GO TO INDEX
CHAPTER 4
CELLS AND TISSUES
TEXT BOOK EXERCISE
1. Encircle the correct answer:(i) What is responsible for the high resolution of the electron microscope?
(a) High magnification
(b) Short wavelength of the electron beam ✓
(c) Use of heavy metals strains
(d) Very thin section
(ii) What is a function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
(a) Aerobic respiration
(b) Intracellular digestion
(c) Synthesis of steroids
(d) Synthesis of protein ✓
(iii) Which statement about the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure is correct?
(a) The less unsaturated the fatty acid, the more fluid nature. ✓
(b) The more unsaturated the fatty acid, the more fluid nature.
(c) Higher the temperature, less fluid nature.
(d) The lower the temperature, more fluid nature
(iv) Which process allow movement in and out of cell
I. Osmosis
II. Diffusion
III. Active transport
(a) I only
(b) I and II only
(c) II and III only
(d) I, II and III ✓
(v) All are postulates of cell theory except
(a) New cell is derived from pre-existing cells.
(b) Cell does not contain the hereditary material. ✓
(c) All living organisms are made up of one or more cells.
(d) Cell is the fundamental unit of life
(vi) Secondary wall is made up of
(a) Pectin and cellulose
(b) Cellulose and protein
(c) Cellulose and lignin ✓
(d) Lignin and pectin
(vii) Select the odd one
(a) Active transport ✓
(b) Diffusion
(c) Facilitated diffusion
(d) Osmosis
(viii) Trace the correct pathway of protein produce from protein factories
(a) RER → Ribosome → Golgi body → Lysosome
(b) Ribosomes → RER → Golgi body → Lysosome ✓
(c) Golgi body → RER → Ribosome → Lysosome
(d) RER → Ribosome → Lysosome → Golgi body
(ix) Cell organelle found in animal cell and help intracellular digestion
(a) Lysosome ✓
(b) Ribosomes
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Golgi apparatus
(x) Select the mismatched
(a) Plastids → Storage of chemicals
(b) Centriole → Help in cell division
(c) Ribosomes → Synthesis of steroids ✓
(d) Mitochondria → Synthesis of ATP
2. Fill In The Blanks
(i) Microscopes are instrument designed to produce magnified visual image.(ii) Resolution of a microscope is defined as the smallest distance between two points.
(iii) Magnification of a light microscope is formed by using mixture of the power of the eyepiece and the objective lens.
(iv) Electron has a much shorter wavelength than visible light, and this allows electron microscopes to produce higher-resolution images.
(v) In plants, the cell wall is composed mainly of strong fibers of cellulose.
(vi) Cell membrane is composed of double layer.
(vii) Diffusion is a passive process, which does not require energy input.
(viii) Plant cell loses water and cytoplasm shrinks in a process called plasmolysis.
(ix) Special type of movement of specic substances through carrier protein is facilitated diffusion.
(x) The microtubules arranged in a very particular pattern to form centriole are 27 in number.
3. Define the following terms:
(i) Exocytosis, (ii) Vesicles, (iii) Cartilage, (iv) Nucleoplasm, (v) Cyclosis, (vi) Plasmolysis, (vii) Resolution, (viii) Tissue, (ix) Magnification, (x) Cisternae, (xi) Micropgraph (xii) Hereditary Information (xiii) Endocytosis
Ans: Definition:
(i) Exocytosis:
The process through which bulky material (e.g. neurotransmitters and protein) is exported outside the cell by secreting them through an energy dependent process is called exocytosis. It is a form of active transport.
Significance: This process add new membrane which replaces the part of cell membrane lost during endocytosis.
(ii) Vesicles:
Structure:
Vesicles are small, membrane-bound spherical sacs. Many vesicles are made in the Golgi body and the endoplasmic reticulum, or are made from parts of the cell membrane.
Vesicles can be classified according to their contents and function, such as Transport vesicles.
Function:
- Vesicles facilitate the metabolism, transport and storage of molecules.
- Transport vesicles transport molecules within the cell.
(iii) Cartilage:
- Cartilage is a type of supporting connective tissue.
- It is a dense connective tissue.
- Cartilage has limited ground substance and can range from semisolid to a flexible matrix.
- e.g: Cartilage present in pina of ear.
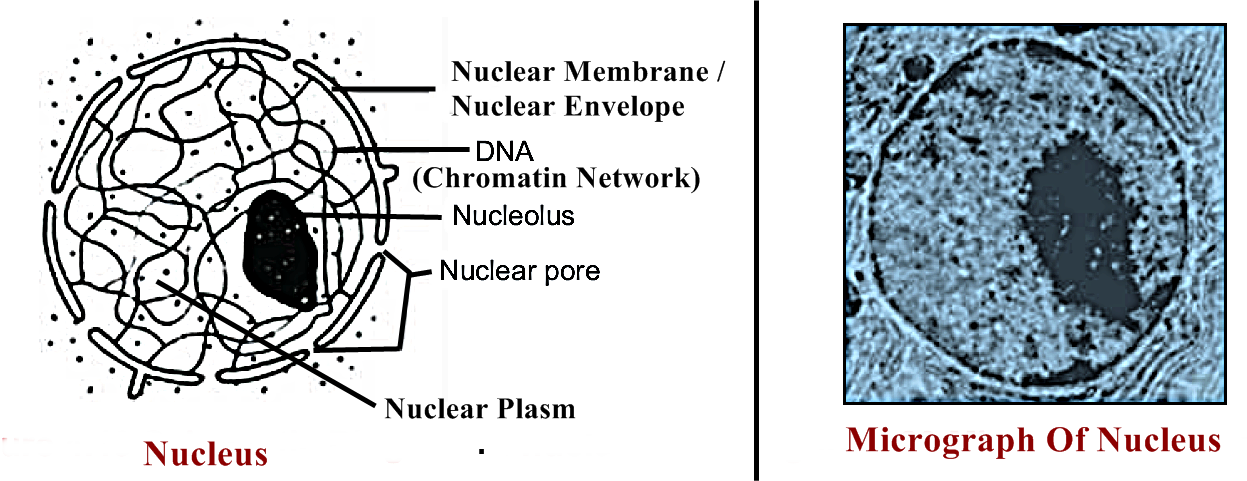
(iv) Nucleoplasm:
Inside nuclear envelope of a nucleus, a granular fluid is present called nucleoplasm. Nucleoplasm contains one or two nucleoli (singular = nucleolus) and network of thread like structure called chromatin network. The genetic material DNA is found in chromatin network.
(v) Cyclosis
Under light microscope, cytoplasm appears as a semi-fluid colloid that fills the cell. The cytoplasm exhibits active streaming movements around the inner surface of the cell. This movement is known as cyclosis.
OR
Cytoplasmic streaming also called protoplasmic streaming, and cyclosis is the flow of the cytoplasm inside the cell, driven by forces from the cytoskeleton. It is likely that its function is, at least in part, to speed up the transport of molecules and organelles around the cell.(vi) Plasmolysis:
Plant cells use osmosis to absorb water from the soil and transport it to the leaves. In hypertonic conditions a plant cell loses water and cytoplasm shrinks and shrinkage of cytoplasm is called plasmolysis.
(vii) Resolution:
The resolution of a microscope is defined as the smallest distance between two points on a specimen that can still be distinguished as two separate objects.
It helps to measure clarity of object.
(viii) Tissue:
A group of similar cells that work together to perform a common function is known as a tissue.
For example: The cells in the small intestine that absorb nutrients look very different from the muscle cells needed for body movement.
(ix) Magnification:
"The enlargement of an image is called magnification." By combining a number of lenses in the correct manner, a microscope can be produced an image that will yield very high magnification values.
(x) Cisternae:
Cisternae are sacs found in ER as well as in Golgi bodies.
- The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) has a double membrane consisting of a network of hollow tubes, flattened sheets, and round sacs. These flattened sheets, hollow folds and sacs are called cisternae.
- The Golgi body consists of a stack of flat membrane-bound sacs called cisternae. The cisternae within the Golgi body consist of enzymes which modify the packaged products of the Golgi body.
(xi) Micrograph:
A photograph of an image taken through a microscope is called micrograph.
(xii) Hereditary Information:
Cells contain the information necessary for the creation of new cells. This information is known as 'hereditary information' and is contained within DNA. DNA (the hereditary information of cells) is passed from 'parent' cells to 'daughter' cells during cell division. The contents of cells from similar species are basically the same.
(xiii) Endocytosis:
- It is the process of cellular ingestion of bulky materials by the infolding of cell membrane.
- The two forms of endocytosis are phagocytosis (cellular eating) and pinocytosis (cellular drinking).
- In phagocytosis cell takes in solid material while in pinocytosis cell takes in liquid in the form of droplets.
4. Distinguish between the following in tabulated form:
(i) Prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell
(ii) Mitochondria and Chloroplast
(iii) Lysosome and Ribosomes
Ans: (i) Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
| Cellular Structure | Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
|---|---|---|
| Example | Bacteria and Cyanobacteria | Animals and plants |
| Nucleus | Without membrane | Proper Nucleus and Membrane bounded |
| Number of chromosomes | One but not true chromosomes | More than One |
| Number of cells | Unicellular | Unicellular and Multicellular Present |
| True membrane bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Lysosomes and Peroxisome | Absent | Present |
| Microtubules | Absent or rare | Present |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Absent | Present |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Ribosomes | Smaller 70S | Larger 80S |
| Vesicles | Present | Present |
| Golgi Apparatus | Absent | Present |
| Chloroplasts | Absent | Present (in plants) |
| Plasma membrane with steroid | Usually no | Yes |
| Permeability of nuclear membrane | Not present | Selective |
| Vacuoles | Absent | Present |
| Cell Size | 1-10 µm | 1-1000 µm |
| Flagella | Submicroscopic in size, composed of only one fiber | Microscopic in size; membrane bound |
OR
| S.NO. | Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nuclear membrane is absent therefore prokaryotic cells do not possess distinct nucleus. | A double nuclear membrane is present. They have well developed nucleus. |
| 2. | They do not have many membrane bound structures e.g. Mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus etc. | They have membrane bounded structures (organelles). |
| 3. | Ribosomes are of small size and freely scattered in cytoplasm. | Ribosomes are of large size and present either on endoplasmic reticulum or free in cytoplasm. |
| 4. | Nucleoplasm is absent. | Nucleoplasm is present. |
| 5. | Single chromosome is found. | Proper chromosome in diploid numbers are present. |
(ii) Mitochondria and Chloroplast
| S.NO. | Mitochondria | Chloroplast |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A mitochondrion is a membrane bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells only. | The chloroplast is a double membrane organelle found in cells of plants and algae. |
| 2. | They are Bean-shaped. | They are Disc-shaped. |
| 3. | It is a colourless organelle. | It is a green-coloured plastids. |
| 4. | Mitochondria is the site of aerobic respiration. | It is the site where photosynthesis takes place. |
| 5. | During aerobic respiration energy is produced in the form of ATP. Therefore it is also called ‘Power house’ of cell. | Chlorophyll absorbs (uses) energy from the sun for photosynthesis. |
| 6. | Matrix and Cristae are the two chambers present in a mitochondrion | Stroma and thylakoid are the two chambers of a chloroplast |
| 7. | During aerobic respiration, It consumes oxygen and release carbon dioxide. | During photosynthesis, it releases oxygen and consumes carbon dioxide. |
| 8. | Mitochondria do not possess any pigments. | Chloroplast is composed of pigments such as chlorophyll etc. |
OR
| S.NO. | Mitochondria | Plastids |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A mitochondrion is a membrane bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells only (Both animal and plant cell). | Plastids are double membrane organelle found in plants and algae. |
| 2. | They are Bean-shaped. | They are Disc-shaped. |
| 3. | They do not contain pigments | They contain different types of coloured pigments.. |
| 4. | Mitochondria is the site of aerobic respiration. | They are the site where photosynthesis takes place. |
| 5. | They produce energy. | They capture (use) energy.. |
| 6. | They contain enzymes which break the food.. | They do not contain enzymes.. |
(iii) Lysosome and Ribosomes
| S.NO. | Lysosome | Ribosomes |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The lysosome is present in the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell (animal cell) only. | The ribosome is present in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell (plant and animal cell). |
| 2. | It is membrane-bound organelle. | It is non-membranous organelle. |
| 3. | Lysosomes are formed by the Golgi body | Eukaryote ribosomes are produced and assembled in the nucleolus. |
| 4. | Lysosomes contain powerful digestive enzymes and membrane protein | Ribosomes are composed of RNA and ribosomal protein. |
| 5. | These are evenly and freely distributed throughout the cytoplasm. | Ribosomes may occur singly in the cytoplasm or in groups or may be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| 6. | Lysosomes can digest cell structures and food molecules such as carbohydrates and proteins. | Ribisomes are the sites where protein synthesis occurs . |
| 7. | It is larger in size than ribosomes, Its size ranges from 0.1 to 1.2 micrometer. | It is comparatively smaller in size than lysosomes, Its size ranges from 20 to 30 nm. |
5. Write short answers of following questions:
(i) Why mitochondria is also called power house of cell?
Ans: Mitochondria is the site of aerobic respiration. During aerobic respiration energy is produced in the form of ATP. Therefore the Mitochondria is also called ‘Power house’ of cell.
(ii) Why iodine used to stain the onion peel?
Ans: Iodine is often used to stain onion cells before microscopic examination to enhance the visibility of the cell. It is used in staining cells of an onion peel on the slide due to following reason.
- Onion bulb is made up of scaly leaves which store starch granules in their cytoplasm of the cells.
- Iodine binds to starch in the granules and develops blue black colour.
- This procedure of staining onion cells with iodine makes the onion cells visible clearly. It also confirms the fact that onion stores reserve food material in the form of starch.
(iii) How electron microscope is different from simple compound microscope?
Ans: (i) Difference Between Light microscope (Simple and Compound) and Electron microscope
| S.NO. | Light microscope (LM) (Simple And Compound Microscope) | Electron Microscope |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | They produce an image of a specimen by using a beam of visible light. | They produce an image of a specimen by using a beam of electrons |
| 2. | A live cell can be imaged by light microscope. | A live cell cannot be imaged by electron microscope. |
| 3. | Magnification of light microscope is lower i.e. 1500 X | Magnification of electron microscope is higher i.e. 250,000 X |
| 4. | It achieves a resolution above 0.2 µm (micrometer). | It achieves a resolution of about 0.2 nm (nanometer), a thousand times improvement over light microscope |
| 5. | Visible light have longer wavelength (400-700 nm). this allows LE to produce lower-resolution images. | Electrons have much a shorter wavelength (1 nm), this allows EM to produce higher-resolution images. |
| 6. | Light microscopes are smaller and lighter, so its easier to move and set-up. | Electron microscopes are large and heavy, so its hard to move and set-up. |
| 7. | Light microscopes are less expensive. | Electron microscope are very expensive. |
| 8. | Light microscope uses glass lenses for magnification. | Electron microscope uses electromagnetic lenses instead of glass lenses. |
| 9. | The images of the specimen is projected into the human eye. | The image can not focus in human eye, therefore, screen or photographic plates are used to review and focus the image. |
| 10. | Simple and compound microscopes are example of light microscopes | SEM and TEM are examples of Electron microscope |
(iv) Why cell membrane is semipermeable in nature?
Ans: All the living organisms are made up of cells. All the exchanges between the cell and its environment have to pass through the cell membrane. The cell membrane is selectively permeable in nature because by process of osmosis it regulates selective movement of molecules i.e ions (e.g. hydrogen, sodium), small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide) and larger molecules (glucose and amino acids) while fencing a majority of chemicals inside the cell. In this way, it controls the movement of substances in and out of the cells and maintains its internal composition.
(v) How facilitated diffusion is different from active transport?
Ans: Difference Between Facilitated Diffusion And Active Transport
| S.NO. | Facilitated Diffusion | Active Transport |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It is the transport of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through the plasma membrane. | It is the transport of molecules from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration through the plasma membrane. |
| 2. | Facilitated diffusion is a passive process and does not require energy. | Active transport is an active process. Thus, it requires energy. |
| 3. | Facilitated diffusion is the movement of substances through a concentration gradient | Active transport is the movement of substances against a concentration gradient |
| 4. | Facilitated diffusion uses both gated channel proteins and carrier proteins in transport. | Active transport uses carrier proteins. Energy is used in the form of ATP to change the shape of the carrier protein. |
| 5. | Facilitated diffusion is used for mainly large, polar molecules which can not cross the phospholipid bilayer | Active transport is used to transport molecules against their concentration gradient. |
(vi) Why cell is considered as the structural and functional unit of living things?
Ans: A cell is considered as the basic structural and functional unit of organisms.
Cell As Structural unit of organisms:
- Microscopic studies reveals that all living organisms are made of one or more cells.
- Therefore, cell is the fundamental and structural unit of all living organisms or the building block of which living things are made.
- Cells are of many different shape and size.
Cell As Functional unit of organisms:
- Cell have to perform different functions.
- All basic functional activities, characteristics of living things, occur in the cell and cell also have ability to reproduce itself.
- Therefore, cell is also a functional unit in all living organisms.
6. Write detailed answers of the following questions:
(i) Describe structure and function of nucleus with the help of diagram.
Ans: NUCLEUS:
The nucleus is the largest organelle in the cell and contains the entire cell's genetic information in the form of DNA.
Occurrence:
- The presence of a nucleus is the primary factor that distinguishes eukaryotes from prokaryotes. A prominent nucleus occurs in eukaryotic cell.
- In animal cell, it is located in the center.
- In plant cell due to presence of a large central vacuole, it is push towards cell membrane.
Structure:
- Nuclear Envelope:
Nucleus is covered by two phospholipids membranes known as nuclear envelope that separates the nucleus and its contents from the cytoplasm. -
Nuclear pores:
Nuclear pores are found in the nuclear envelope and help to regulate the exchange of materials (such as RNA and proteins) between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. -
Nucleoplasm:
Inside nuclear envelope, a granular fluid is present called nucleoplasm. -
Nucleolus:
In nucleus an aggregation of RNA is also present called nucleolus.
It is a dark spot. - Chromatin Net Work:
In non-dividing cell the genetic material is found in the form of net work in the nucleus called chromatin net work. -
Chromosomes:
Chromosomes are visible only during cell division. They are composed of DNA and protein.
Function:
- It stores the cell's hereditary material, or DNA.
- It controls all the activity of a cell.
(ii) What is microscope? Describe types of microscopes?
Ans: MICROSCOPE:
Definition:
Microscope was simply a tube with lenses at each end and its magnification ranged from 3X to 9X.
It is define as:
Microscopes are instruments designed to produce magnified visual or photographic images of objects too small to be seen with the naked eye.
TYPES OF MICROSCOPE:
There are two microscopes are used in microscopy i.e:
- Light microscope (LM)
- Electron microscope (EM)
(a) Light Microscope:
-
Source:
In a light microscope, visible light passes through the specimen (the biological sample under observation).
A photograph of an image taken through a microscope is called micrograph. -
Visibility:
A live cell can be imaged by light microscope. -
Resolution:
The light microscope can magnify the object up to 1000 times -
Magnification:
The magnification of a light microscope is formed by using a mixture of the powers of the eye piece and the objective lens.
Total magnification of an image with a compound light microscope = power of the objective lenses X power of the eye piece.
If the power of the objective lenses is at 4x, 10x, 40x and
The power of the eye piece is (typically) 10x.
That is the object can be magnified, 40x, 100x or 400x.
Similarly, a 10x eyepiece used with a 10x objective lens will produce a magnification of 100x.
Electron Microscopes:
-
Source:
Electron microscopes are differ from light microscopes.
They produce an image of a specimen by using a beam of electrons rather than a beam of light.
Electrons have a much shorter wavelength than visible light, and this allows electron microscopes to produce higher-resolution images than standard light microscopes. -
Visibility:
Electron microscopes can be used to examine not just whole cells, but also the subcellular structures and compartments within them.
A live cell cannot be imaged by electron microscope. -
Resolution:
Electron microscope has a resolution as small as 0.2 nanometer (nm)
. -
Magnification
Magnification upto 250,000 times.
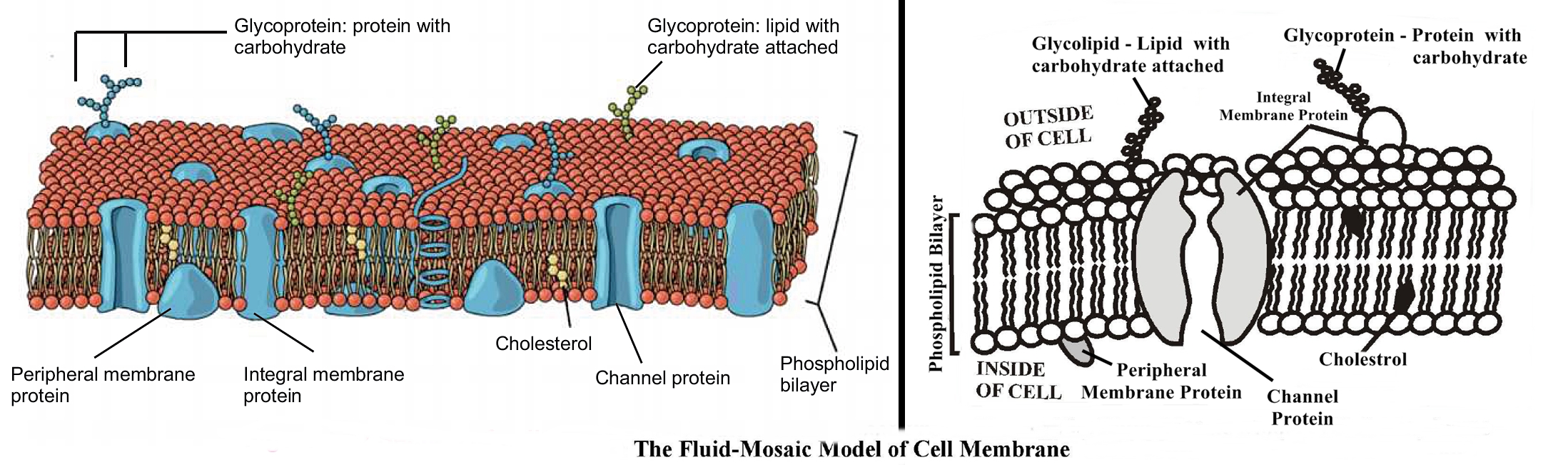
(iii) Describe fluid mosaic model of cell membrane also draw the diagram.
Ans: Structure of the cell membrane - the fluid mosaic model:
S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson proposed the Fluid Mosaic Model of the cell membrane in 1972.
This model describes that:
- Phospholipid acting like matrix and conjugated glycoproteins (glucose and protein together) may float freely in this matrix.
- This model describes the structure of the cell membrane as a fluid structure with various protein and carbohydrate components floating freely in the membrane. Therefore, it is also called unit membrane.
Functions:
-
Protect:
► The cell membrane surrounds and protects the cytoplasm. -
Perform Exchange of Substances:
► All the exchanges between the cell and its environment have to pass through the cell membrane.
► It performs many important functions within the cell such as osmosis, diffusion, transport of nutrients into the cell, processes of ingestion and secretion. -
Semi-permeable barrier:
► The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions (e.g. hydrogen, sodium), small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide) and larger molecules (glucose and amino acids) and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cells.
SHORT QUESTION & ANSWERS
Q.1: What is Cell?Ans: Cell:
"Cells are the smallest form of life i.e cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living things and all tissues and organs are composed of cells." It is a set of organelles made up of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids.
The contents of cells from similar species are basically the same. The activity of an organism depends on the total activity of independent cells.
Q.2: Who discovered the neucleus?
Ans: In 1833, Robert Brown, an English botanist, discovered a spherical body called nucleus in the cell of orchids.
Q.3: Name the types of animal tissues.
Ans: Animal Tissues:
Humans and other large multicellular animals are made up of four basic types of tissue:
-
Epithelial tissue
a) Simple
i. Squamous
ii. Cubodial
iii. Columnar
b) Startified
i. Squamous
ii. Cubodial
iii. Columnar
iv. Transitional -
Connective tissue
a) Supporting
i. Cartilage
ii. Bone
iii, Adipose
b) Fluid
i. Blood -
Muscular tissue,
a) Skeletal
b) Cardiac
c) Smooth - Nervous tissue.
Q.4: Name The types of plant tissues?
Ans: Plant Tissues:
Plants cells are made up of two basic types of tissues
-
Meristematic tissues
a) Apical Meristematic Tissue
b) Lateral Meristematic Tissue -
Permanent Tissues
a) Simple Permanent Tissue
i. Epidermal
ii. Ground
iii. Supporting
b) Complex or Compound Or Vascular Tissues
i. Xylem
ii. Phloem
Q.5: What is the difference between cell wall and cell membrane?
Ans: Difference between cell wall and Cell membrane:
| S.No | Cell Wall | Cell Membrane |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It is the outer most boundary of plant cells, bacterial cells and fungal cells. | It is the membrane which surrounds cytoplasm, but in plant cell it is surrounded by cell wall. |
| 2. | It is mainly composed of cellulose and pectin. | It is mainly composed of lipids and proteins. |
| 3. | It is made up of three main layers primary wall, middle lamella, secondary wall. | It is made up of protein and lipid bilayer in which protein molecules float. |
| 4. | It is permeable membrane. It gives definite shape and rigidity to plant. | It is selectively permeable membrane; In animal cells infolds of cell membrane take in materials in the form of vacuole. |