worked a lot for better relations with each other and soon direct trade will also start between the two countries.
India is a big exporter in the world and an important market for the leading countries of the world.
5 ) MUSLIM STATES OF CENTRAL ASIA:
The Muslim states of central Asia are not the neighbouring states of Pakistan but they are very near to Pakistan. One Muslim state of Central Asia Tajikistan is situated very near to Pakistan.
Pakistan has good relations with all Islamic states of Central Asia. It has trade relations with these states.
6) ARABIAN SEA:
In the south of Pakistan is the Arabia Sea. The coastal area of Pakistan is 700 km. The Arabian Sea is an important trade route of the world, which has great strategic importance. Three sea ports Karachi Port, namely Port Qasim and Gawadar Port have been built on this coast.
CONCLUSION:
The Islamic Republic of Pakistan is situated in South Asia. It has great geographical, economic and political importance in this region due to its ideal location. All the neighbouring countries of Pakistan, namely China,. Iran, India and Afghanistan have great importance in the world and due to these countries, Pakistan has great importance.
The Arabian Sea is a very important trade route of the world.
Chapter No.4 - Land and Climate of Pakistan - Short Question Answers - Pakistan Studies For Class X
Go To Index
LAND AND CLIMATE OF PAKISTAN
Text Book Exercise
Q.1: Describe the location of Pakistan in four sentences.
Ans. Location of Pakistan:-
- The Islamic Republic of Pakistan is located between latitude of 23.35° to 37.05° north and extends from longitude 60.50° to 77.50°. Its total area is 7,96,096 sq km. Pakistan consists of four provinces, a Federal Capital Area and Federally Administered Tribal Areas (F.A.T.A.).
- Pakistan is situated in the southern side of Asia. To its west Iran, to the east India to the north China, and to the North-west, Afghanistan is situated.
- The Arabian Sea is situated in its south.
Q.2: Name the neighbouring countries of Pakistan.
Ans. Neighbouring Countries of Pakistan:
Following are the neighbouring countries of Pakistan.
1) Iran. (Situated in the South-West).
2) India. (Situated in the East).
3) China. (Situated in the North).
4) Tajikistan (Situated in the North).
5) Afghanistan. (Situated in the North-West).
Q.3: State the importance of the location of Pakistan in four sentences.
Ans. Importance of the Location of Pakistan:
Pakistan is situated in the southern part of Asia. It is, therefore, considered as a part of South Asia ans is very important country. Pakistan's location is ideal in South Asia because all the countries like Iran, India, China and Afghanistan have great political, geographical and economic importance. These countries have great importance in the world and due to these countries, Pakistan has got central position. in Asia.
The Arabian Sea is a very important trade route of the world, which is situated in the south of Pakistan.
Pakistan is situated near oil producing gulf countries and in the middle of the Muslim World. Therefore, The Muslim states of Central Asia are also very near to Pakistan.
Q.4: Name three mountains of Pakistan.
Ans. Following are the three mountains of Pakistan.
1) The Himalayan Mountains.
2) The Karakoram Mountains.
3) The Ladakh Mountains.
Q.5: Write three sentences on the importance of North Eastern Mountains range.
Ans. Importance of North Eastern Mountain Range:
The north eastern Mountains are very beneficial for Pakistan.
- They provide natural defence to Pakistan from northern side due to their height. They protect Pakistan from cold freezing winds from north pole.
- Water comes in the rivers of Punjab due to heavy rainfall on these mountains.
- The most important forest area of Pakistan is also situated in this region where these mountains are situated. Some valuable minerals arc also found in this region, which are important for the sound economy of the country.
Q.6: Name three-ports of Pakistan and which is the largest port of Pakistan.
Ans. Ports of Pakistan:
Following are the three ports of Pakistan.
1) Karachi Port.
2) Port Muhammad bin Qasim.
3) Gwadar Port.
Karachi port is the largest port of Pakistan.
Q.7: Name three deserts of Pakistan. Which is the biggest desert of Pakistan?
Ans. Deserts of Pakistan:
Following are the three deserts of Pakistan.
1) Thal Desert.
2) Thar Desert.
3) Nara Desert.
Thar Desert is the biggest desert of Pakistan.
Q.8: Write three sentences on the importance of Upper and Lower plains of Indus for the economy of Pakistan.
Ans. Importance of Upper and Lower Plains of Indus for Pakistan:
- The plains in which river Indus flows are called Indus plains.
- The Upper and Lower Indus plains are the most fertile lands of Pakistan and more than 60% cultivation in Pakistan is done in these two plains.
- Almost all types of crops are grown in these plains. As Pakistan is an agricultural country and its economy is based on agriculture, these plains are playing a leading role in our economy.
Q.9: Write three sentences on the climate of Pakistan.
Ans. Climate of Pakistan:
- As far as the climate of Pakistan is concerned, it is continental type of climate. Pakistan is situated in the north of Tropic of Cancer. It is situated in the western part of monsoon region.
- In summers, the climate of almost all areas of Pakistan is very hot except the northern areas where the climate is pleasant.
- Winters are very cold in all areas of Pakistan. Pakistan is an area of less rainfall.
Q.10: Name climatic regions of Pakistan.
Ans. Climatic Regions of Pakistan:
Following are the main climatic regions of Pakistan.
1) Sub-Tropical Continental Highland.
2) Sub-Tropical Continental Plateau.
3) Sub-Tropical Continental Lowland.
4) Sub-Tropical Coast land.
Q.11: Define environmental pollution in three sentences.
Ans. Environmental Pollution:
- An Undesirable change in the characteristics of the air, water or land that can adversely affect the health is called pollution.
- Pollution means destabilizing the balance of atmospheric composition. It has emerged as a big problem throughout the world.
- Air pollution, water pollution and land pollution are the main types of pollution.
Q.12: Suggest three steps to reduce environmental pollution?
Ans. Steps to Reduce Environmental Pollution:
Following Steps can be taken to reduce pollution.
1) Environmental Awareness:
Environmental awareness must be created among the people to control it. Through T.V., newspapers and conferences, awareness must be created.
2) Separation of Poisonous Chemicals:
Poisonous chemical substances must be separated and cleaned before water is drained into rivers and lakes.
3) Less Use of Fuel Emitting Gases:
There should be less use of fuel emitting gases. "CNG" type of fuel should be adopted.
Q.13. Describe in three sentences the relationship between population growth and environmental pollution.
Ans. Relationship between Population Growth and the Environmental Pollution:
- Environmental pollution has emerged as a big problem throughout the world today. Ecology has emerged as a new science to make people aware about the pollution of water, air and land.
- It is due to the rapid growth of population that new industries are established, new cities and towns are set up with the passage of time.
- Rapid industrialization, large use of pesticides, deforestation are the main causes of pollution which are due to rapid growth of population in the world.
Chapter No.4 - Land and Climate of Pakistan - Fill In The Blanks and MCQs - Pakistan Studies For Class X
Go To Index
LAND AND CLIMATE OF PAKISTAN
Fill In The Blanks:
1. The long border between Pakistan and Afghanistan is called Durand Line.2. Pakistan is divided into four climatic regions.
3. The coastal area of Pakistan are Makran and Sindh.
4. The climate of the upper Indus plains of Pakistan is hot and dry.
5. The water evaporation is about 4% in the atmosphere.
6. Water maintains 7% of the total weight of human body.
7. People of the northern region in Pakistan performer household activities during winter.
8. In the south west of Pakistan Iran is our neighbouring country.
9. Baluchistan has an area of 347190 square kilometers.
10. The word FATA means Federally Administered Tribal Area.
11. Hub and Lyari rivers flow in The Kirthar Range of maintains.
12. The biggest salt mine in the world is in Pakistan's Punjab province.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Select the best Answer, from the given options.
1. The official name of Pakistan is ______.* Islamic Republic of Pakistan.
* People Republic of Pakistan
* Socialist-Republic of Pakistan
* Democratic Republic of Pakistan
2. The total area of Pakistan is _______ square kilometres.
* 596096
* 796096
* 696096
* 896069
3. FATA is situated in this province of Pakistan. ________.
* Punjab
* Balochistan
* Sindh
* K.P.K.
4. Sindh province is spread over ________ square kilometres.
* 140,914
* 340,914
* 240,914
* 440,914
5. Pakistan is situated in the _______ side of Asia.
* Eastern
* Northern
* Southern
* Western
6. _______ is connected with Pakistan through road and rail.
* China
* Turkmenistan
* Afghanistan
* Iran
7. To the north of Pakistan, _______ is situated.
* China
* India
* Afghanistan
* Iran
8. India is situated to the _______ of Pakistan.
* East
* South
* West
* North
9. In the _______ part of Pakistan, Iran is situated.
* East
* South
* West
* North
10. ________ is situated in the South of Pakistan.
* China
* Arabian Sea
* India
* Afghanistan
11. Durand Line is the boundary between Pakistan and _______.
* China
* Iran
* India
* Afghanistan
12. Gawadar Port is situated in ________.
* Punjab
* Balochistan
* Sindh
* K.P.K.
13. __________ is connected with Pakistan through Karakoram Highway.
* India
* Iran
* China
* Afghanistan
14. Pakistan provides transit route to _________ for trade.
* India
* Saudi Arabia
* Turkmenistan
* Afghanistan
15. Pakistan is divided into _______ physical regions.
* 4
* 6
* 5
* 7
16. Pakistan has been divided into ______ climatic zones.
* 2
* 4
* 3
* 5
17. ______ is the biggest desert of Pakistan.
* Thal
* Cholistan
* Thar
* Nara
18. Indus River forms its delta near _______ .
* Karachi
* Thatta
* Hyderabad
* Khairpur
19. The Upper Indus plain is also known as______ plain.
* Punjab
* Sindh
* K.P.K.
* Balochistan
20. _______ plain is also known as Lower Indus Plain.
* Punjab
* K.P.K.
* Sindh
* BalochiStan
21. _______ is the biggest plateau of Pakistan.
* Punjab
* K.P.K.
* Sindh
* Balochistan
22. The height of K-2 is _______ metres.
* 8600
* 8400
* 8200
* 8500
23. Durand Line is ______ km long.
* 4222
* 2252
* 4242
* 2262
24. ________ Port is the biggest port of Pakistan.
* Karachi
* Gwadar
* Bin Qasim
* Pasni
25. Pakistan, Iran and _________ are the founder members of E.C.O.
* China
* Afghanistan
* Turkey
* Turkmenistan
26. _________ is the biggest International airport of Pakistan.
* Islamabad
* Lahore
* Sialkot
* Karachi
27. Gandhara civilization is situated in ________ province of Pakistan.
* Punjab
* Balochistan
* Sindh
* K.P.K.
28. Kashmir is the main dispute between Pakistan and __________.
* India
* China
* Iran
* Saudia Arabia
29. Pakistan, Afghanistan and ________ have signed a protocol on the supply of gas.
* India
* Turkmenistan
* Iran
* Saudia Arabia
30. Health resorts of Pakistan, Muree, Ayubia and Nathiagali are situated in the ________ Mountain.
* Pir panjal
* Ladakh
* Himalaya
* Hindu Kush
31. Karakoram range is about _______ metres high.
* 4000
* 6000
* 5000
* 7000
32. The mountains cover _______ forest of our country.
* 60%
* 80%
* 70%
* 90%
33. __________ Pass is called the gateway to South Asia.
* Tochi
* Bolan
* Khyber
* Lawari
34. The coastal area of Pakistan is ______ km long.
* 700
* 600
* 500
* 800
35. Water consists of about ________% of the total weight of a human body.
* 60
* 70
* 65
* 80
Saturday 20 June 2020
Application - Requesting to Visit any Place
Go To Index
Application To Visit Pakistan Steel Mill
Application To Visit Pakistan Steel Mill
1. Write An Application To The Headmaster/ Headmistress Of Your School Requesting Him / Her To Visit Pakistan Steel Mills and Making Necessary Arrangement for Transport
To,
The Principal / Headmaster/ Headmistress,
X-Y-Z School,
Karachi.
SUBJECT: Permission to visit Pakistan Steel Mill.
Respected Sir / Madam,
With due respect, I beg to say that the students of our class wanted to visit Pakistan Steel Mills Karachi. We shall be accompanied by three of our senior teachers. This trip will be a beneficial trip for us, from which we can make increment in our knowledge by watching how machines actually work. We can also pick a valuable information for the forth-coming technical exhibition.
We will be grateful to you if you allow us to visit Pakistan Steel Mills and make necessary arrangements for transport.
Thanking You,
Your Obedient Pupil,
XYZ
Student of Class IX
XYZ
Student of Class IX
15th May, 2020.
________________
Applications- Asking For Certificate
Go To Index
Application For Character Certificate
1. To the Principal / Headmaster / Headmistress of your school requesting him / her to issue a Character Certificate
To,
The Principal / Headmaster / Headmistress,
X-Y-Z School,
Karachi.
SUBJECT: NEED FOR CHARACTER CERTIFICATE.
Respected Sir / Madam,
I have the honour to inform you that I have passed the Matric with A Grade from your school. Now for taking admission in the college I shall need a character certificate.
I, therefore, request you to issue me a character certificate. I'll be grateful to your this act of kindness.
Thanking you,
Your's Obediently,
X-Y-Z.
4th September, 2020
X-Y-Z.
4th September, 2020
Application For Transfer Certificate
2. To the Principal / Headmaster / Headmistress of your school requesting him / her to issue a Transfer Certificate (T.C.)
To,
The Principal / Headmaster / Headmistress,
X-Y-Z School,
Saddar, Karachi.
SUBJECT: NEED FOR TRANSFER CERTIFICATE.
Respected Sir / Madam,
I am a student of your school studying in class IX at present, I feel extremely sorry to inform you that I shall not be able to prolong my studies in your esteemed school as my father is leaving with all the members of his family to Oman in connection with a job.
Therefore under the above circumstances, I would request you to issue me a Transfer Certificate which will enable me to seek admission in a school in Oman.
Thanking You for your anticipation in this regard.
Your's Obediently,
X-Y-Z.
4th February, 2020
X-Y-Z.
4th February, 2020
OR
Application For Sports Certificate
3. To the Principal / Headmaster / Headmistress of your school requesting him / her to issue a Sports Certificate for the event in which you took part.
Friday 19 June 2020
English X - Chapter No.25 - MCQs and Fill In the Blanks
Go To Index
THE CUSTOMS OF VARIOUS REGIONS OF PAKISTAN
MCQs and Fill In the Blanks
Multiple Choice Questions
1. In thee north of Pakistan are the _______ mountains with their silvery waterfalls and cool lakes.
a. grassy
b. snow-copped
c. barren
d. tall
2. The tribal people and the Pathan of the north are sturdy and ________.
a. healthy
b. beautiful
c. brave
d. strong
3. The proud father announces the birth of a son by _____.
a. fire crackers
b. rifle shots
c. dancing
d. singing
4. The Pathans are very _____ by nature.
a. polite
b. hospitable
c. decent
d. sobre
5. Quaid-e-Azam called the Punjab _____ of Pakistan.
a. brain
b. vital organ
c. heart
d. soul
6. The University of Taxila flourished in the Punjab about _____ years ago.
a. 500
b. 1500
c. 2,000
d. 2,500
7. The _____ of Cbiniot is famous all over the country.
a. sport goods
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
8. The ____ of Sialkot are famous.
a. sport goods
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
9. The _______ of Wazirabad is famous.
a. sport goods
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
10. The _____ of Multan is famous all over. country.
a. sport goods
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
11. The _______ of Gujrat and Bhawalpur is also famous.
a. Pottery
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
12. Punjabi girls amuse themselves by dancing the _____ at wedding ceremonies.
a. luddi
b. bhangra
c. disco
d. classical
13. Punjabi men express their joy by dancing the _______ at wedding ceremonies.
a. luddi
b. bhangra
c. disco
d. classical
14. Mela Chiragan is held every year on the eve of the urs of saint ________.
a. Baba Farid
b. Data Ganj Baksh
c. Madbu Lal Hussain
d. Baba Uddin Zakariya
15. People of Baluchistan keep themselves warm by using a ________ in cold weather.
a. heater
b. burner
c. stove
d. sandly
16. In _____ the wedding food Is brought along with, the baraat.
a. Khyber Pakhtunkbwa
b. Baluchistan
c. Punjab
d. Sindh
17. The ancient civilization of Sindh dates back to _____ B.C.
a. 500
b. 1000
c. 2,000
d. 2,500
18. The ruins of Moen jo Daro are ______ years old.
a. 3,000
b. 4,000
c. 5,000
d. 6,000
19. The Ek Tara and ______ are typical musical instruments of Sindh.
a. Sarangi
b. Aighoza
c. Murli
d. Piano
20. The Sindhi ______ is admired all over Pakistan as well as in foreign countries.
a. cutlery
b. embroidery
c. music
d. pottery
2. The Pathans are sturdy and war-like people.
3. They like roasted mutton and Chapli Kababs.
4. The Punjab is a seat of learning.
5. The University of Taxila flourished about two thousand and five hundred years ago.
6. The Punjabi farmers sit in the Chopal in th evening.
7. The geographical variations of Pakistan are reflected in the customs of the people of various regions of our country.
8. The power of a tribe depends upon the number of its menfolk.
9. The birth of a son is regarded as a great blessing for the family.
10. The Pathans are very hospitable to their guests.
11. The generosity to their guests is well-known.
12. The Punjab has been called the "Heart of Pakistan" by the Quaid-i-Azam.
13. The inlaid furniture of Chiniot, the sports goods of Sialkot, the cutlery of Wazirabad, the pottery of Gujrat and Bahawalpur are known all over the country.
14. Mahya' and 'Heer' are the famous folk songs of the Punjab.
15. Luddi and Bhangra dances are performed at the time of weddings.
16. The Balochistan is made up of vast barren lands and dry mountains.
17. Extreme climate has made life very difficult for the people.
18. The Balochis lead a simple life and they usually sit and sleep on the floor.
19. The traditional jewelry of Balochistan is beautifully designed.
20. The civilization of Sindh, (the Valley of Mehran) is one of the oldest in the world.
21. The folk-music of Sindh is very sweet and melodious.
22. 'Alghoza’ and 'Ek-Tara' are the popular instrument of Sindh.
23. The Sindhi embroidery is admired all over Pakistan as well as in foreign countries.
24. The women of Balochistan wear most of their jewellery all the time.
25. The habits, dialects and dress vary from place to place.
3. The proud father announces the birth of a son by _____.
a. fire crackers
b. rifle shots
c. dancing
d. singing
4. The Pathans are very _____ by nature.
a. polite
b. hospitable
c. decent
d. sobre
5. Quaid-e-Azam called the Punjab _____ of Pakistan.
a. brain
b. vital organ
c. heart
d. soul
6. The University of Taxila flourished in the Punjab about _____ years ago.
a. 500
b. 1500
c. 2,000
d. 2,500
7. The _____ of Cbiniot is famous all over the country.
a. sport goods
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
8. The ____ of Sialkot are famous.
a. sport goods
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
9. The _______ of Wazirabad is famous.
a. sport goods
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
10. The _____ of Multan is famous all over. country.
a. sport goods
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
11. The _______ of Gujrat and Bhawalpur is also famous.
a. Pottery
b. inlaid furniture
c. embroidery
d. cutlery
12. Punjabi girls amuse themselves by dancing the _____ at wedding ceremonies.
a. luddi
b. bhangra
c. disco
d. classical
13. Punjabi men express their joy by dancing the _______ at wedding ceremonies.
a. luddi
b. bhangra
c. disco
d. classical
14. Mela Chiragan is held every year on the eve of the urs of saint ________.
a. Baba Farid
b. Data Ganj Baksh
c. Madbu Lal Hussain
d. Baba Uddin Zakariya
15. People of Baluchistan keep themselves warm by using a ________ in cold weather.
a. heater
b. burner
c. stove
d. sandly
16. In _____ the wedding food Is brought along with, the baraat.
a. Khyber Pakhtunkbwa
b. Baluchistan
c. Punjab
d. Sindh
17. The ancient civilization of Sindh dates back to _____ B.C.
a. 500
b. 1000
c. 2,000
d. 2,500
18. The ruins of Moen jo Daro are ______ years old.
a. 3,000
b. 4,000
c. 5,000
d. 6,000
19. The Ek Tara and ______ are typical musical instruments of Sindh.
a. Sarangi
b. Aighoza
c. Murli
d. Piano
20. The Sindhi ______ is admired all over Pakistan as well as in foreign countries.
a. cutlery
b. embroidery
c. music
d. pottery
Fill In The Blanks:
1. The Pathans celebrate the birth of a son by firing Rifle-shots.2. The Pathans are sturdy and war-like people.
3. They like roasted mutton and Chapli Kababs.
4. The Punjab is a seat of learning.
5. The University of Taxila flourished about two thousand and five hundred years ago.
6. The Punjabi farmers sit in the Chopal in th evening.
7. The geographical variations of Pakistan are reflected in the customs of the people of various regions of our country.
8. The power of a tribe depends upon the number of its menfolk.
9. The birth of a son is regarded as a great blessing for the family.
10. The Pathans are very hospitable to their guests.
11. The generosity to their guests is well-known.
12. The Punjab has been called the "Heart of Pakistan" by the Quaid-i-Azam.
13. The inlaid furniture of Chiniot, the sports goods of Sialkot, the cutlery of Wazirabad, the pottery of Gujrat and Bahawalpur are known all over the country.
14. Mahya' and 'Heer' are the famous folk songs of the Punjab.
15. Luddi and Bhangra dances are performed at the time of weddings.
16. The Balochistan is made up of vast barren lands and dry mountains.
17. Extreme climate has made life very difficult for the people.
18. The Balochis lead a simple life and they usually sit and sleep on the floor.
19. The traditional jewelry of Balochistan is beautifully designed.
20. The civilization of Sindh, (the Valley of Mehran) is one of the oldest in the world.
21. The folk-music of Sindh is very sweet and melodious.
22. 'Alghoza’ and 'Ek-Tara' are the popular instrument of Sindh.
23. The Sindhi embroidery is admired all over Pakistan as well as in foreign countries.
24. The women of Balochistan wear most of their jewellery all the time.
25. The habits, dialects and dress vary from place to place.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)